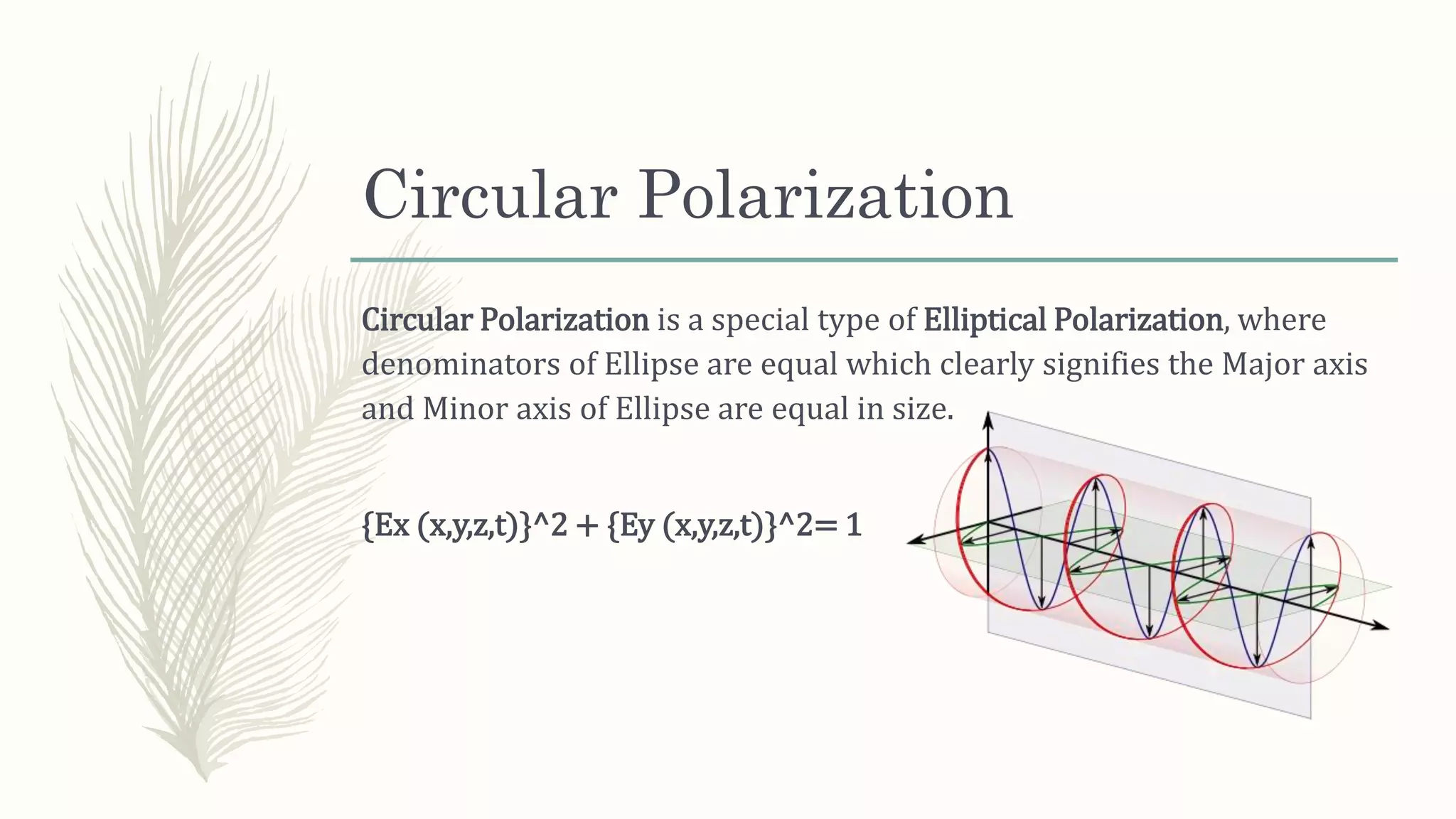
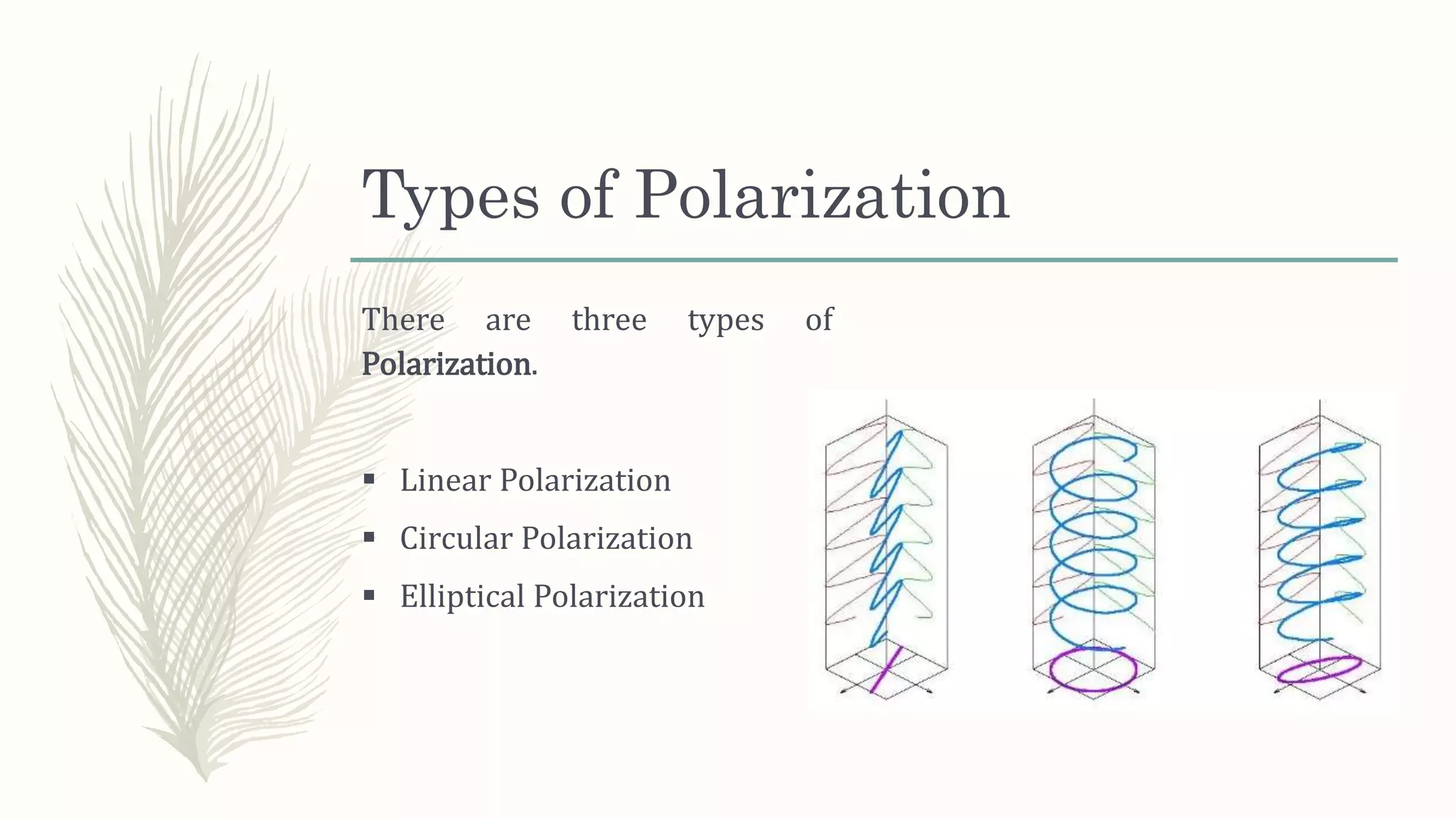
This document discusses different types of polarization of electromagnetic waves. It defines polarization as the path of the electric field vector of an EM wave over time at a fixed point in space. There are three main types of polarization: linear, where the electric field follows a straight line; circular, where it follows a perfect circle; and elliptical, where the path is an ellipse. Linear polarization occurs when the ratio of the electric field components is constant. Elliptical polarization can be right-handed or left-handed. Circular polarization is a special case of elliptical polarization where the ellipse major and minor axes are equal.


![Linear Polarization
In Linear Polarization, the electric
field vector traverses a linear path
with respect to time at any point in
space.
Considering a wave travelling in z
direction can be represented
using,
E(x,y,z,t) = Ex (x,y,z,t)ax + Ey
(x,y,z,t)ay
The wave is said to be Linear
Polarization if the ratio of y
component to that of the x
component is a constant, i.e.,
[Ex (x,y,z,t)] / [Ey (x,y,z,t)]= k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polarization-200401153310/75/Wave-Polarization-4-2048.jpg)