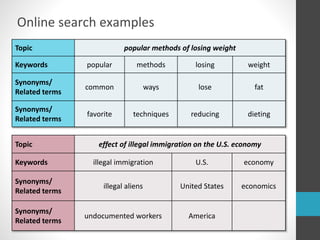
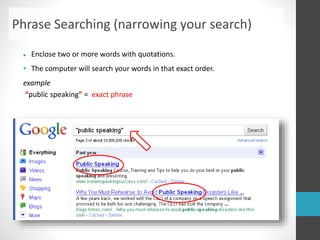
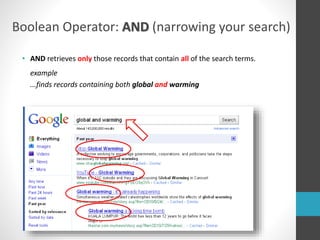
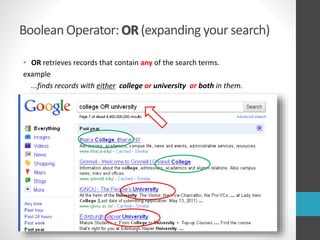
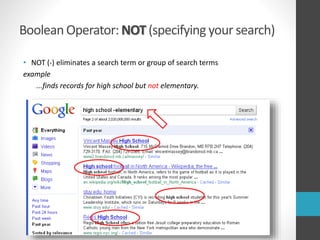
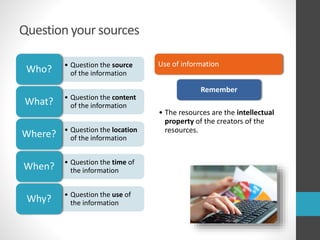
This document provides guidance on research and information literacy. It outlines strategies for conducting academic research, including how to differentiate between primary and secondary sources. It describes how to perform a literature search and online searches for information. The document discusses how to evaluate sources and provides examples of reliable academic databases like ERIC and JSTOR that contain peer-reviewed research. It also offers tips for developing search strategies, such as using keywords, synonyms, and Boolean operators to narrow or broaden searches effectively.