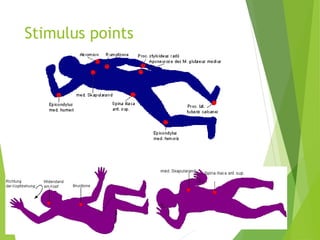
Vojta therapy is a treatment method developed by Dr. Vaclav Vojta in the 20th century that uses light pressure on specific stimulus zones of the body to elicit involuntary motor responses and movement patterns. It is intended to treat disorders of the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system. The therapy activates reflex locomotion through positions like prone, supine, and side lying, with goals of improving postural control, extension against gravity, and stepping movements. Regular application of Vojta therapy is believed to have wide-ranging benefits like improved respiratory function, autonomic regulation, motor skills, and cognitive abilities.