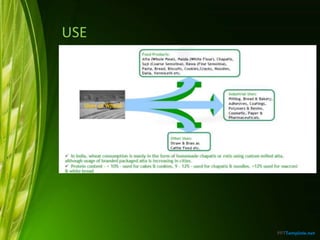
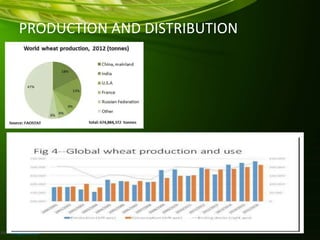
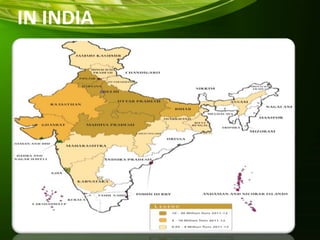
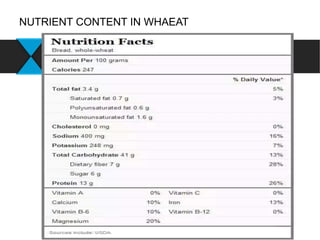
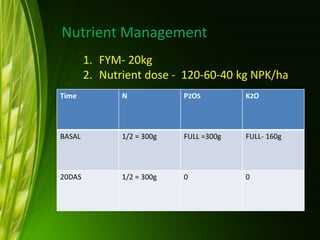
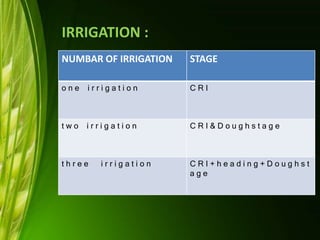
This document provides information about wheat production in India. It discusses that wheat is the most widely grown cereal grain in the world. In India, wheat is commonly grown in the alluvial soils of the Gangetic plains and black cotton soils of central India. Optimal growing conditions include temperatures between 20-25°C during growth and dry, warm weather during harvesting. Common wheat varieties grown in India include T. aestivum and T. durum. The document outlines best practices for soil preparation, planting, irrigation, fertilizer application, weed control and harvesting of wheat crops in India.