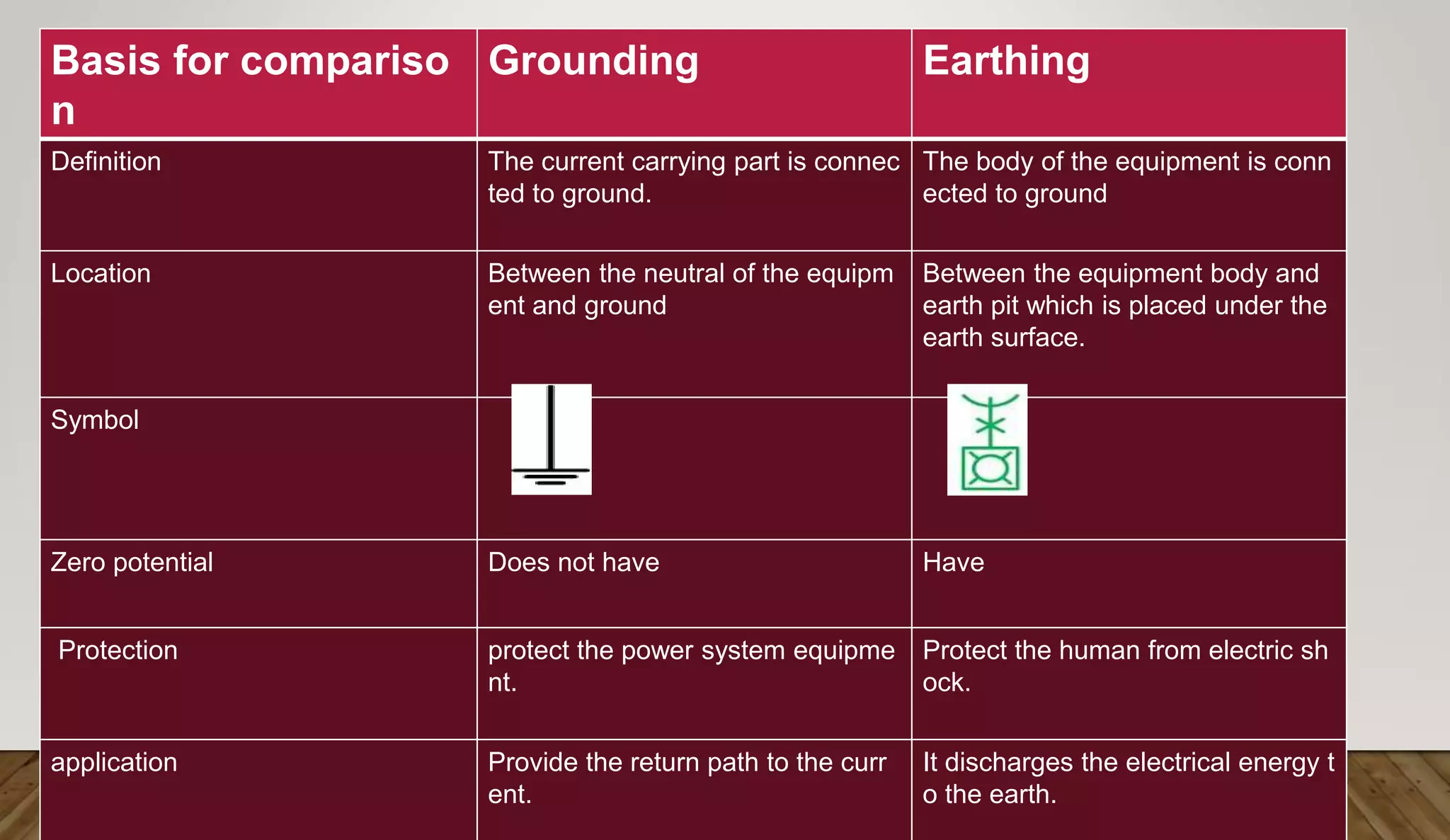
The document explains the concepts of earthing and grounding in electrical engineering, outlining their definitions, purposes, and methods. Earthing connects electrical equipment to the earth to protect against electric shock and equipment damage, while grounding involves connecting current-carrying parts to the ground. Both practices are critical for ensuring safety and stability in electrical systems.