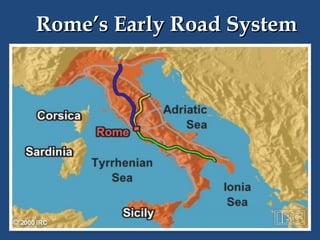
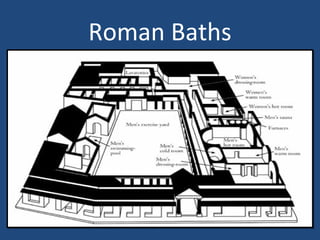
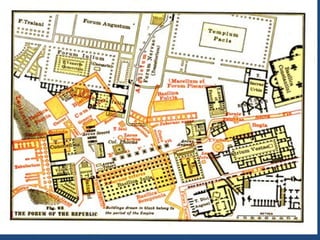
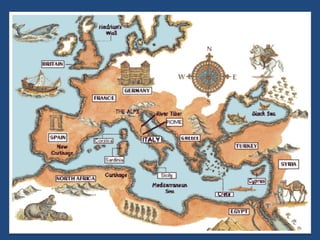
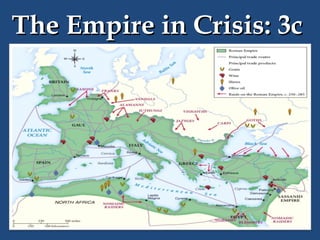
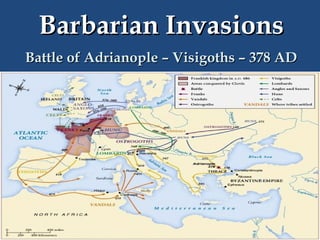
This document provides an overview of ancient Rome, including famous sights and structures like the Colosseum, Circus Maximus, aqueducts, and forums. It then discusses the transition from Roman Republic to Empire, highlighting figures like Julius Caesar, Augustus, and Constantine. The rise of Christianity in the empire and reasons for Rome's eventual fall are also examined.