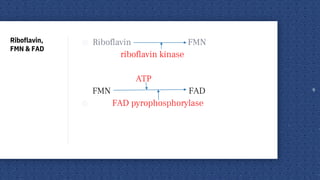
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is an important vitamin for dogs. It acts as a precursor for FMN and FAD, which are cofactors in enzymes involved in energy production and metabolism. Signs of a deficiency include dermatitis, weight loss, weakness, and eye lesions like cloudiness or discharge. Riboflavin is found in many foods like meat, eggs, dairy and leafy greens. Dogs need around 2.2-5.3 mg of riboflavin per kg of diet daily to meet their nutritional needs.



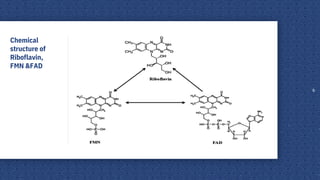
![o Riboflavin is d-Ribitol & it’s
hydroxyl group at position 5
is substituted by a 7,8-
dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-
dihydrobenzo[g]pteridin-
10(2H)-yl moiety.
o Formula –C17 H20 N4 O6
4
Structure of
Riboflavin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vitaminb2-200412085527/85/Vitamin-b2-4-320.jpg)