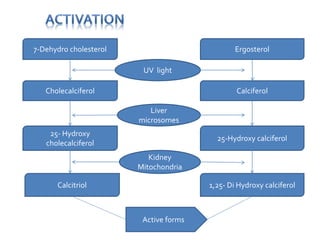
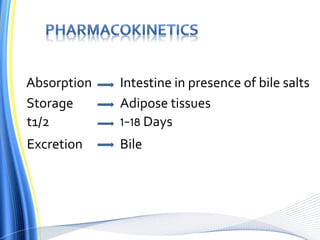
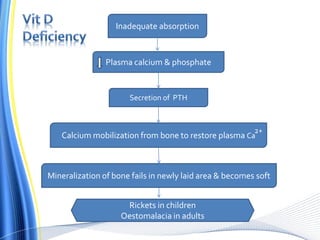
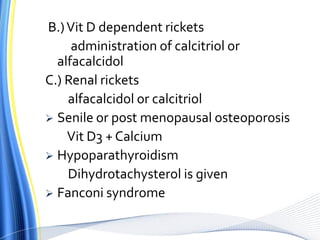
Vitamin D has three main isoforms - vitamins D1, D2, and D3. Vitamin D is fat soluble and helps maintain calcium and phosphate levels. It is produced in the skin from exposure to UV light and is hydroxylated in the liver and kidneys to form active calcitriol. Calcitriol enhances absorption of calcium and phosphate from the intestine and bone and promotes renal reabsorption of calcium and phosphate. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults by inhibiting bone mineralization. Treatment depends on the type of deficiency and may involve supplements of vitamin D, calcium, or analogues like calcitriol or alfacalcidol.