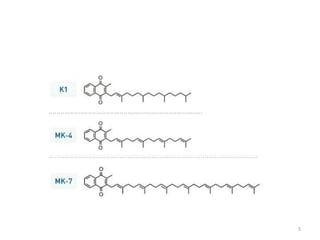
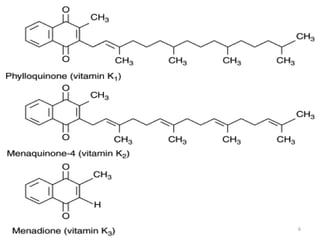
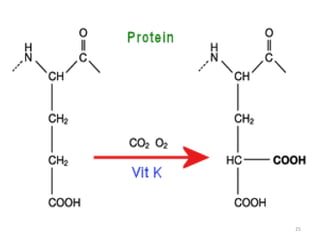
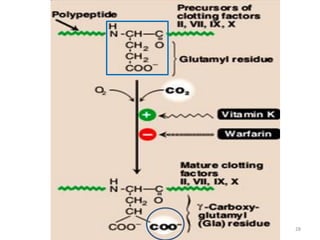
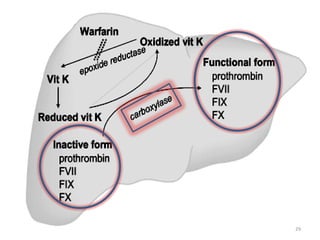
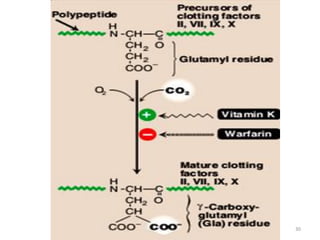
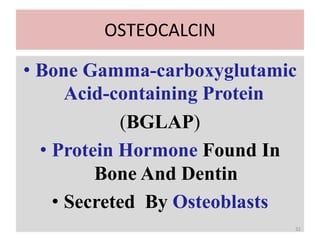
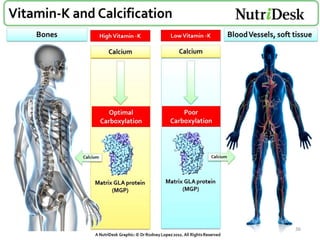
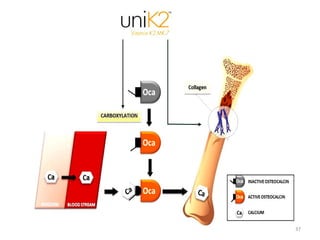
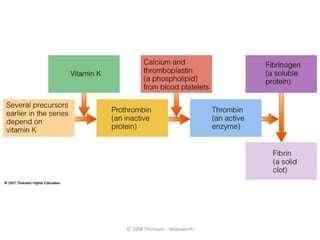
Vitamin K is a group of fat-soluble vitamins that includes phylloquinone (vitamin K1), menaquinones (vitamin K2), and menadione. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health. It is found in green vegetables and synthesized by gut bacteria. Newborns are at risk for vitamin K deficiency due to sterile intestines and low levels in breastmilk, so they are given a prophylactic vitamin K shot.