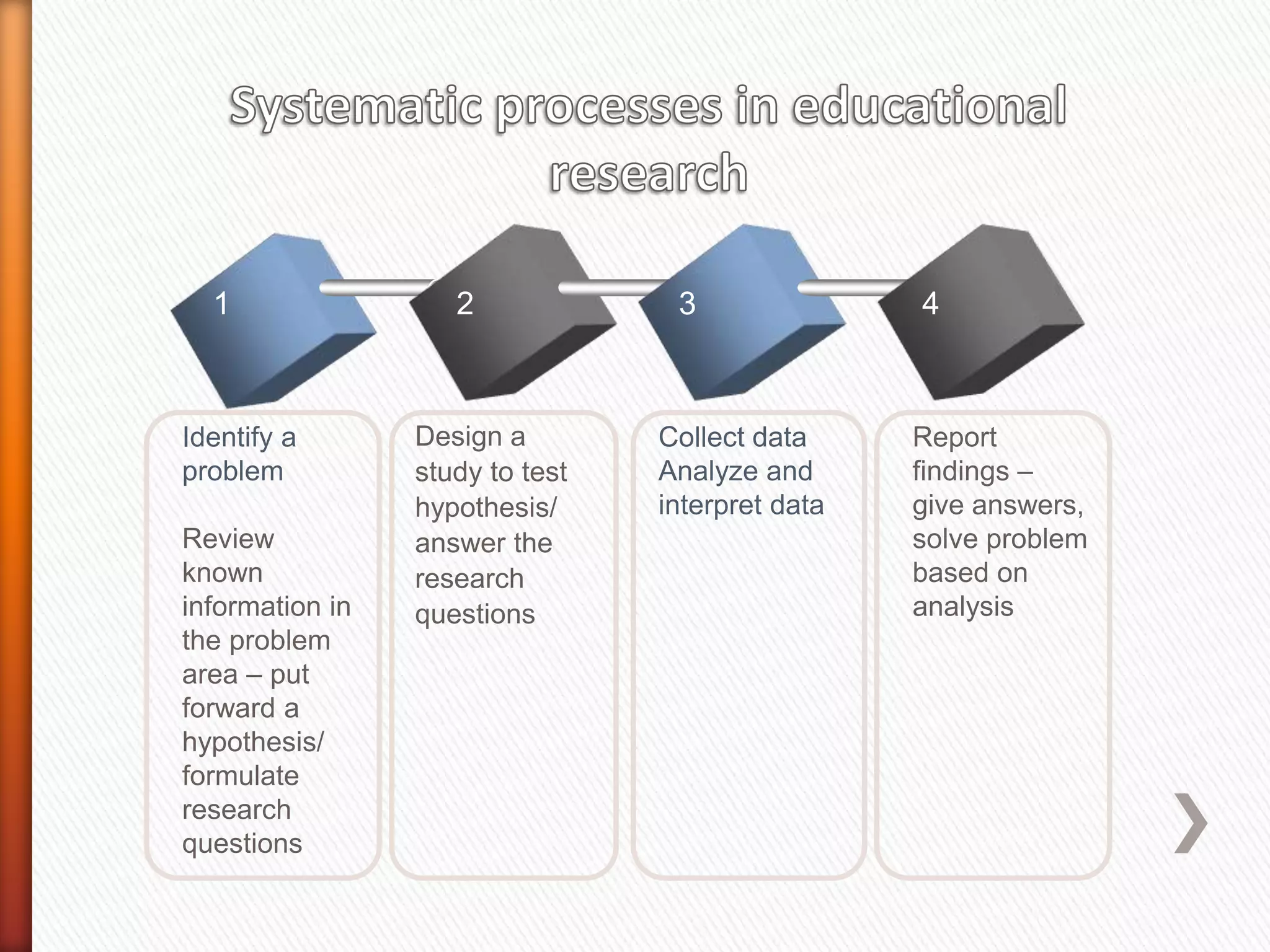
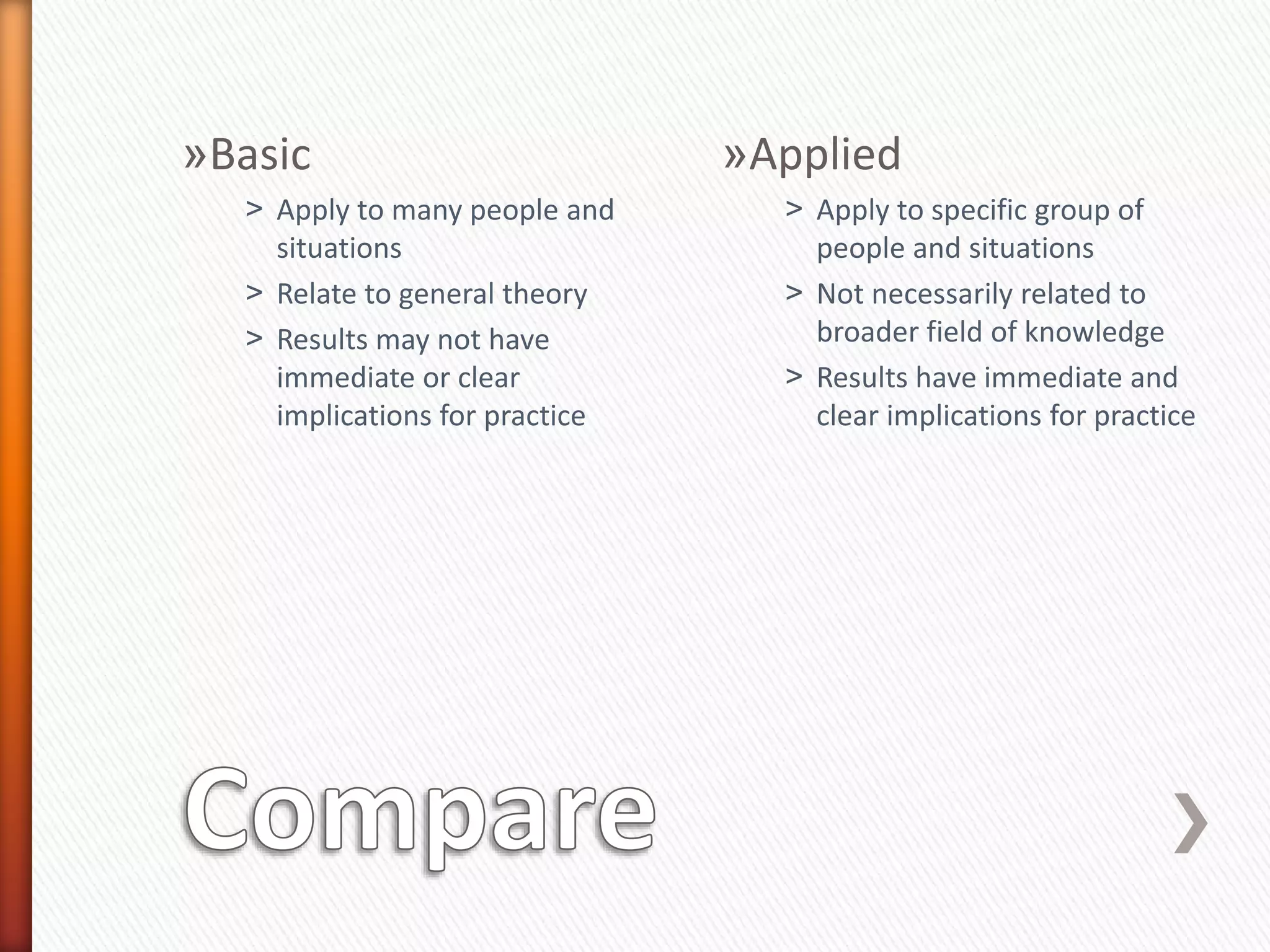
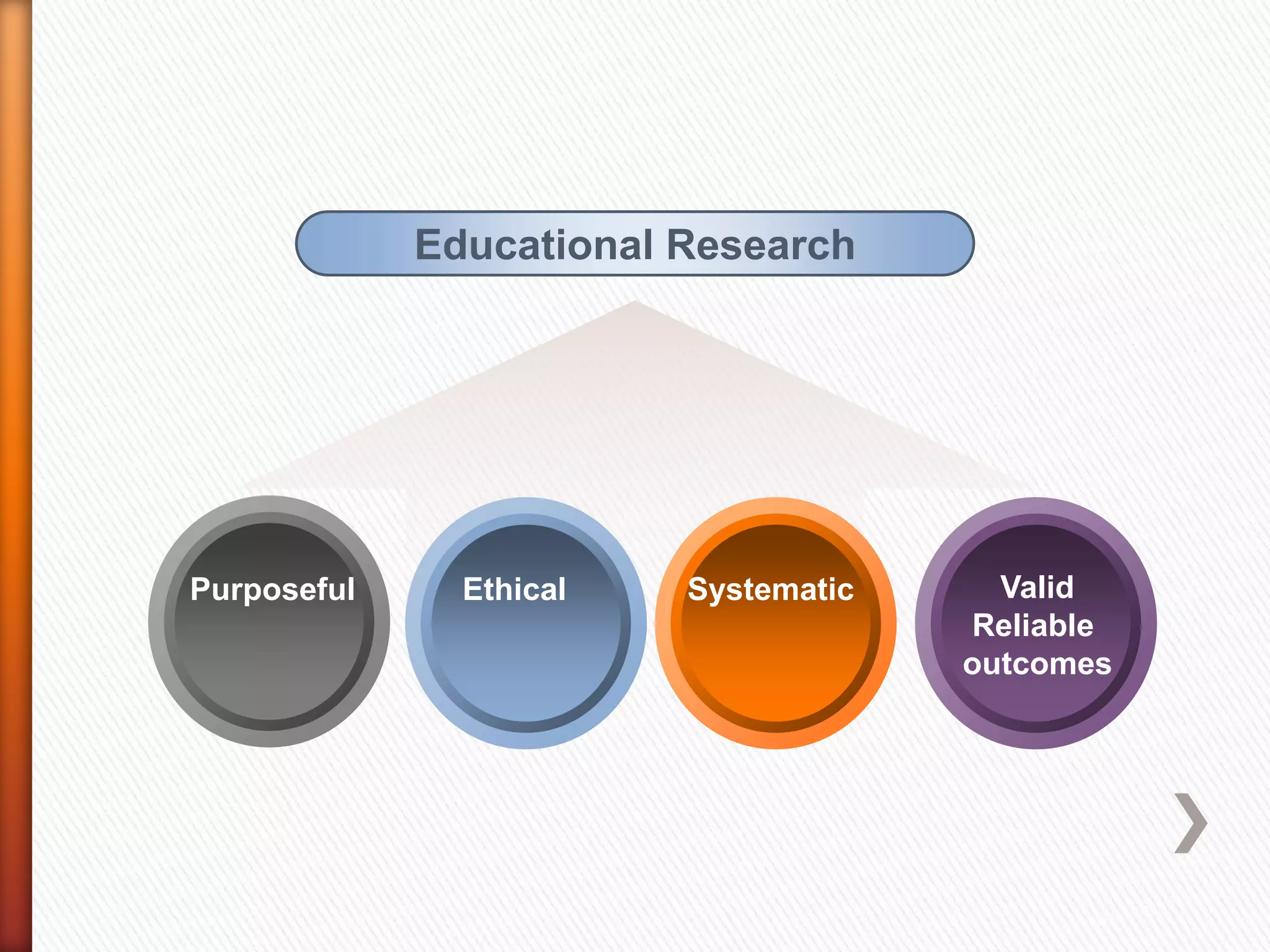
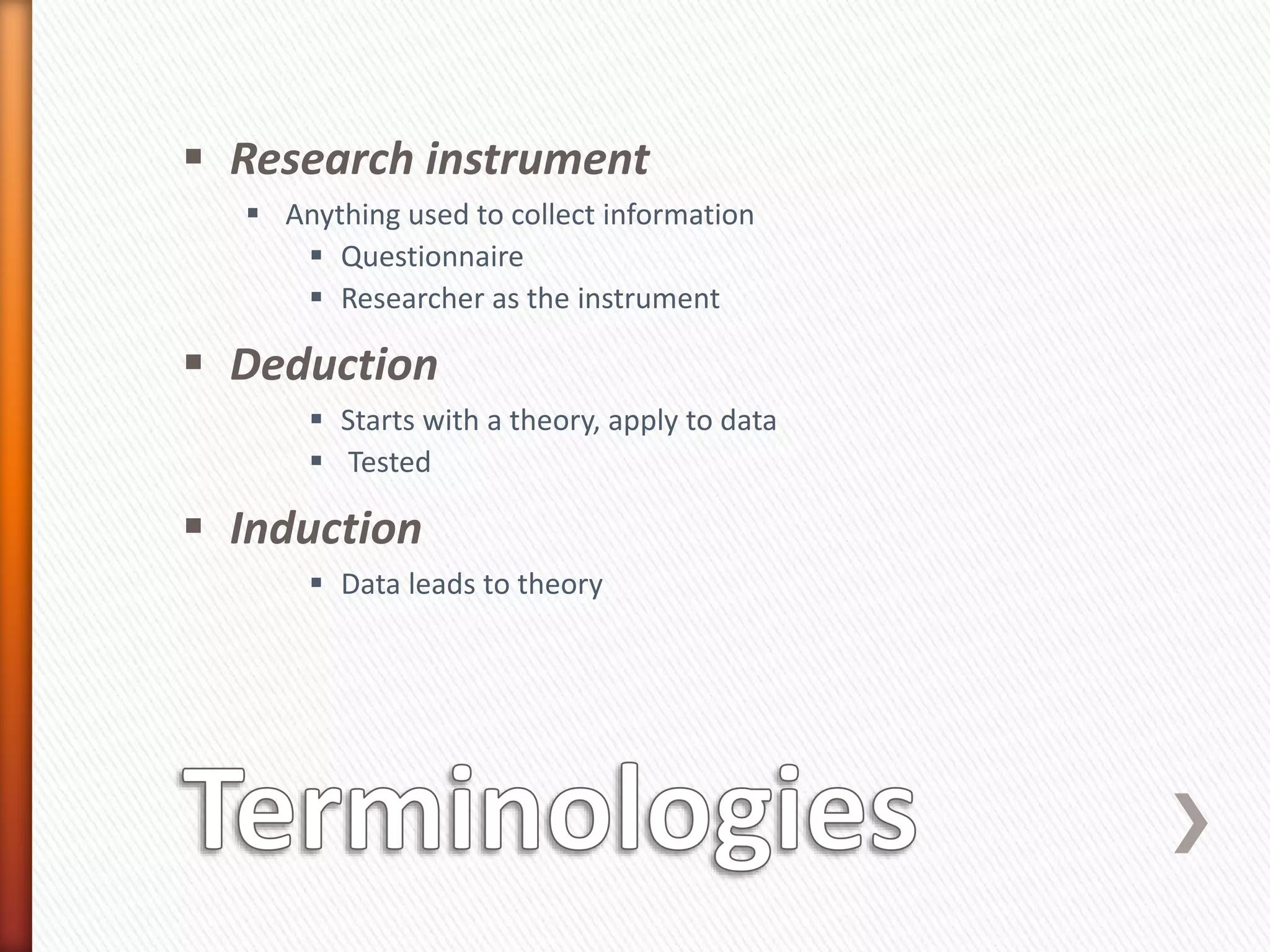
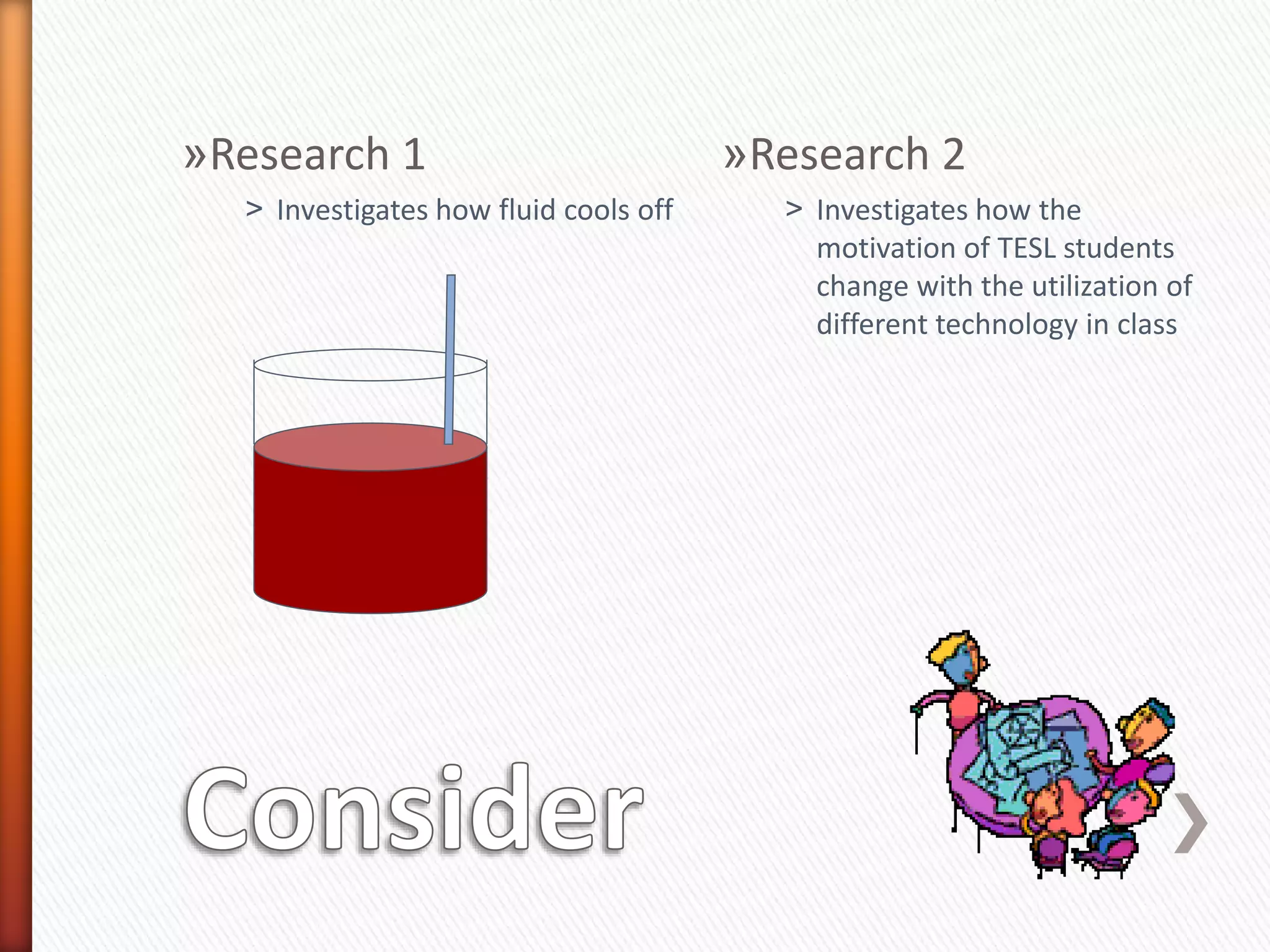
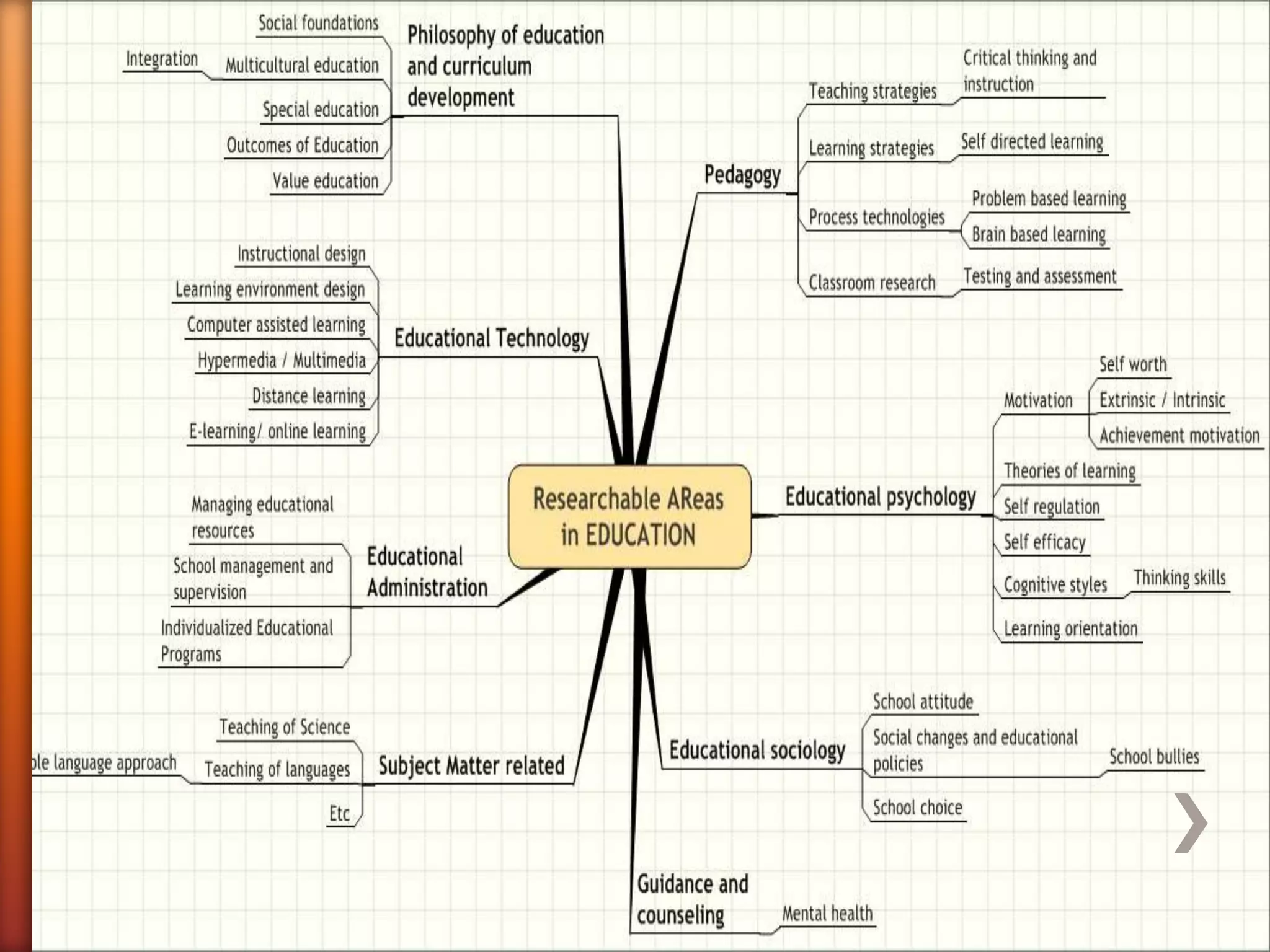
This document provides an overview of key concepts and processes related to educational research methodology. It discusses topics such as variables, hypotheses, theories, research instruments, data analysis approaches, and the differences between basic and applied research. Examples are provided to illustrate research studies investigating how fluid cools off and how technology impacts student motivation. Guidance is also given on formulating research questions and developing a research portfolio.