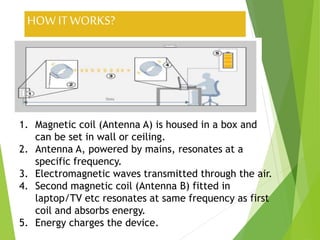
Wireless electricity refers to the transmission of electrical energy without wires, using techniques like inductive and capacitive coupling or power beaming. While the concept has historical roots with figures like Nikola Tesla, recent advancements by MIT scientists are bringing wireless power closer to practical use for devices like cell phones and electric cars. Despite its benefits in reducing clutter and e-waste, challenges such as standardization, retrofitting costs, and potential energy theft remain.