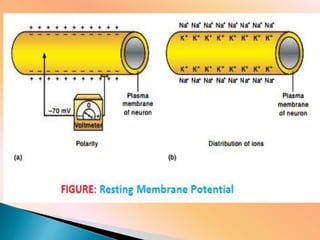
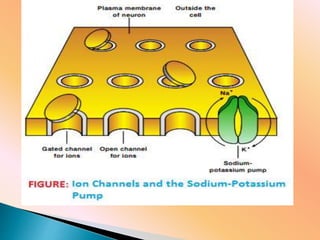
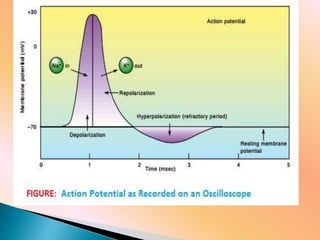
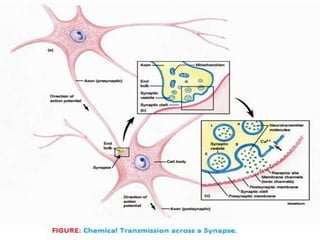
This document discusses the resting membrane potential in neurons. It explains that the plasma membrane of a resting neuron is polarized with negatively charged fluid inside and positively charged fluid outside, resulting in a resting membrane potential of around -70 mV. This polarization is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump and concentration gradients of sodium and potassium ions. When an action potential is triggered, the permeability to sodium ions increases, causing depolarization and propagating the nerve impulse down the axon.