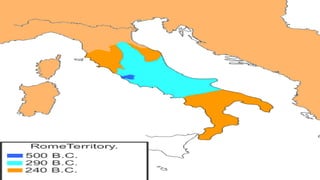
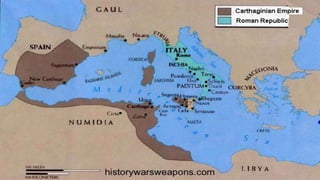
Rome began as a small town on the Tiber River and grew into a massive empire through military expansion and conquest over centuries. It transitioned from a monarchy to a republic ruled by elected officials and senators. Internal political struggles and the rise of influential figures like Julius Caesar led to the end of the republic and establishment of the Roman Empire under Augustus in 27 BC. The empire reached its peak but then declined due to economic troubles, corruption, and invasions, with the western half falling in 476 AD.