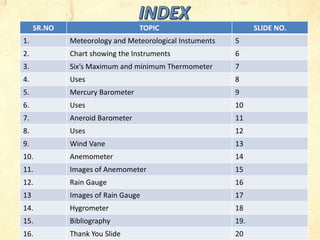
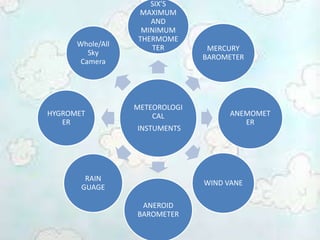
The document discusses various meteorological instruments used in weather forecasting, including thermometers, barometers, anemometers, and hygrometers, along with their functions and applications. It includes detailed descriptions of instruments' operational principles, such as the mercury barometer and aneroid barometer, and how they measure atmospheric pressure. Additionally, it highlights the importance of accurate measurements in meteorology and the use of innovative tools like all-sky cameras for observing weather conditions.