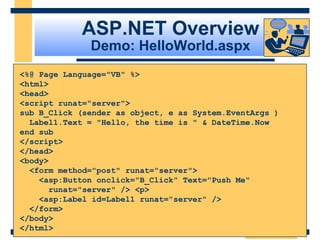
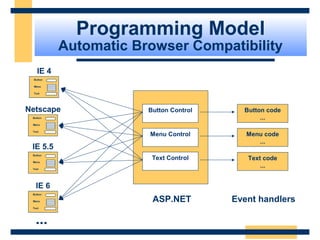
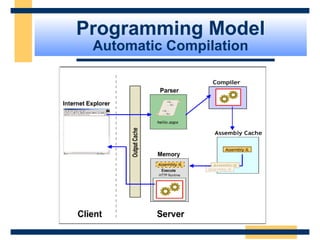
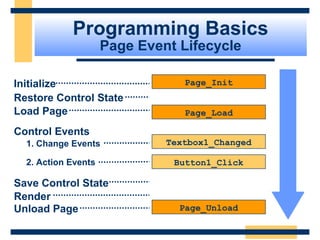
This document provides an introduction and overview of ASP.NET and Web Forms. It discusses the background of ASP and how ASP.NET was developed to address challenges with ASP. The key features of ASP.NET, including Web Forms, Web Services, and the .NET Framework are described. The document then covers the ASP.NET programming model based on controls and events, and how postbacks maintain page state without requiring additional code. It also introduces the ASP.NET object model and server-side controls.