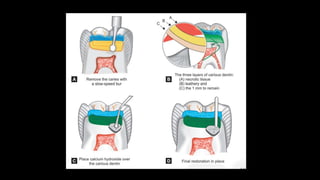
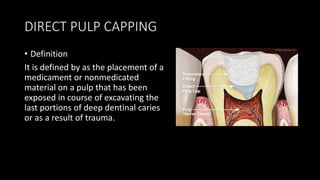
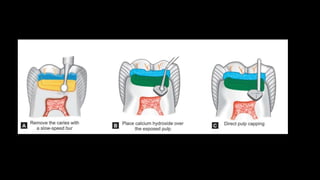
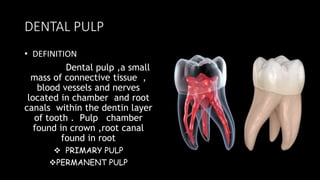
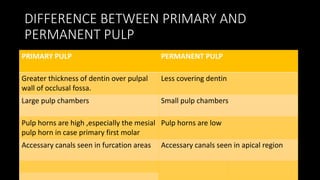
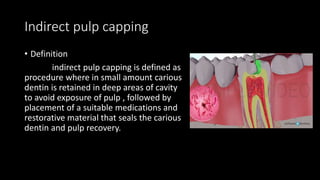
Dental pulp is the connective tissue inside teeth. Pulp capping procedures involve placing a medicament over exposed pulp to promote healing and formation of new dentin. Indirect pulp capping retains deep caries near the pulp and seals it off, while direct pulp capping treats small mechanical exposures of the pulp. Calcium hydroxide is commonly used as it promotes dentin bridge formation. Success is indicated by maintained vitality, lack of pain, and minimal inflammation over subsequent appointments.









![Cavity flushed with saline and dried with cotton p;oints
Site is covered with calcium hydroxide [ Ca OH 2]
Reminder cavity is filled with reinforced zinc oxide
eug;enol [ZOE] cement
Final restoration done followed by placement of
crown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalpulpandpulpcapping-230730050027-5817da5d/85/DENTAL-PULP-AND-PULP-CAPPING-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![Two appointment procedure
after first appointment [6 to8 weeks later ]
Between the appointment history must be negative and
temporary restoration should be intact
If reparative dentin bridge is formed , a permanent
restoration restoration followed by full coverage
restoration is chosen
If there is some amount of caries , remaining on re
entry carefully removed ,now somewhat sclerotic may
reveal a sound base of dentin without pulp exposure
Previous remaining carious dentin will have become
dried out, flaky and easily removed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalpulpandpulpcapping-230730050027-5817da5d/85/DENTAL-PULP-AND-PULP-CAPPING-pptx-14-320.jpg)