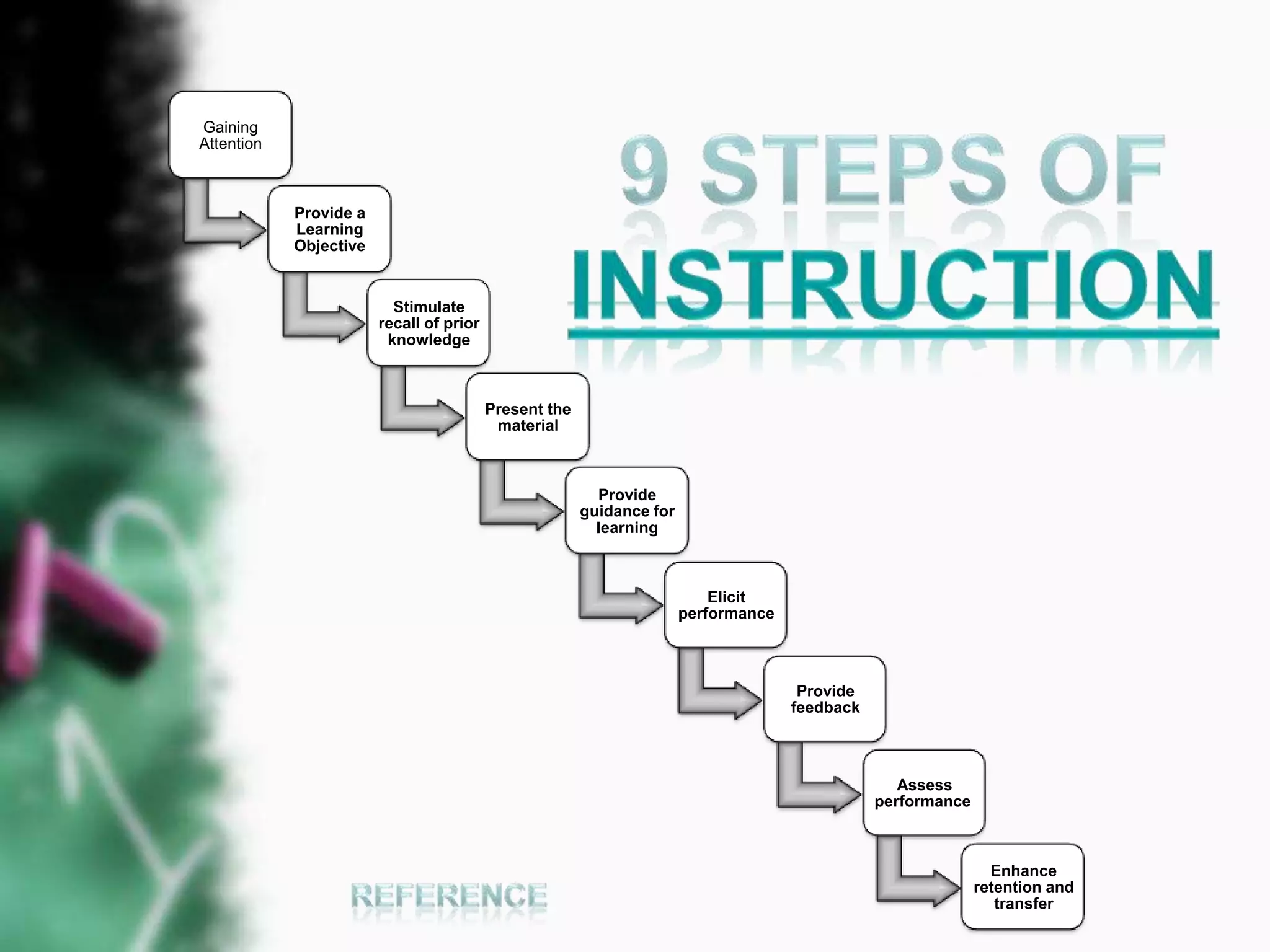
The Gagné Instructional Model outlines 9 steps to effective instructional design: 1) gaining attention, 2) informing learners of objectives, 3) stimulating recall of prior knowledge, 4) presenting the material, 5) providing guidance for learning, 6) eliciting performance, 7) providing feedback, 8) assessing performance, and 9) enhancing retention and transfer. The model correlates these instructional events with cognitive learning processes and considers different levels of learning.

![Description
“[Gagnés nine steps are] general considerations
to be taken into account when designing
instruction. Although some steps might need to be
rearranged (or might be unnecessary) for certain
types of lessons, the general set of considerations
provide a good checklist of key design steps”
(Good, Brophy, 1977).
• Correlates specific events of instruction with
cognitive learning process
• Demonstrates a concern for the different levels
of learning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gagninstructionalmodel-copy-131223165226-phpapp02/75/Gagne-s-Instructional-Model-2-2048.jpg)