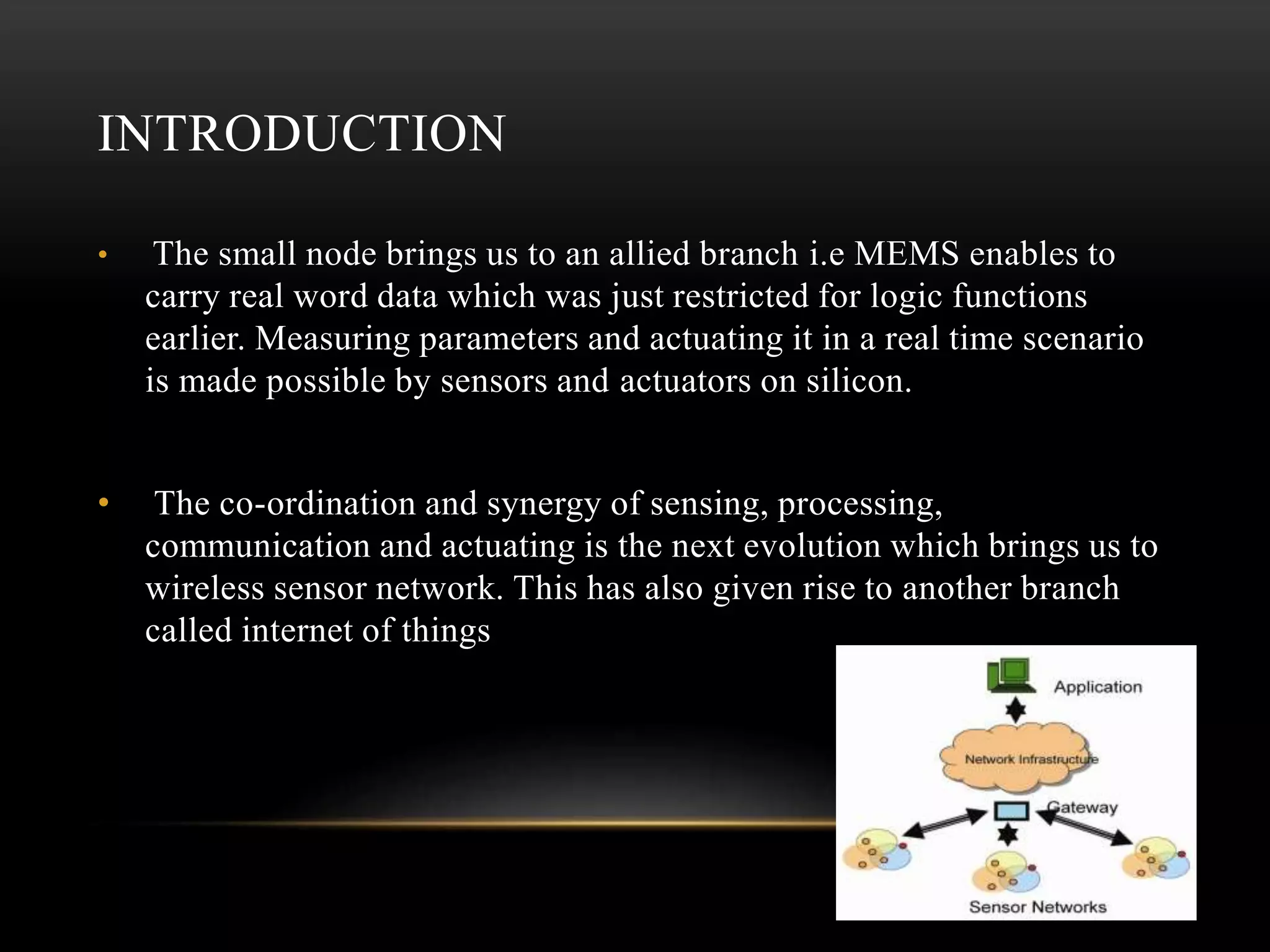
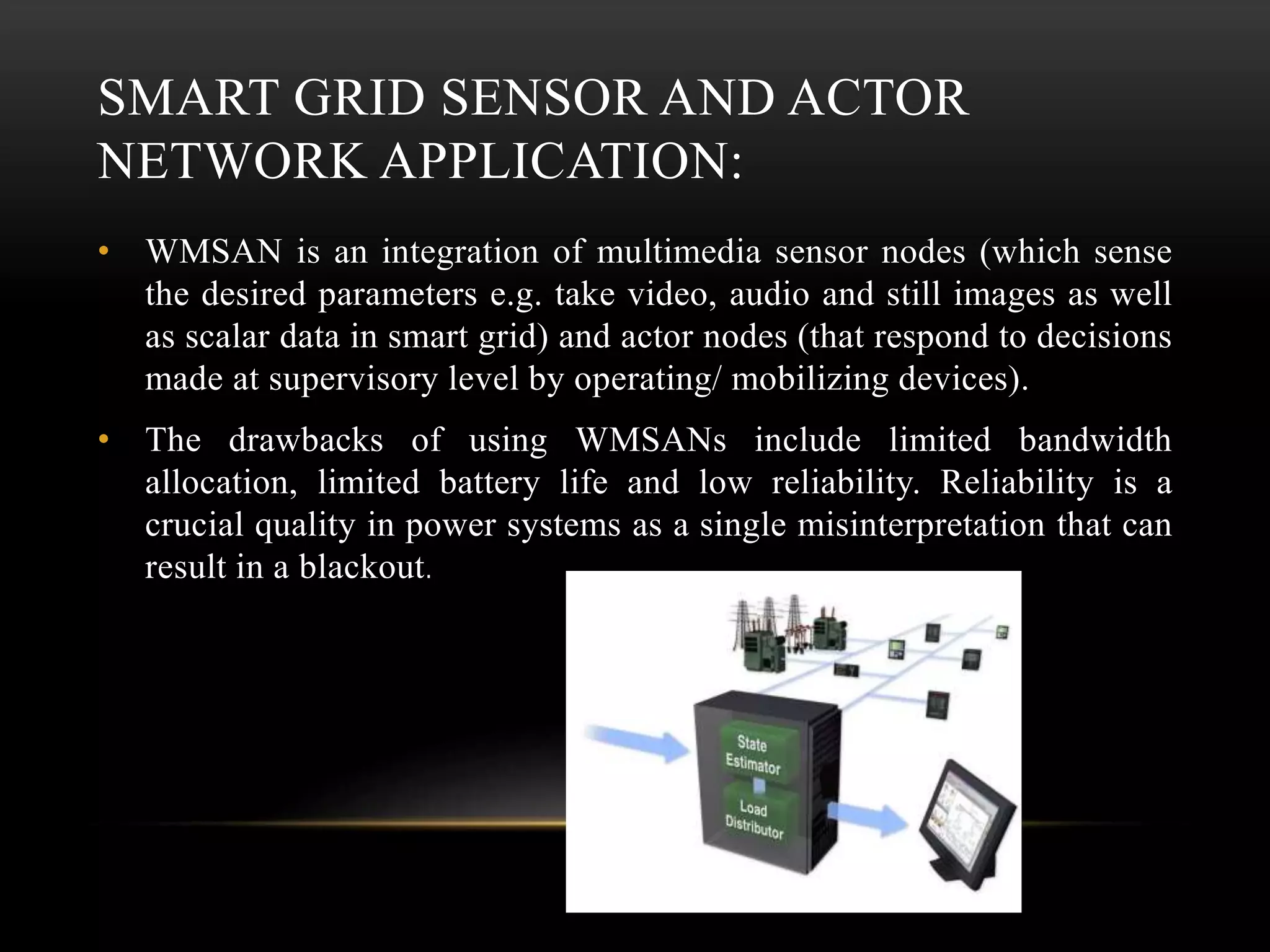
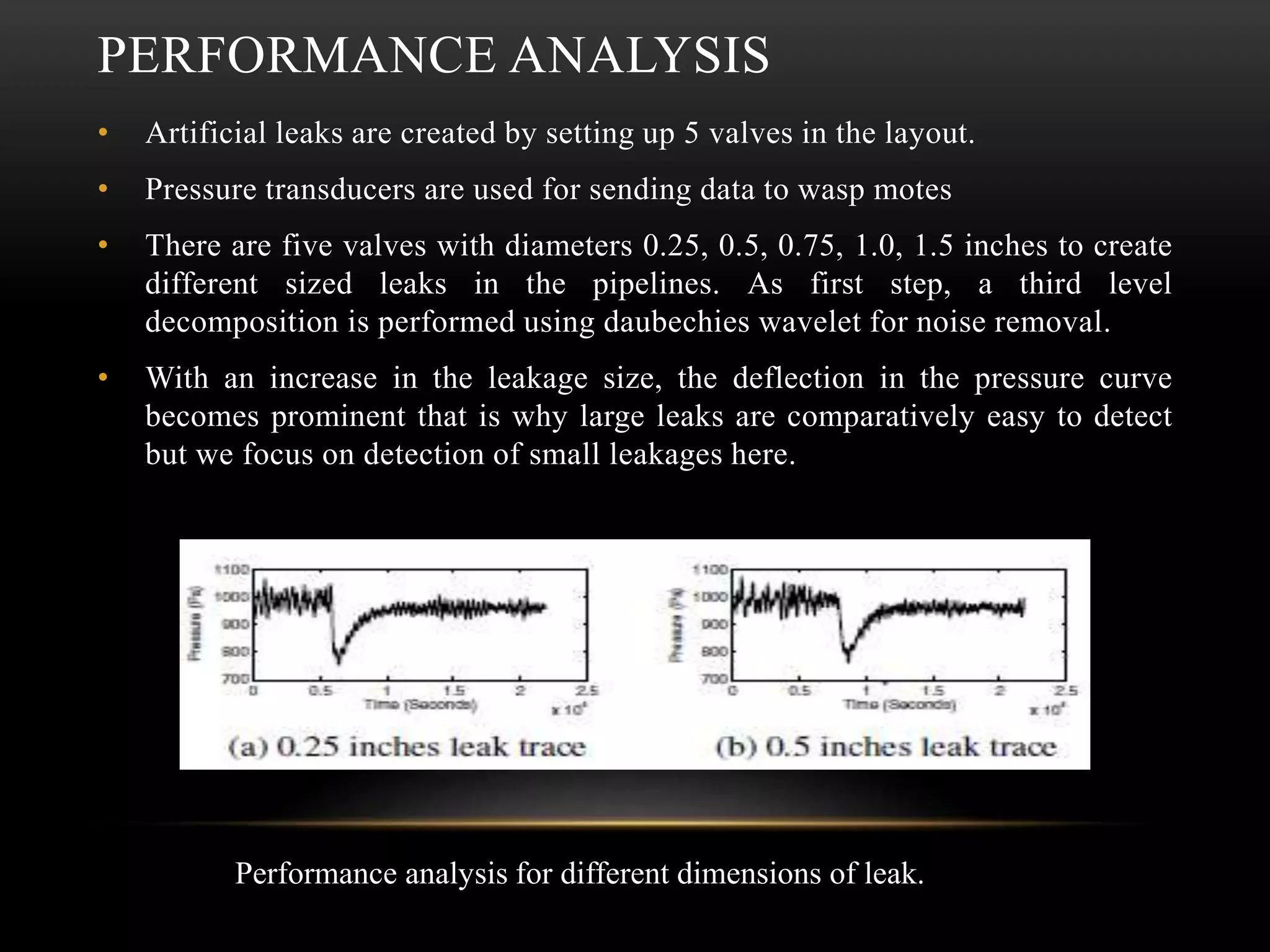
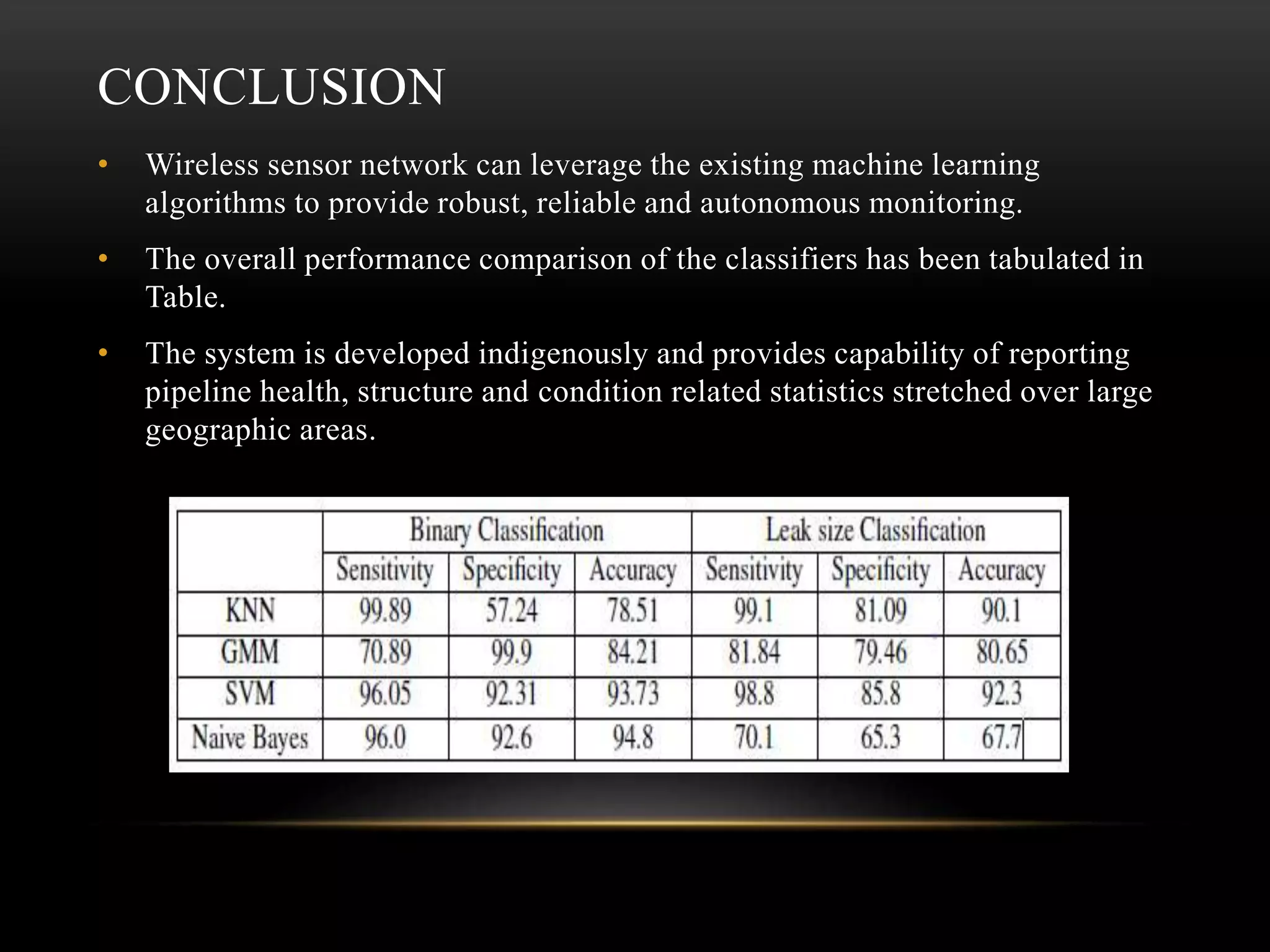
The document discusses the advancements and applications of wireless sensor networks (WSNs), particularly focusing on leak detection and monitoring in pipelines. It highlights various applications in military, medical, industrial, and urban areas, explaining how WSNs utilize machine learning for real-time data processing and decision-making. The paper concludes that WSNs, combined with robust machine learning algorithms, can provide effective monitoring solutions for pipeline health and other applications.