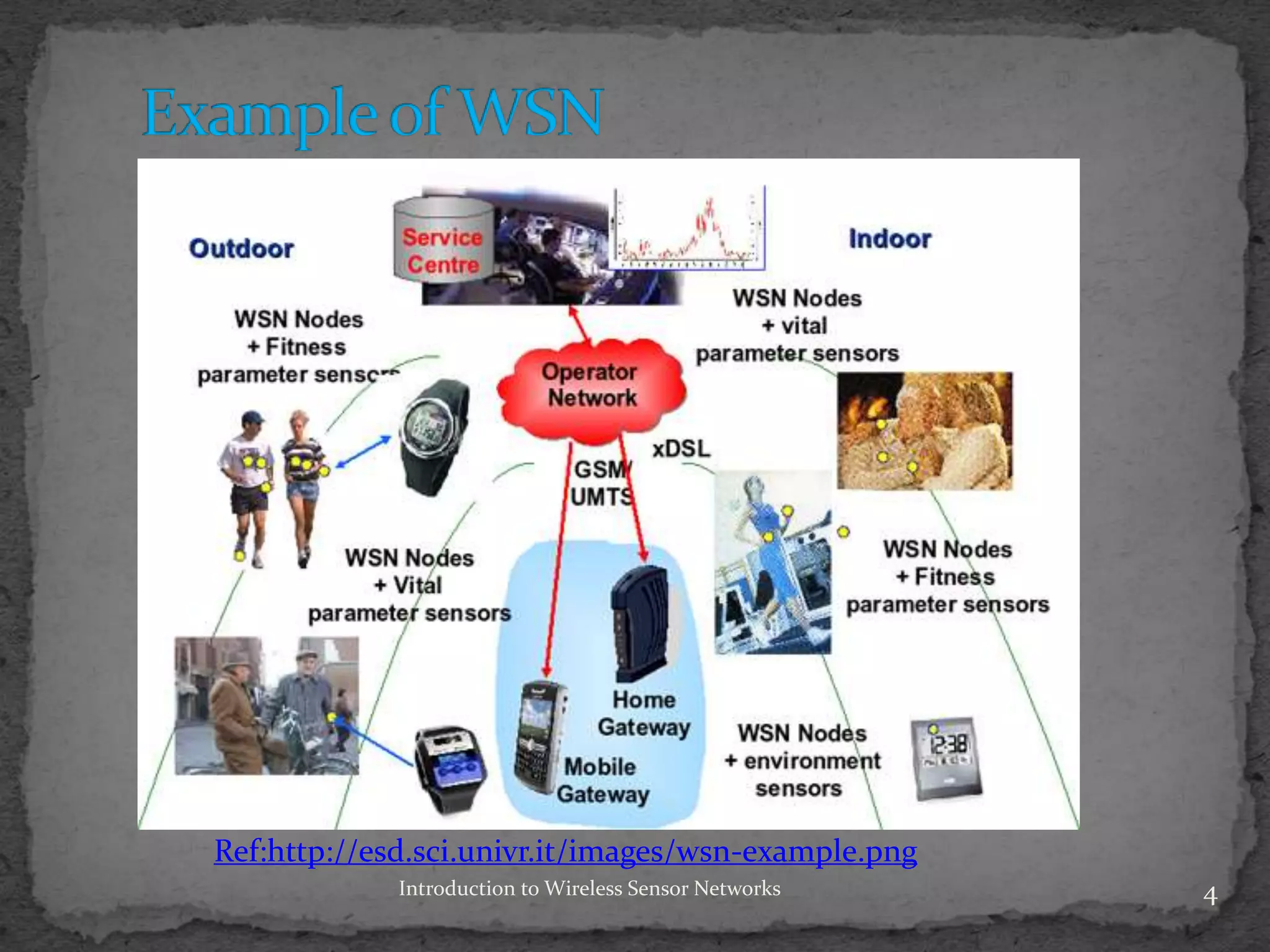
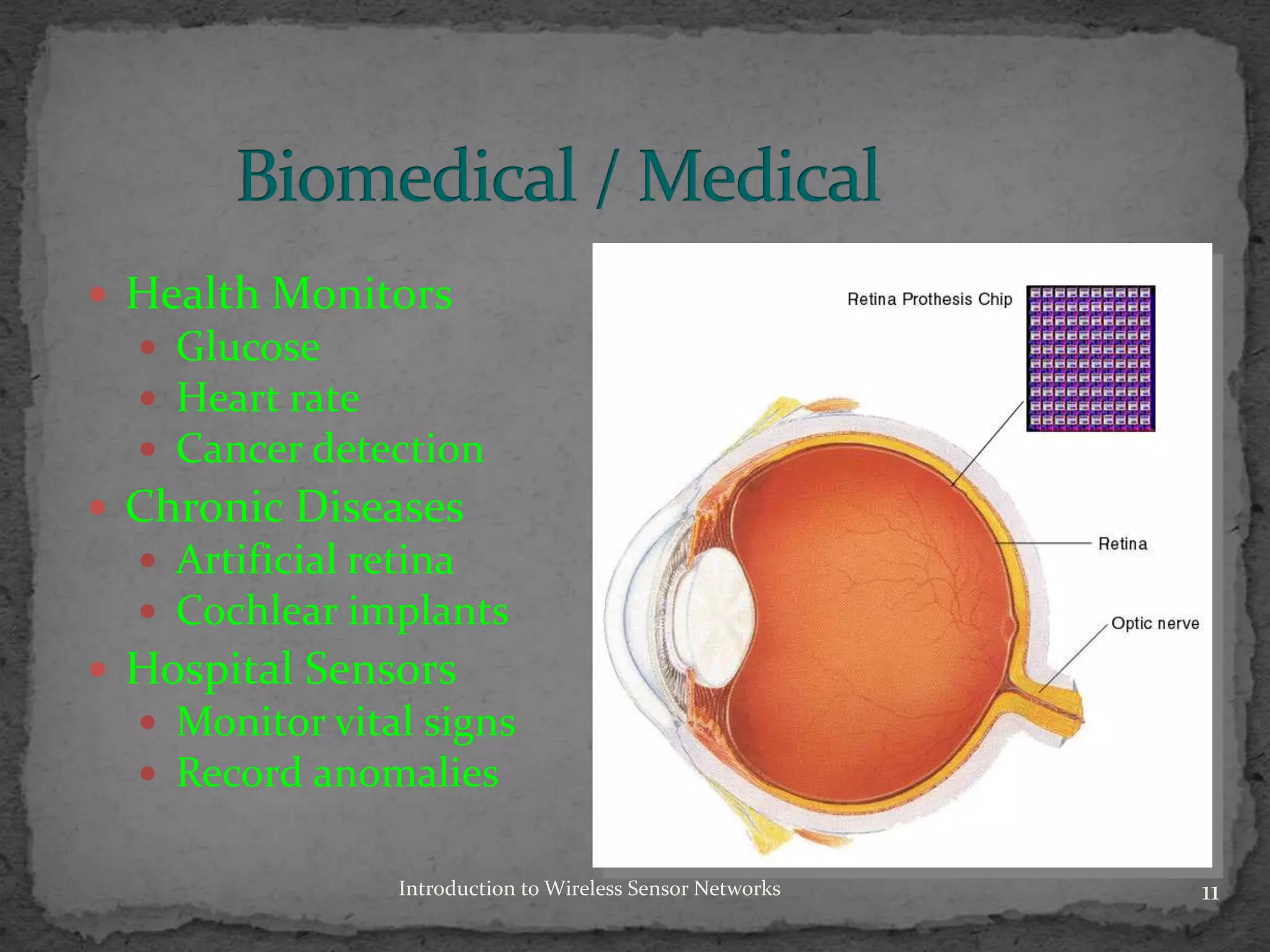
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) comprise distributed sensors that collaborate to gather and process information about physical phenomena. They differ from ad hoc networks by primarily using broadcast communication, being limited by power and computational capabilities, and requiring self-organization. Applications include environmental monitoring, military surveillance, health monitoring, and potential future uses in smart infrastructure.