Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times



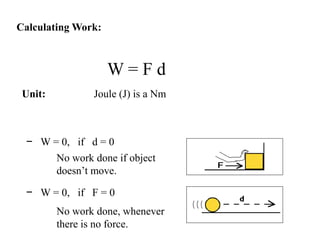
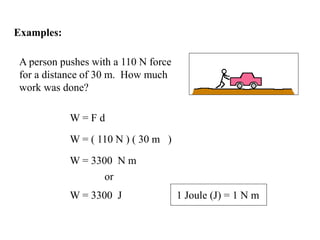

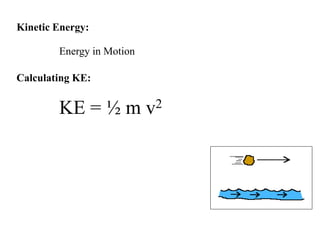
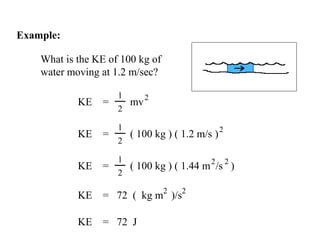
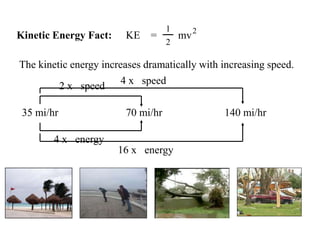
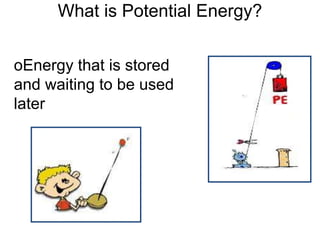


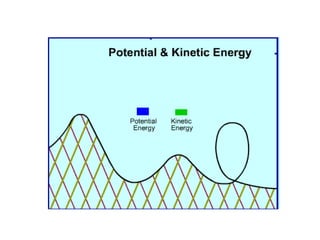
The document discusses different types of energy: - Work is done when a force causes an object to move, and is calculated as work (W) equals force (F) multiplied by distance (d). - Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is calculated as kinetic energy (KE) equals one-half mass (m) multiplied by velocity (v) squared. - Potential energy is stored energy due to an object's position or state, such as height, and is calculated as potential energy (PE) equals mass (m) multiplied by gravity (g) multiplied by height (h).












