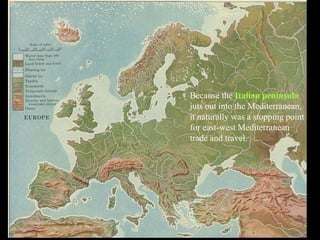
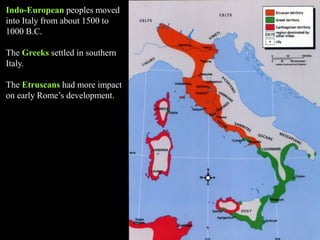
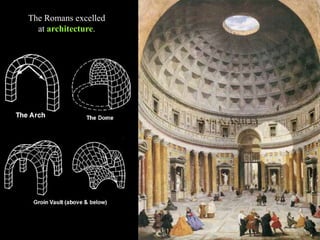
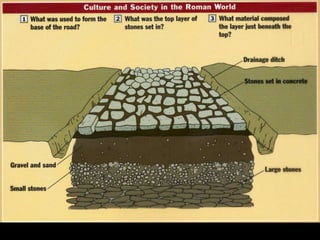
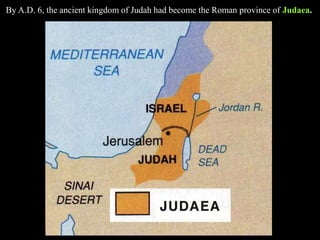
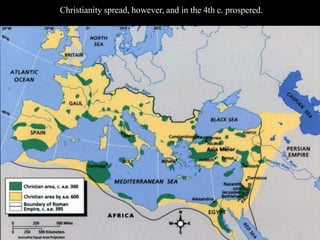
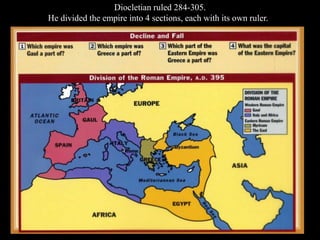
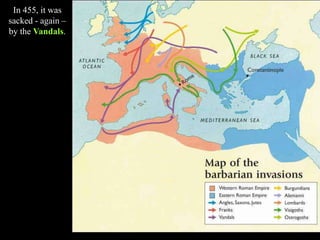
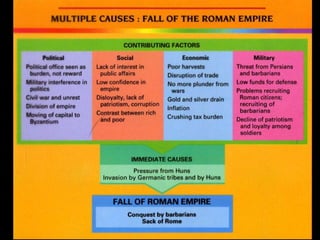
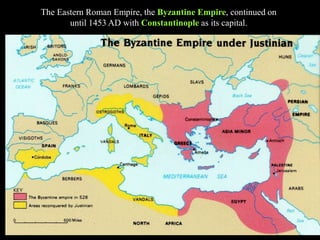
1) The Italian peninsula was well situated for east-west Mediterranean trade and saw migrations of Indo-European peoples beginning around 1500 BC. The Greeks and Etruscans settled parts of Italy, with the latter influencing early Rome's development.
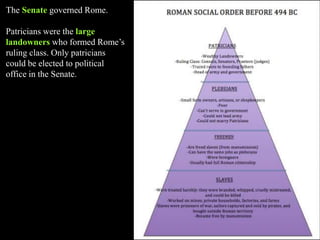
2) By 264 BC, Rome had defeated its neighbors and controlled almost all of Italy, devising the Roman Confederation to rule its territories. Rome was initially divided between patrician landowners and plebeian small landowners and merchants, though the plebeians gained some political rights over time.
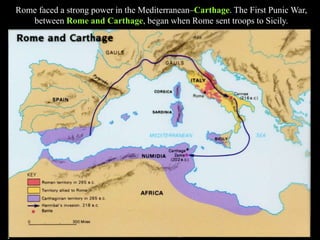
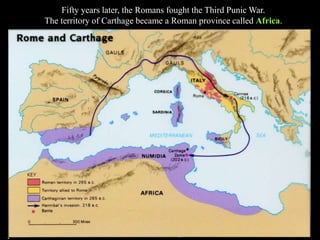
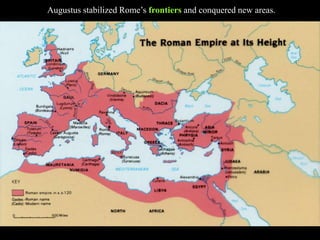
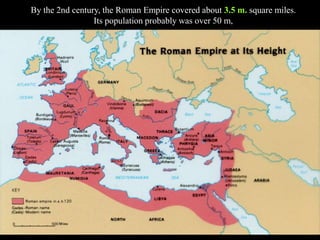
3) Rome defeated Carthage in the Punic Wars and became the dominant power in the western Mediterranean by the mid-2nd century BC. This