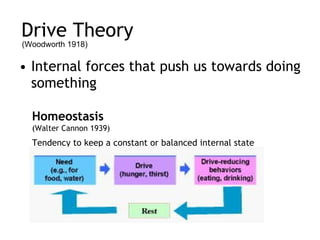
The document discusses different theories of motivation including instinct theory, drive theory, incentive theory, arousal theory, and Maslow's hierarchy of needs. It also covers biological motives like hunger and thirst, stimulus motives including sensory stimulation, curiosity and exploration, and competence. Learned social motives such as achievement, power, and affiliation are mentioned as well.