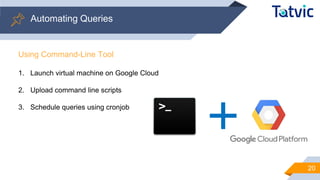
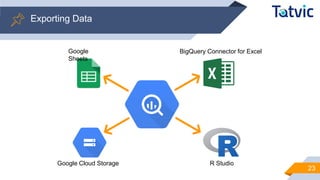
The document outlines a webinar focused on interacting with BigQuery, covering its architecture, integrations, and advanced query techniques. Key topics include automating queries, exporting data to various formats, and best practices for query writing. Additional sections discuss joining online and offline data to create comprehensive user journey analyses.







![17
Useful Functions
• BigQuery functions are more or less similar in nature to that of regular SQL
• However, there are some functions which act differently to an extent
COUNT([DISTINCT] field [, n]) REGEXP_MATCH('str', 'reg_exp')
EXACT_COUNT_DISTINCT(field) REGEXP_REPLACE('orig_str', 'reg_exp', 'replace_str')
GROUP_CONCAT('str' [, separator]) DATEDIFF(<timestamp1>,<timestamp2>)
FIRST(expr), LAST(field) DAY/MONTH/HOUR/MINUTE(<timestamp>)
STRING(numeric_expr),
INTEGER(expr)
TABLE_DATE_RANGE(prefix, timestamp1, timestamp
2)
CONCAT('str1', 'str2', '...') ROW_NUMBER()
DATE(<timestamp>) RANK()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinarinteractingwithbigqueryandworkingwithadvancedqueries-171206133544/85/Webinar-Interacting-with-BigQuery-and-Working-with-Advanced-Queries-17-320.jpg)