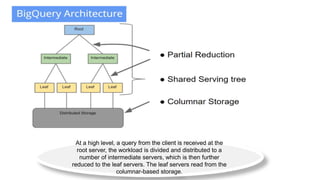
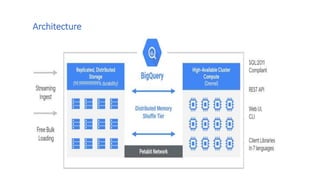
BigQuery is Google Cloud Platform's interactive big data service that allows users to analyze massive datasets in seconds using SQL-like queries. It offers a scalable and fast way to query terabytes of data without the expense of maintaining servers or databases. BigQuery organizes data into a project-dataset-table hierarchy and uses a distributed architecture to efficiently process queries across servers.