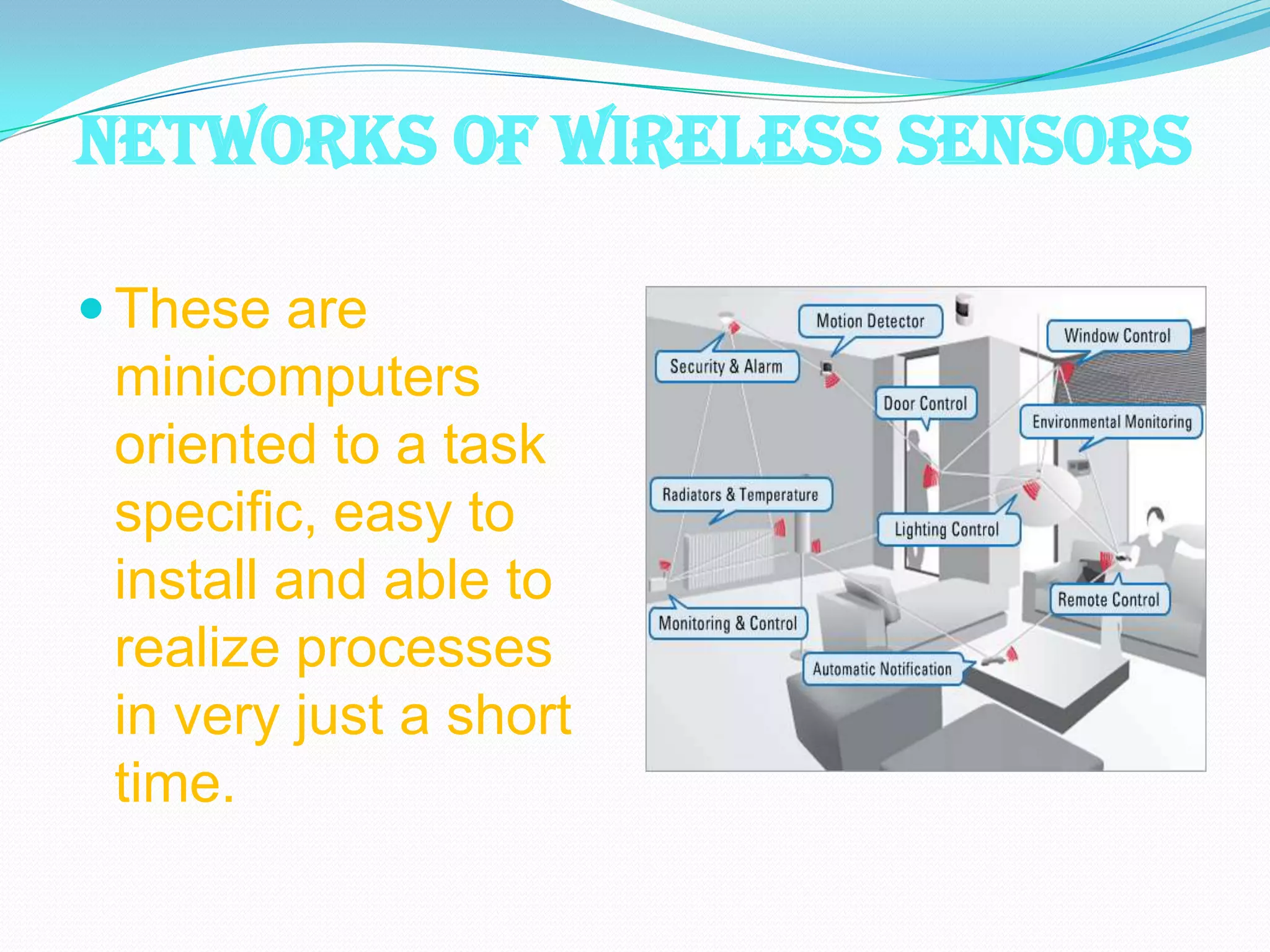
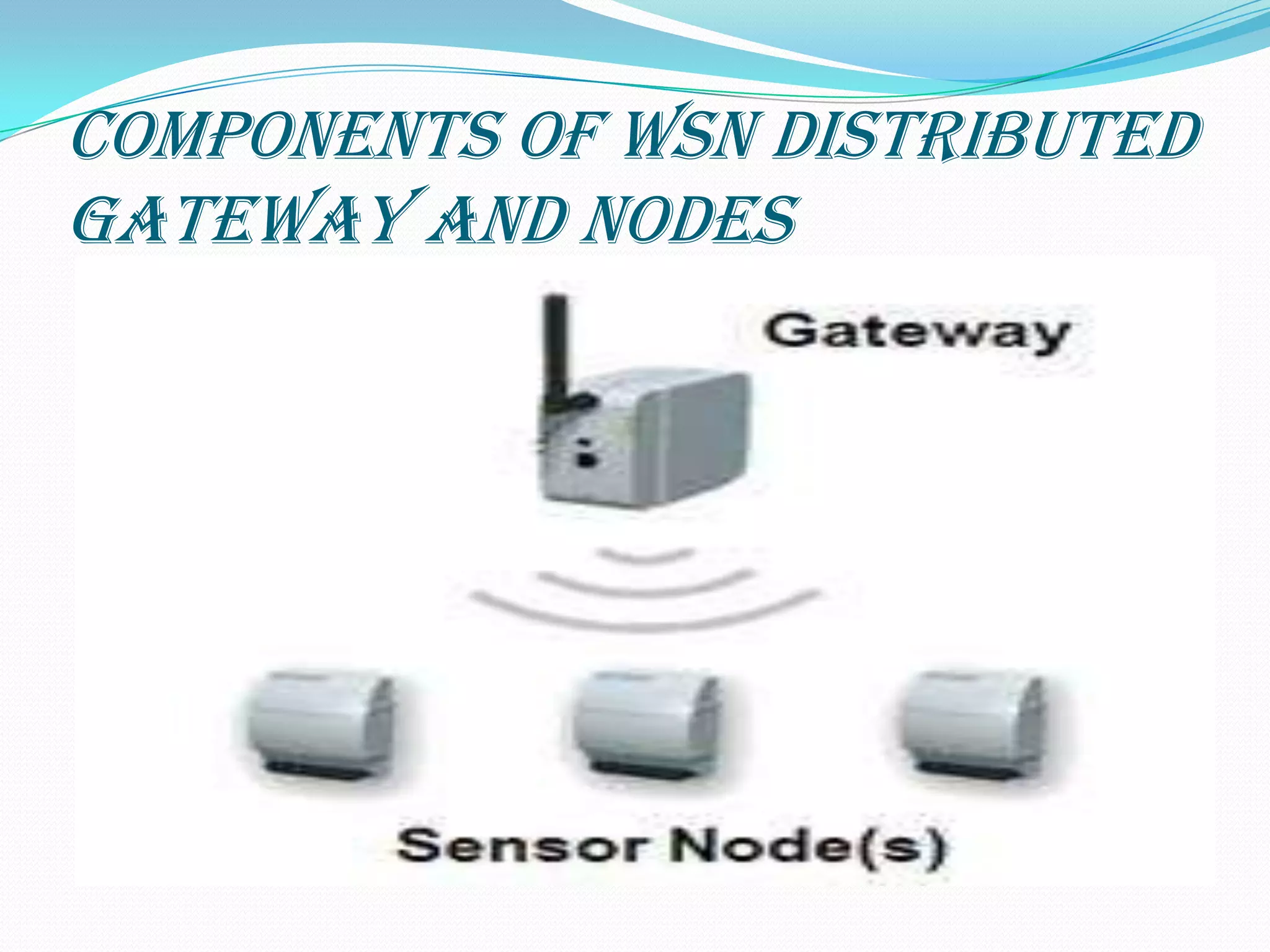
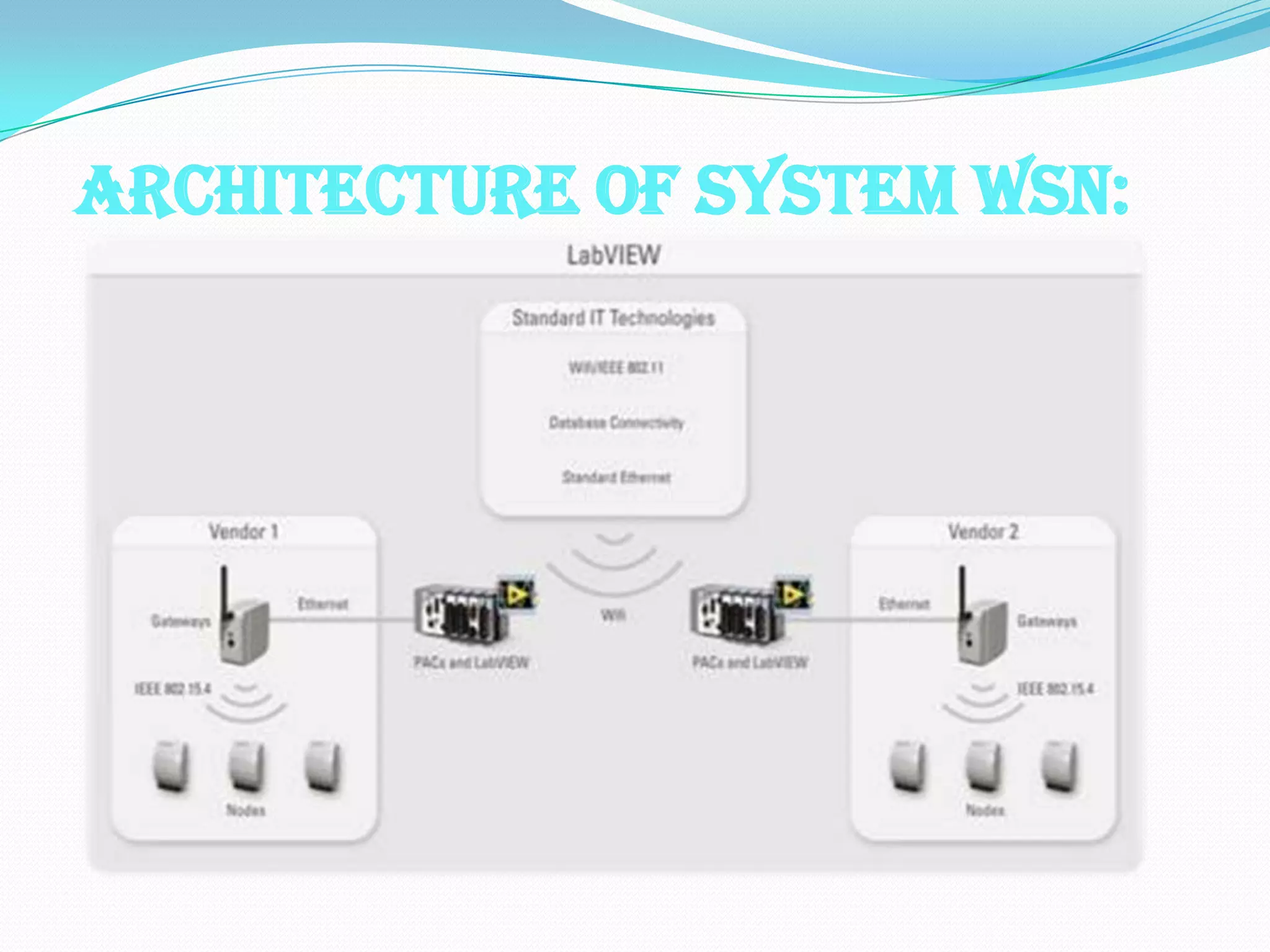
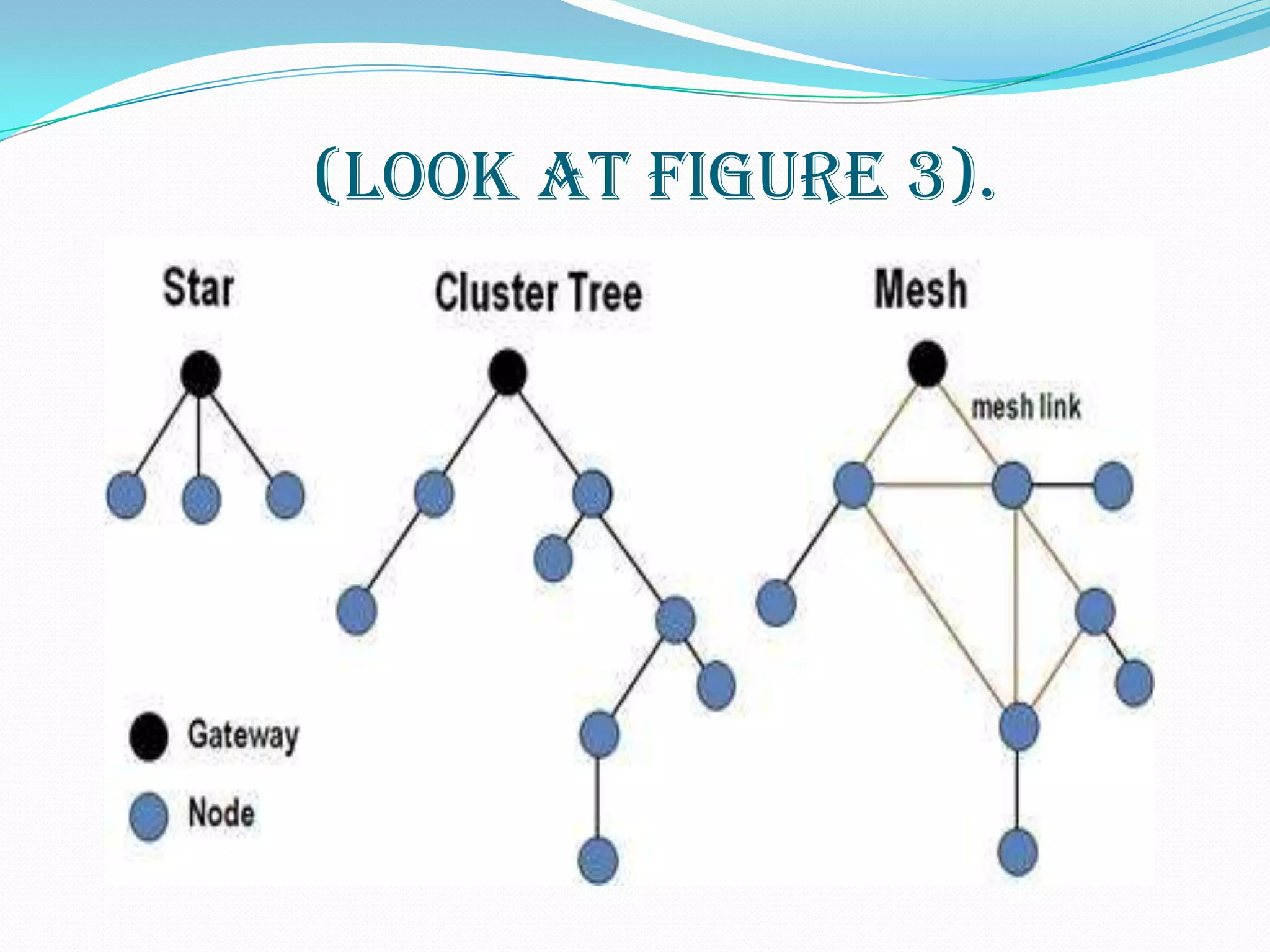
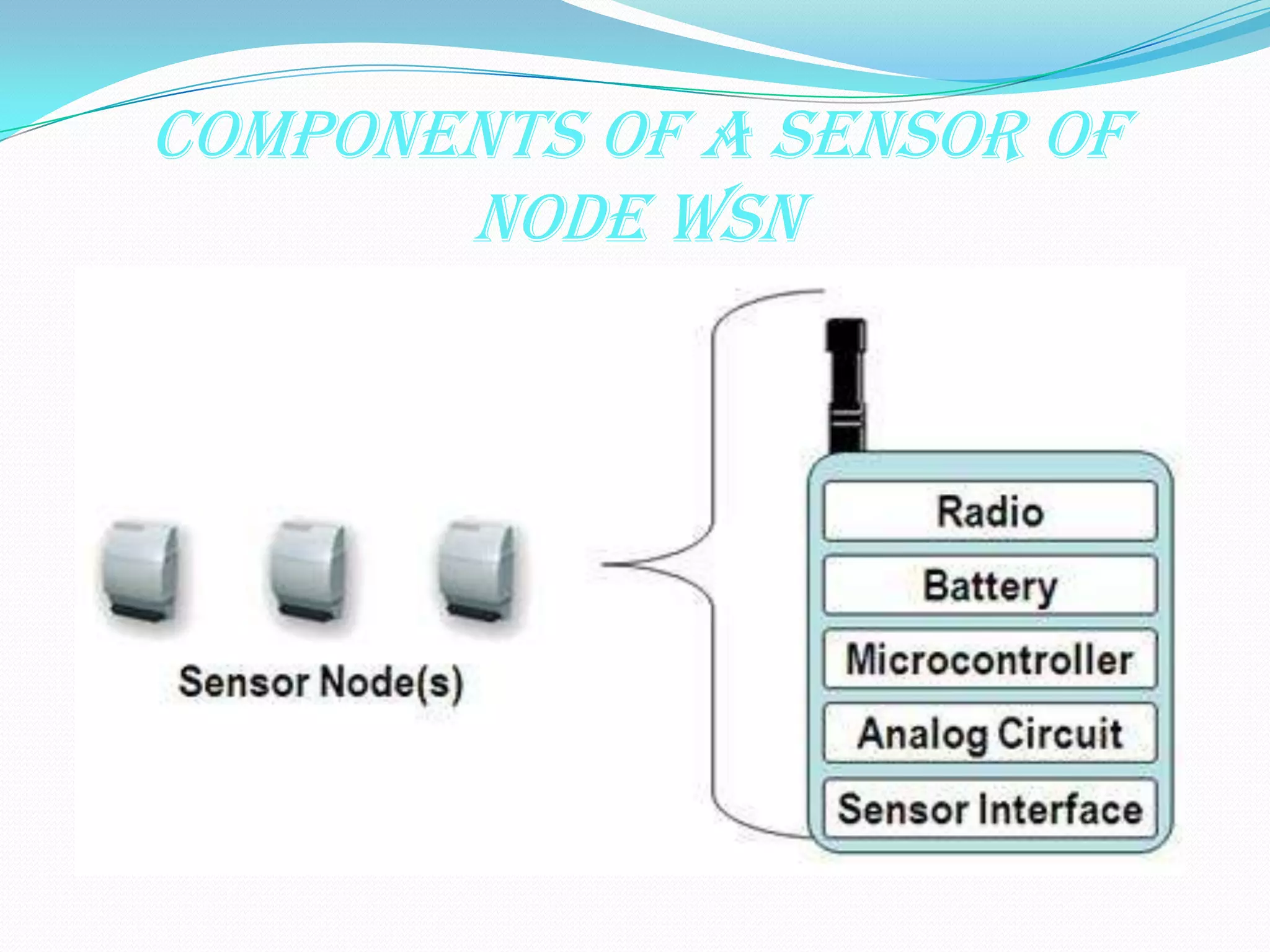
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) consist of distributed sensor nodes that self-organize to monitor environmental conditions over a wide area. They have many potential applications including health monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, and environmental monitoring. Each sensor node contains a radio, battery, microcontroller, and sensor interface. The network architecture uses gateways to connect the wireless sensor nodes to wired networks. Key challenges are minimizing energy usage to extend battery life since many applications require years of unattended operation.