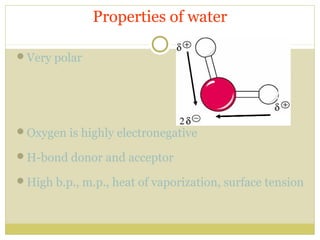
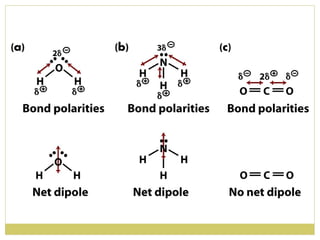
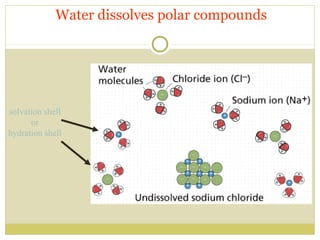
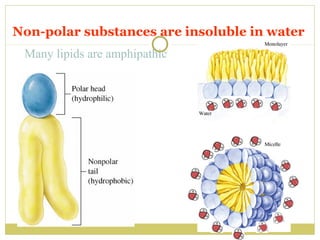
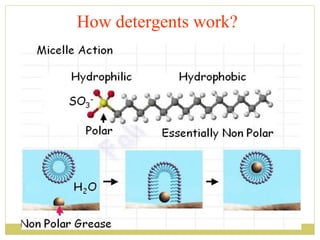
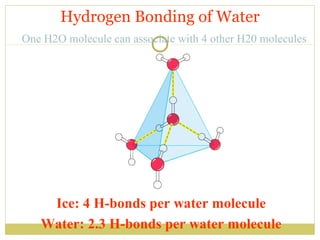
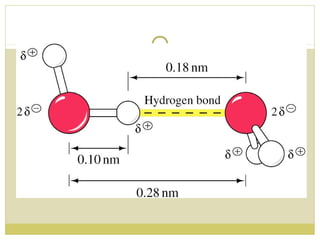
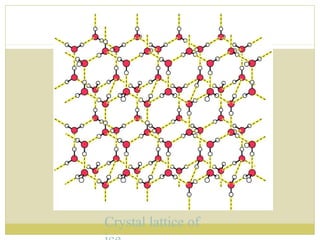
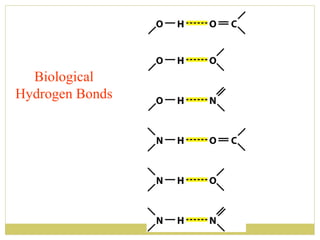
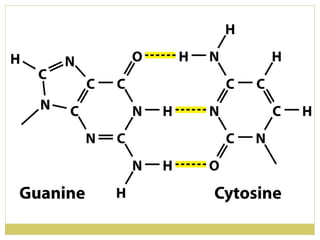
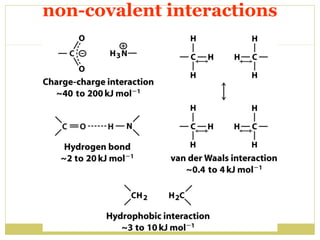
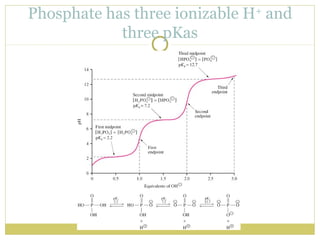
This document discusses several key properties of water including its polarity, hydrogen bonding ability, and role in solvation. Water can dissolve polar substances due to hydrogen bonding interactions in a solvation shell. Nonpolar substances are insoluble in water. Hydrogen bonding between water molecules forms a crystal lattice in ice and allows water to have unusual properties like a high boiling point. The pH scale is used to describe hydrogen ion concentration in aqueous solutions. Weak acids and bases only partially dissociate in water according to their acid dissociation constants (Ka) and pKa values. Buffers resist changes in pH through the dynamic equilibrium between a weak acid and its conjugate base as described by the Henderson-Hasselbach equation.




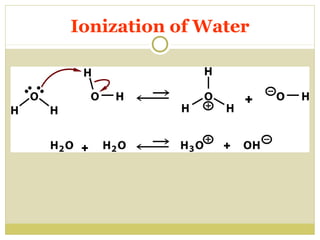
![Ionization of Water
H20 + H20
H2 0
Keq= [H+] [OH-]
[H2O]
H3O+ + OHH+ + OHKeq=1.8 X 10-16M
[H2O] = 55.5 M
[H2O] Keq = [H+] [OH-]
(1.8 X 10-16M)(55.5 M ) = [H+] [OH-]
1.0 X 10-14 M2 = [H+] [OH-] = Kw
If [H+]=[OH-] then [H+] = 1.0 X 10-7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-17-320.jpg)
![pH Scale
Devised by Sorenson (1902)
[H+] can range from 1M and
1 X 10-14M
using a log scale simplifies notation
pH = -log [H+]
Neutral pH = 7.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-18-320.jpg)

![Acid/conjugate base pairs
HA + H2O
HA
A- + H3O+
A- + H+
HA = acid ( donates H+)(Bronstad Acid)
A- = Conjugate base (accepts H+)(Bronstad Base)
Ka = [H ][A ]
[HA]
+
-
pKa = - log Ka
Ka & pKa value describe tendency to loose
H+
large Ka = stronger acid
small Ka = weaker acid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-21-320.jpg)
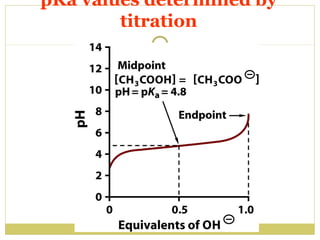


![Henderson-Hasselbach Equation
1) Ka = [H ][A ]
[HA]
+
-
HA = weak acid
A- = Conjugate base
2) [H+] = Ka [HA]
[A-]
3) -log[H+] = -log Ka -log [HA]
[A-]
4) -log[H+] = -log Ka +log [A-]
[HA]
5) pH = pKa +log [A-]
[HA]
* H-H equation describes
the relationship between
pH, pKa and buffer
concentration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-26-320.jpg)
![Case where 10% acetate ion 90% acetic
acid
• pH = pKa + log10
[0.1 ]
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
[0.9]
• pH = 4.76 + (-0.95)
• pH = 3.81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-27-320.jpg)
![Case where 50% acetate ion 50% acetic
acid
• pH = pKa + log10
[0.5 ]
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
[0.5]
• pH = 4.76 + 0
• pH = 4.76 = pKa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-28-320.jpg)
![Case where 90% acetate ion 10% acetic
acid
• pH = pKa + log10
[0.9 ]
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
[0.1]
• pH = 4.76 + 0.95
• pH = 5.71](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-29-320.jpg)
![Cases when buffering fails
• pH = pKa + log10
[0.99 ]
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
[0.01]
• pH = 4.76 + 2.00
• pH = 6.76
• pH = pKa + log10
[0.01 ]
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
[0.99]
• pH = 4.76 - 2.00
• pH = 2.76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waterstructure-140222062745-phpapp01/85/Water-structure-30-320.jpg)