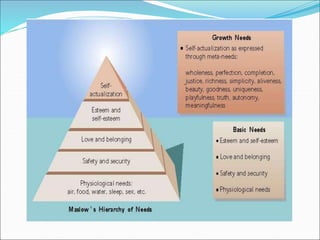
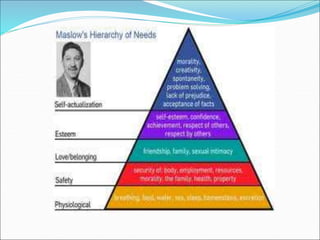
This document provides an overview of motivation from a psychological perspective. It discusses different theories of motivation including instinct theory, drive theory, and incentive theory. Instinct theory proposes that behaviors are genetically programmed for survival and reproduction. Drive theory views behavior as reducing internal tension from unmet biological needs. Incentive theory states behavior is motivated by external rewards. Motives can be primary, stimulus-based, or secondary and learned. The document also covers emotion, facial expressions, lie detectors, and Maslow's hierarchy of needs.