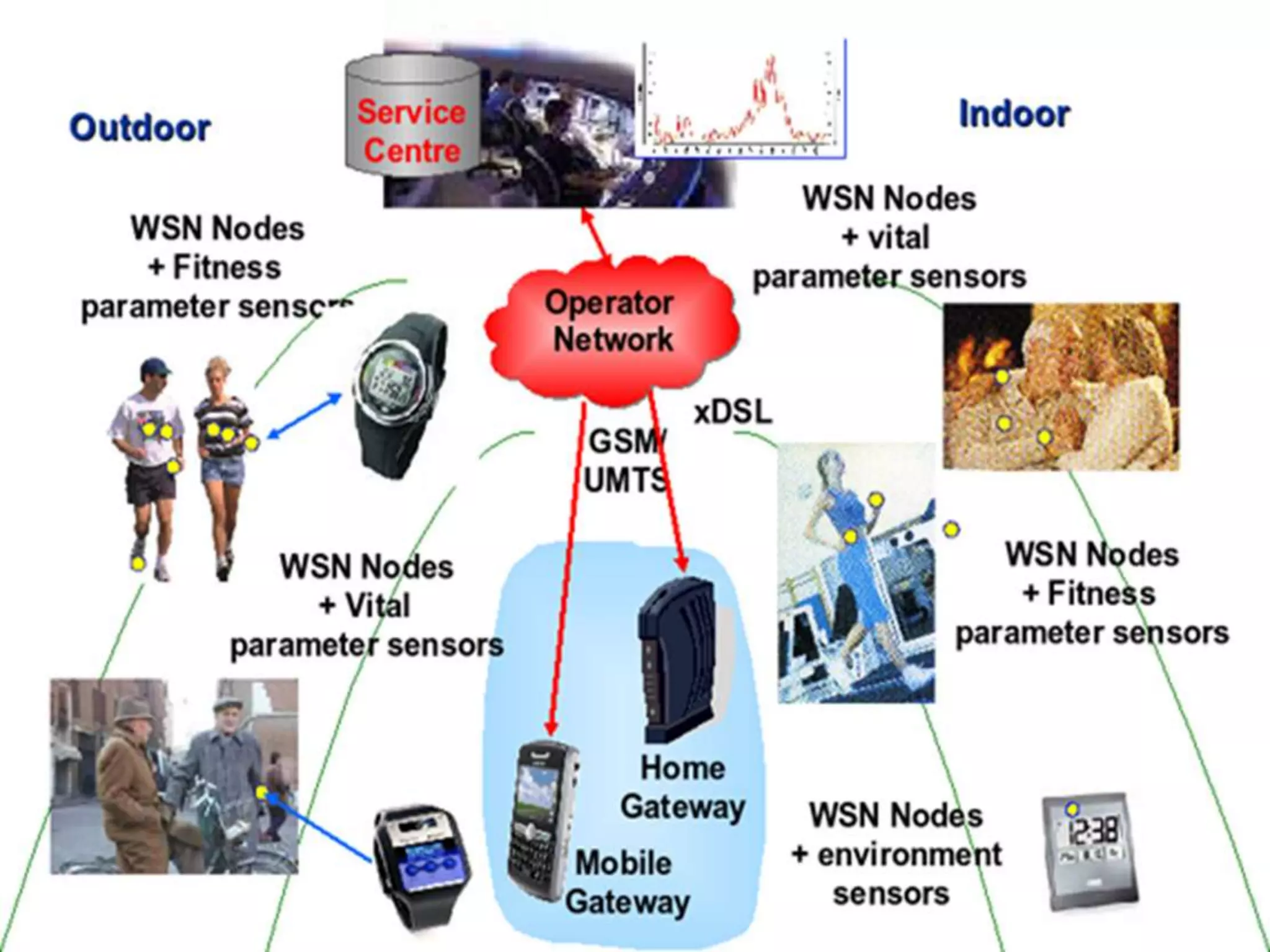
Wireless sensor networks consist of sensors distributed in an ad hoc manner to sense physical phenomena and process the gathered information. They use broadcast communication and have limited power, energy, and computational capabilities compared to traditional networks. Wireless sensor networks can monitor objects, areas, and interactions between objects and spaces through applications in environmental monitoring, precision agriculture, military surveillance, healthcare, and more. They are self-organizing and can operate in extreme conditions, with future applications including smart homes, medical monitoring, traffic management, and industrial/commercial automation.