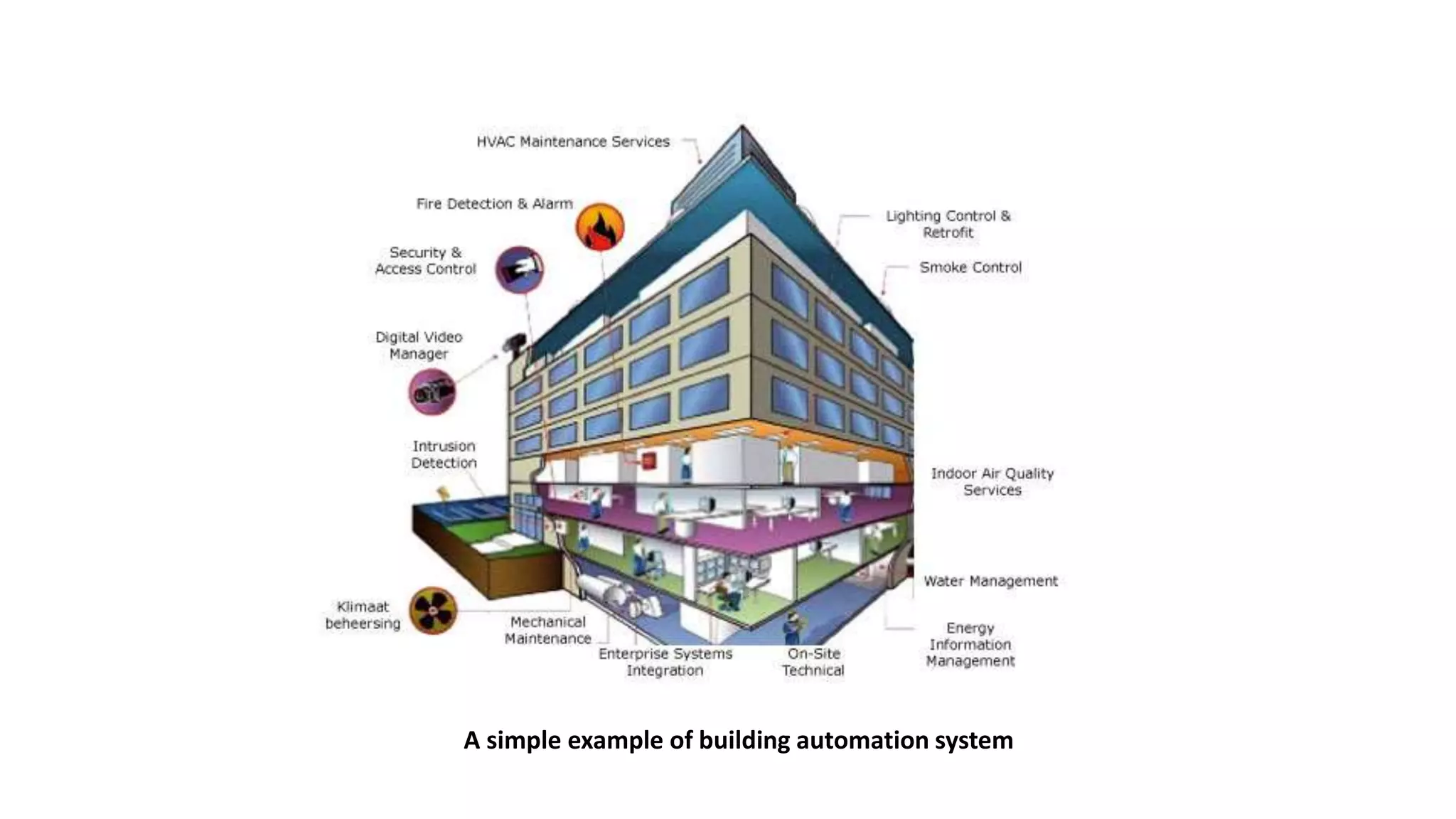
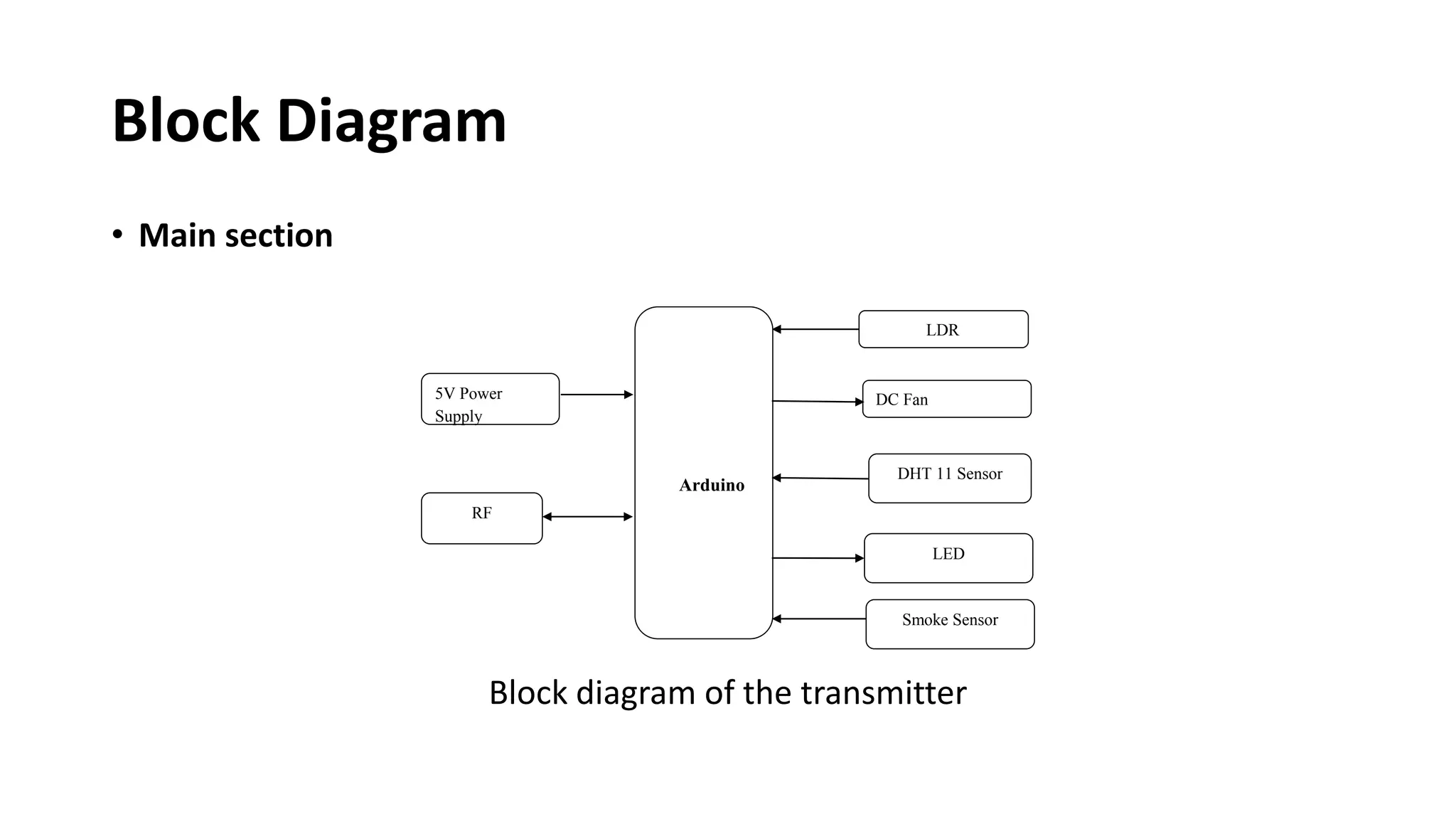
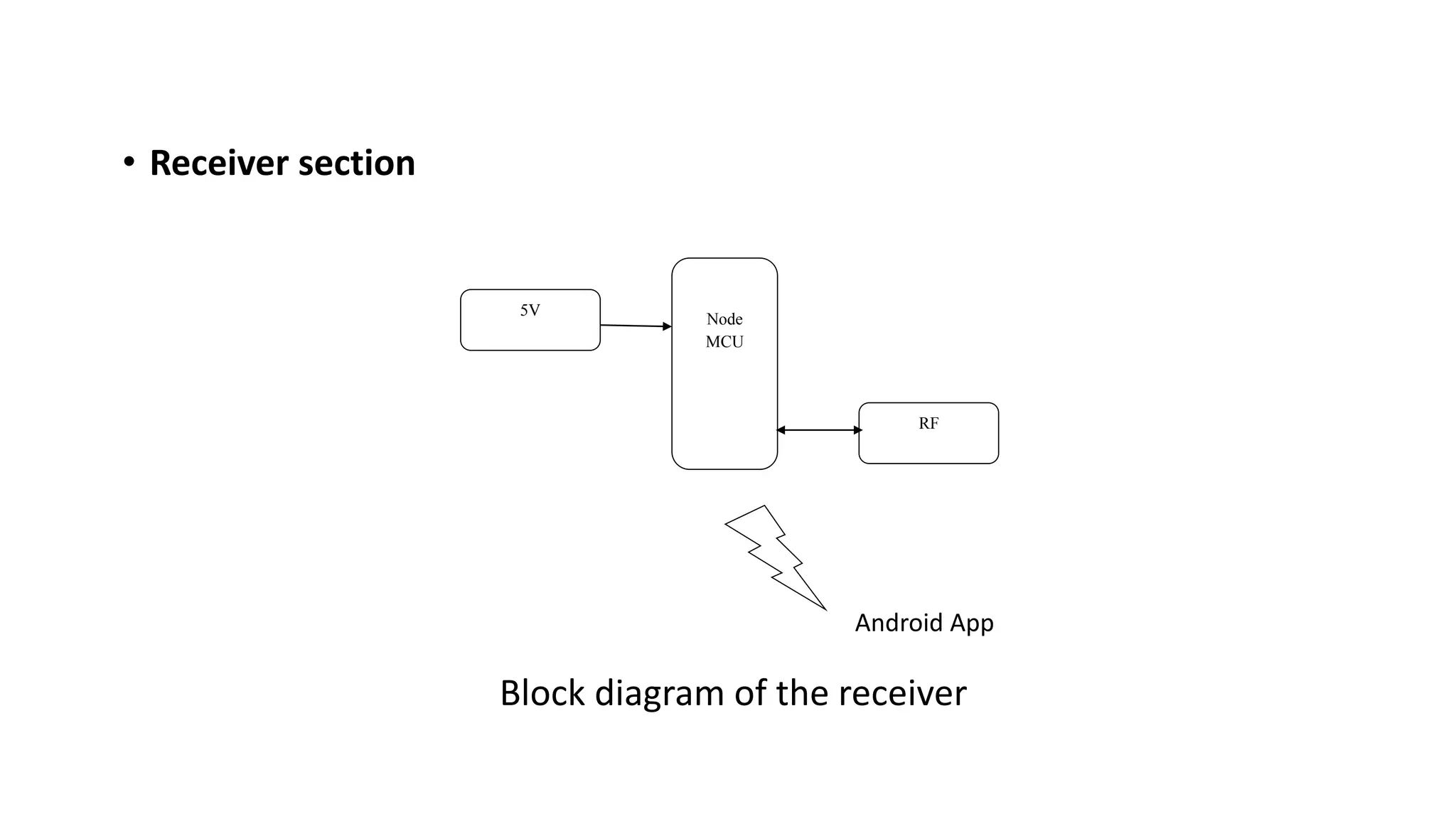
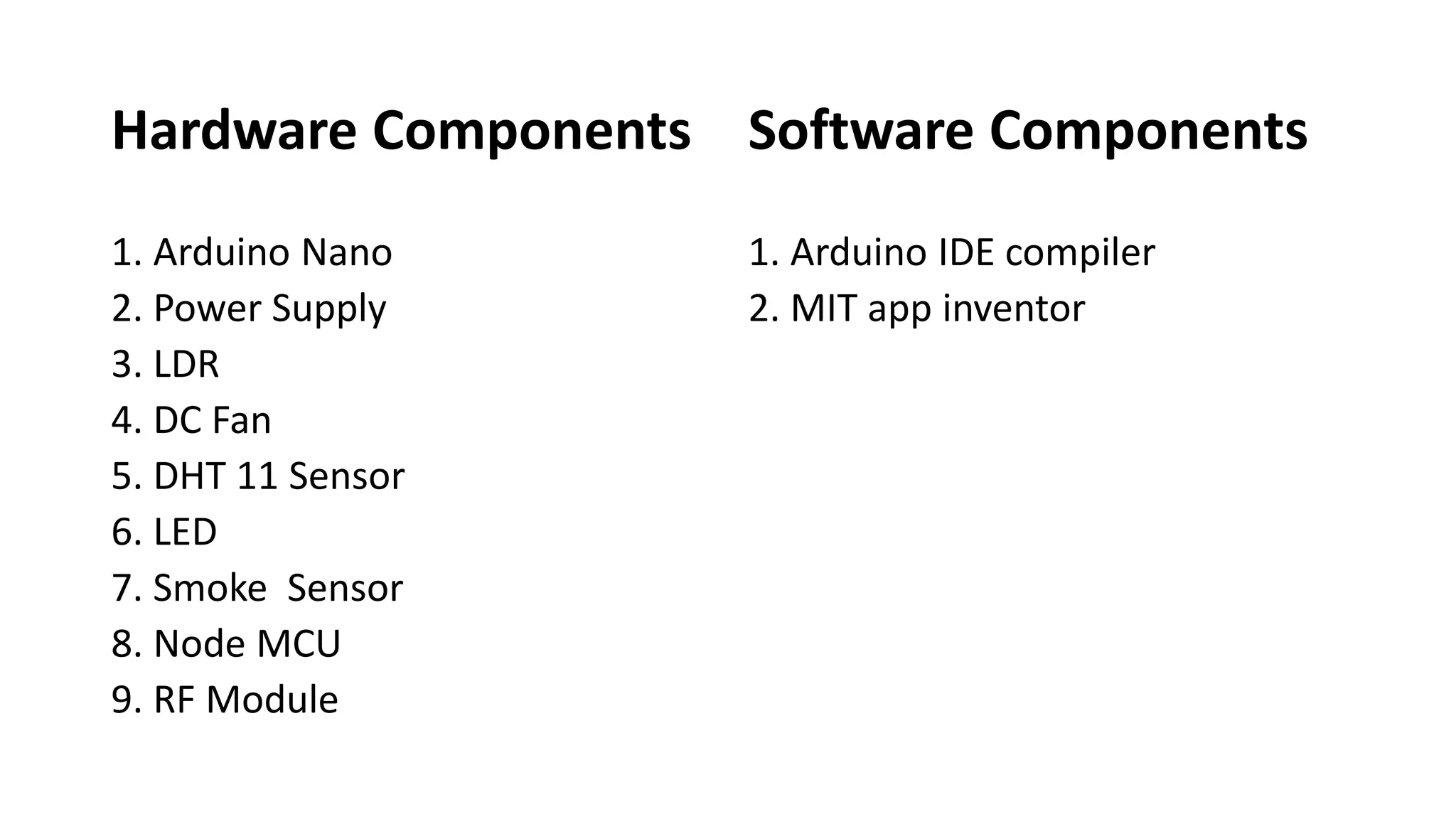
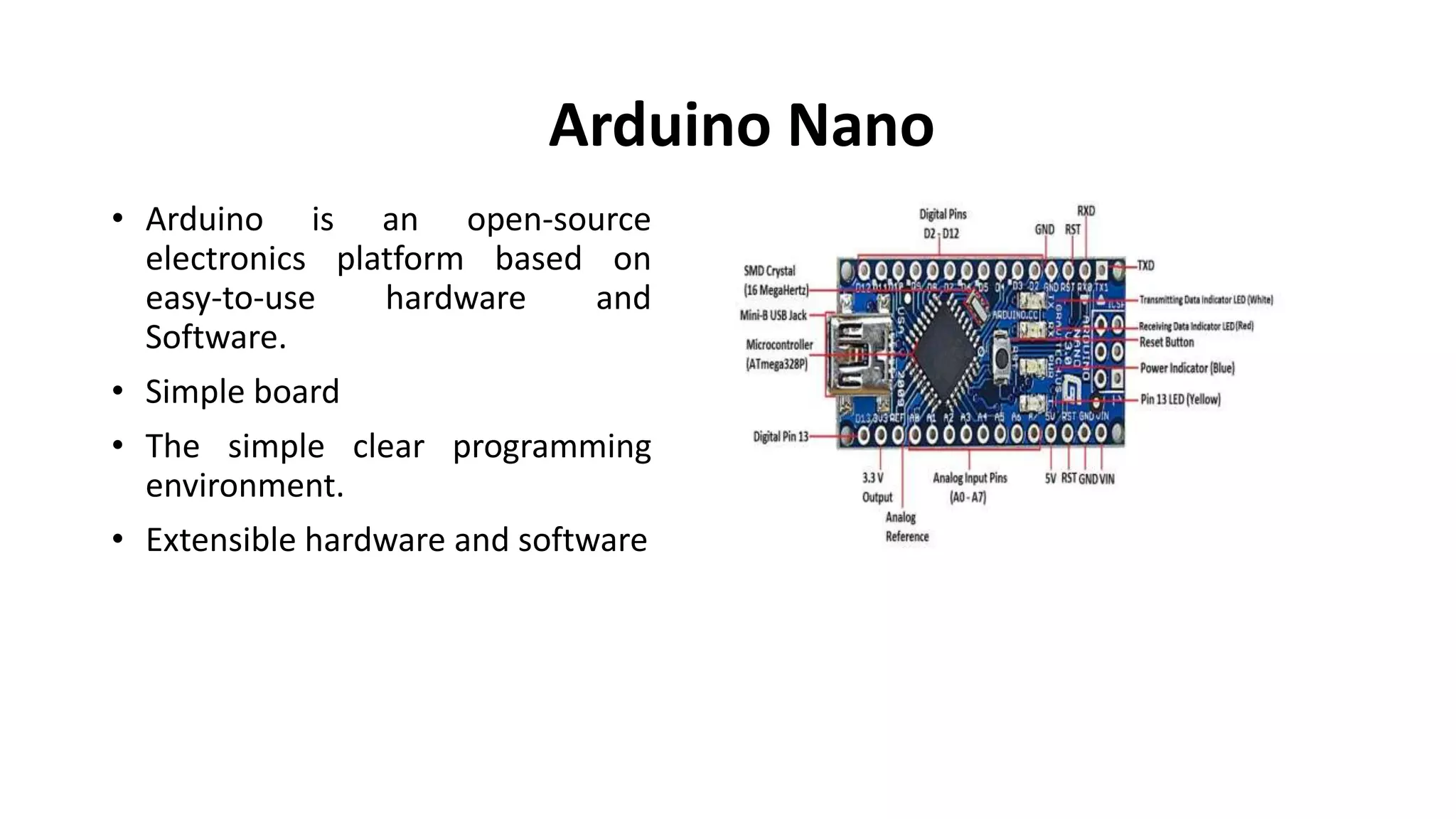
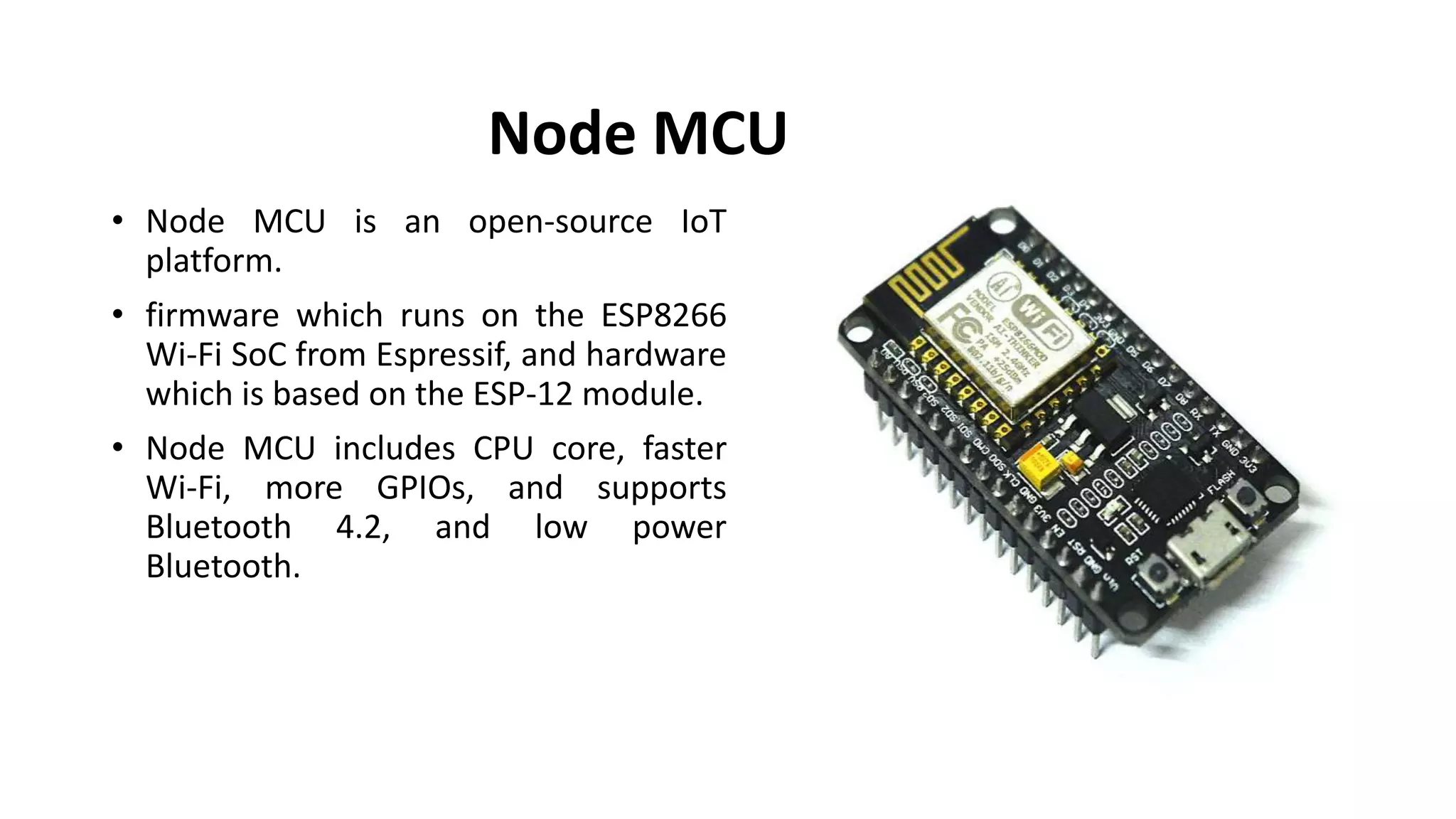
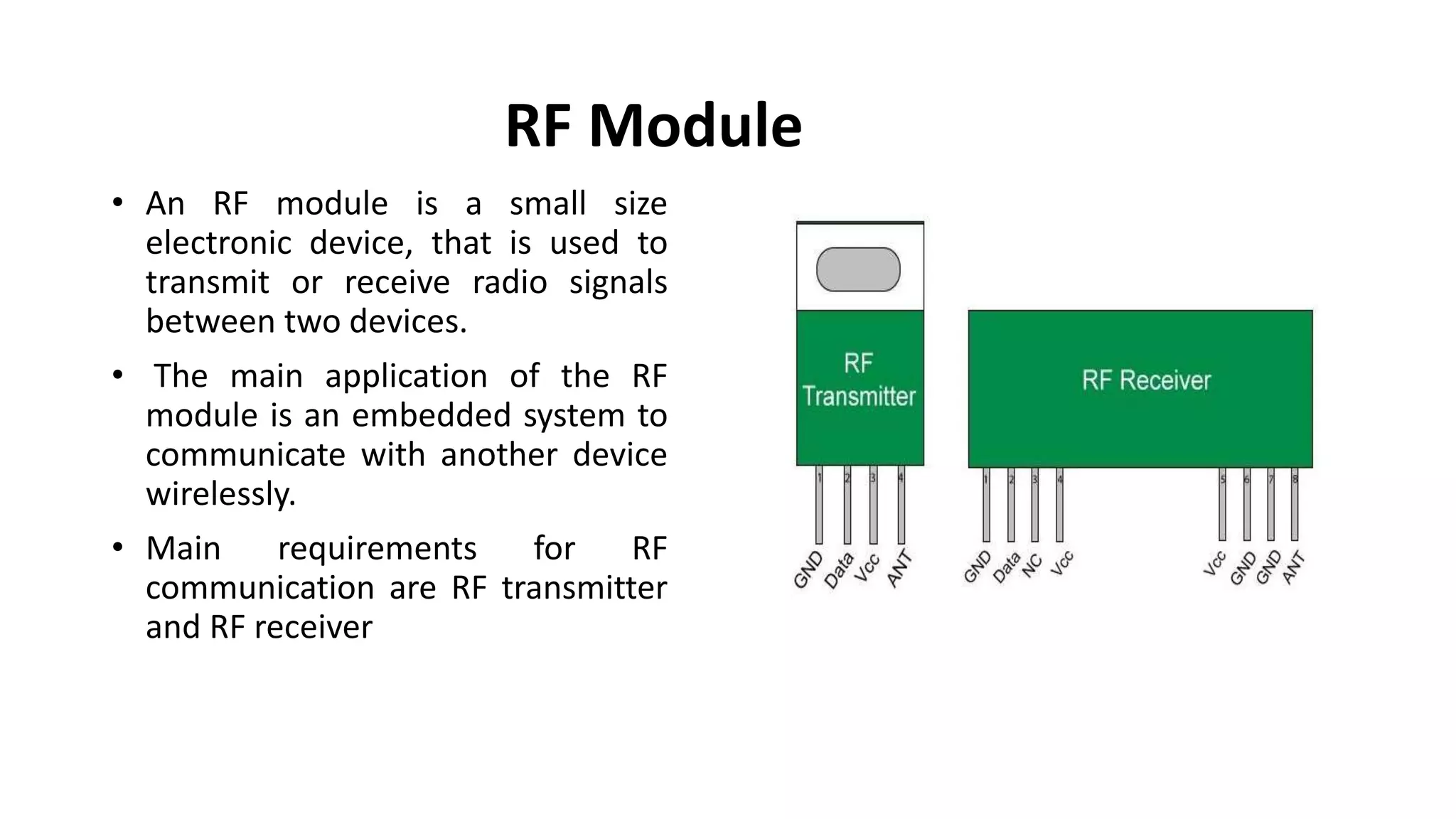
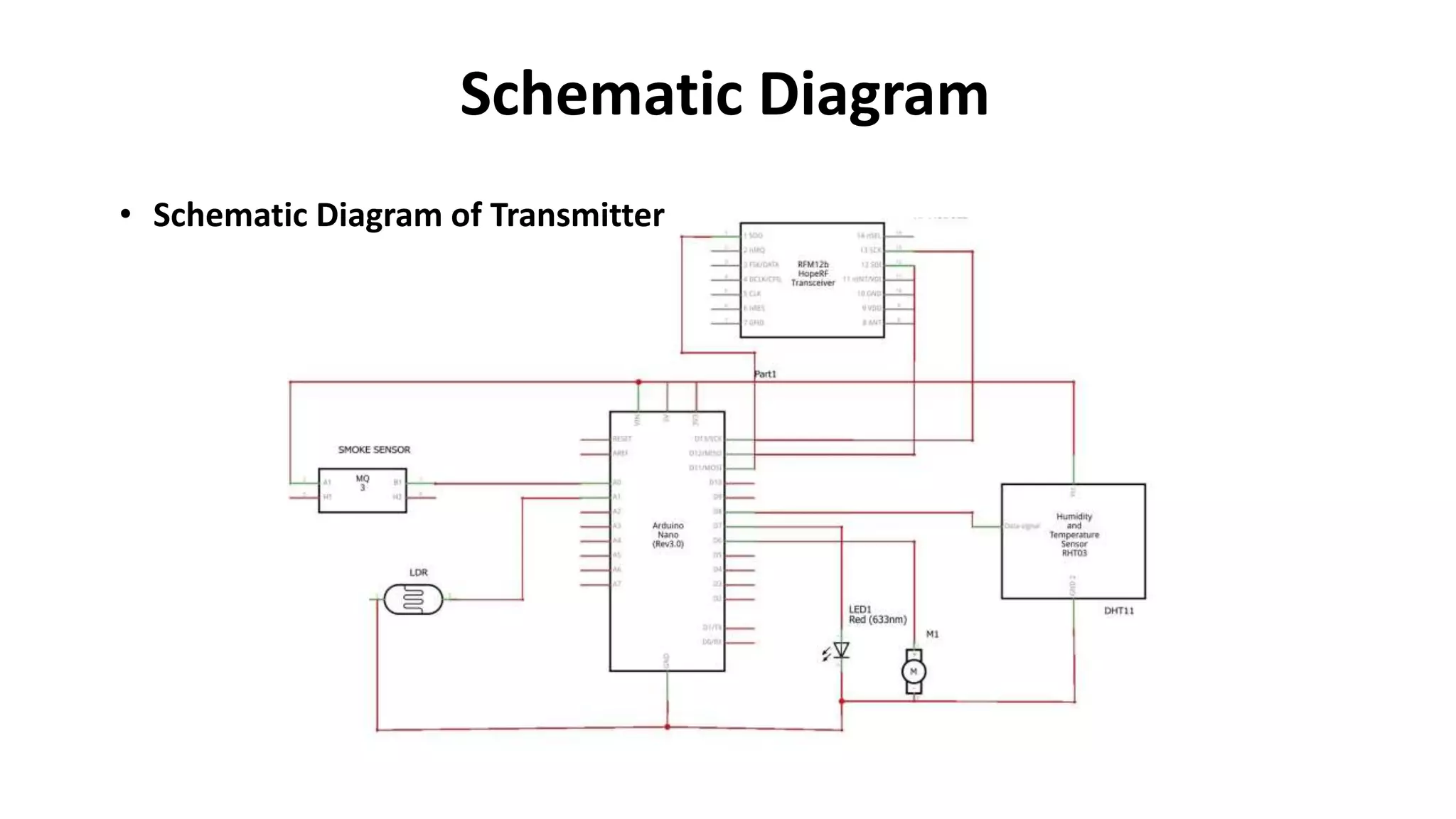
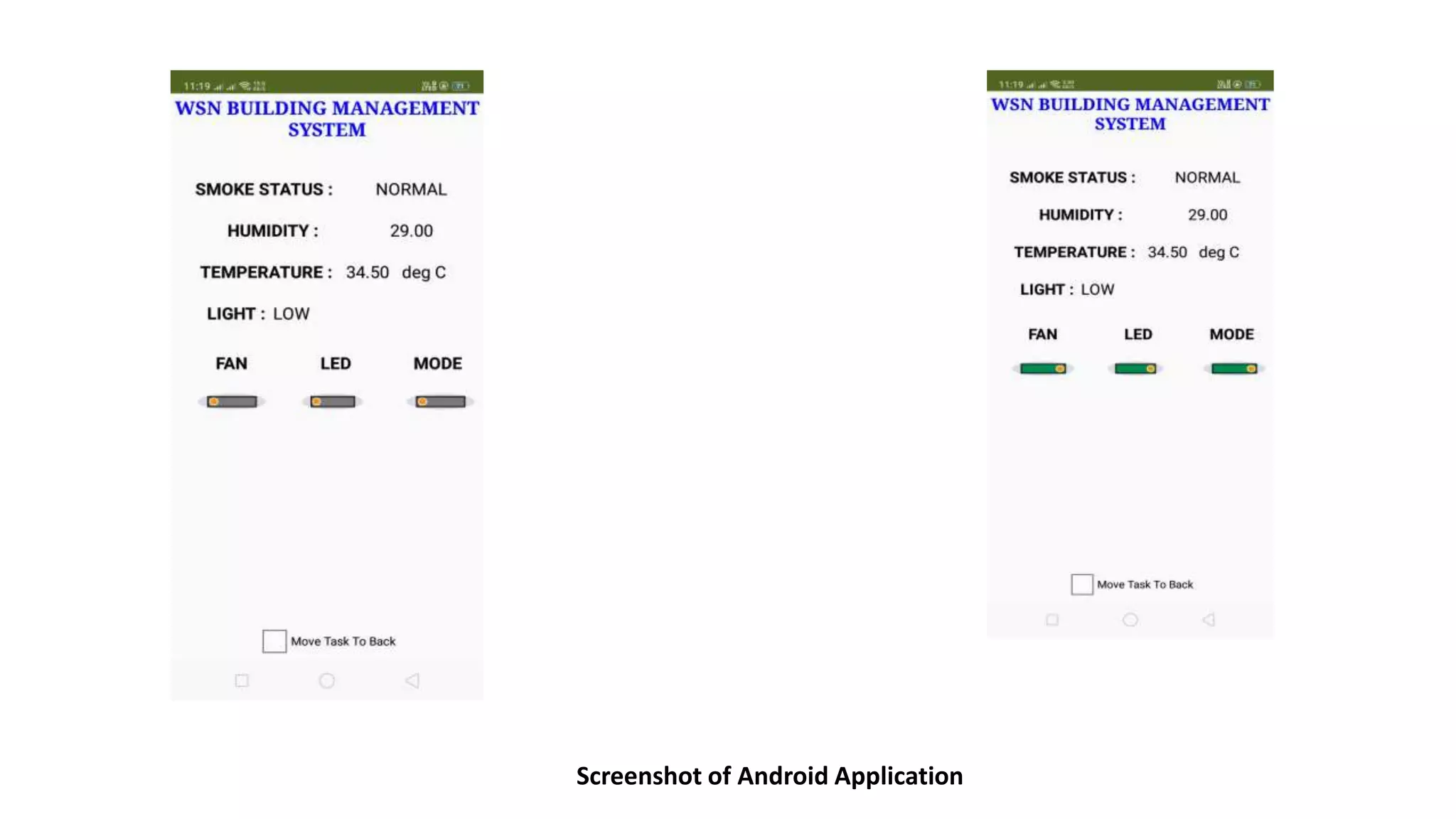
The document outlines a project on designing a wireless sensor network for building management systems, focusing on data collection and processing for improved control of building environments. It discusses various components, advantages, and applications of the system, highlighting energy efficiency and safety benefits. The project proposes future enhancements by integrating advanced technologies like Zigbee and GSM.