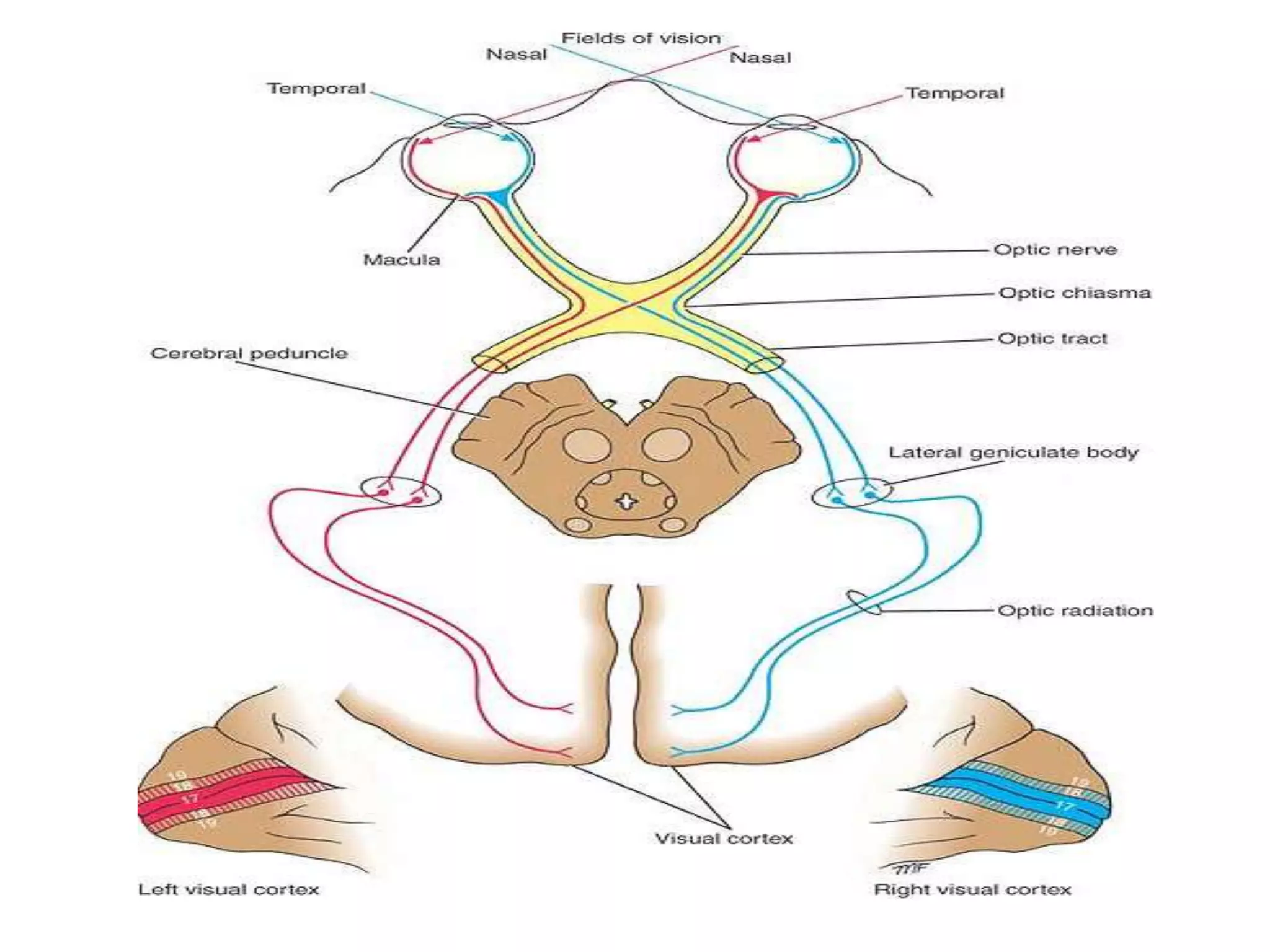
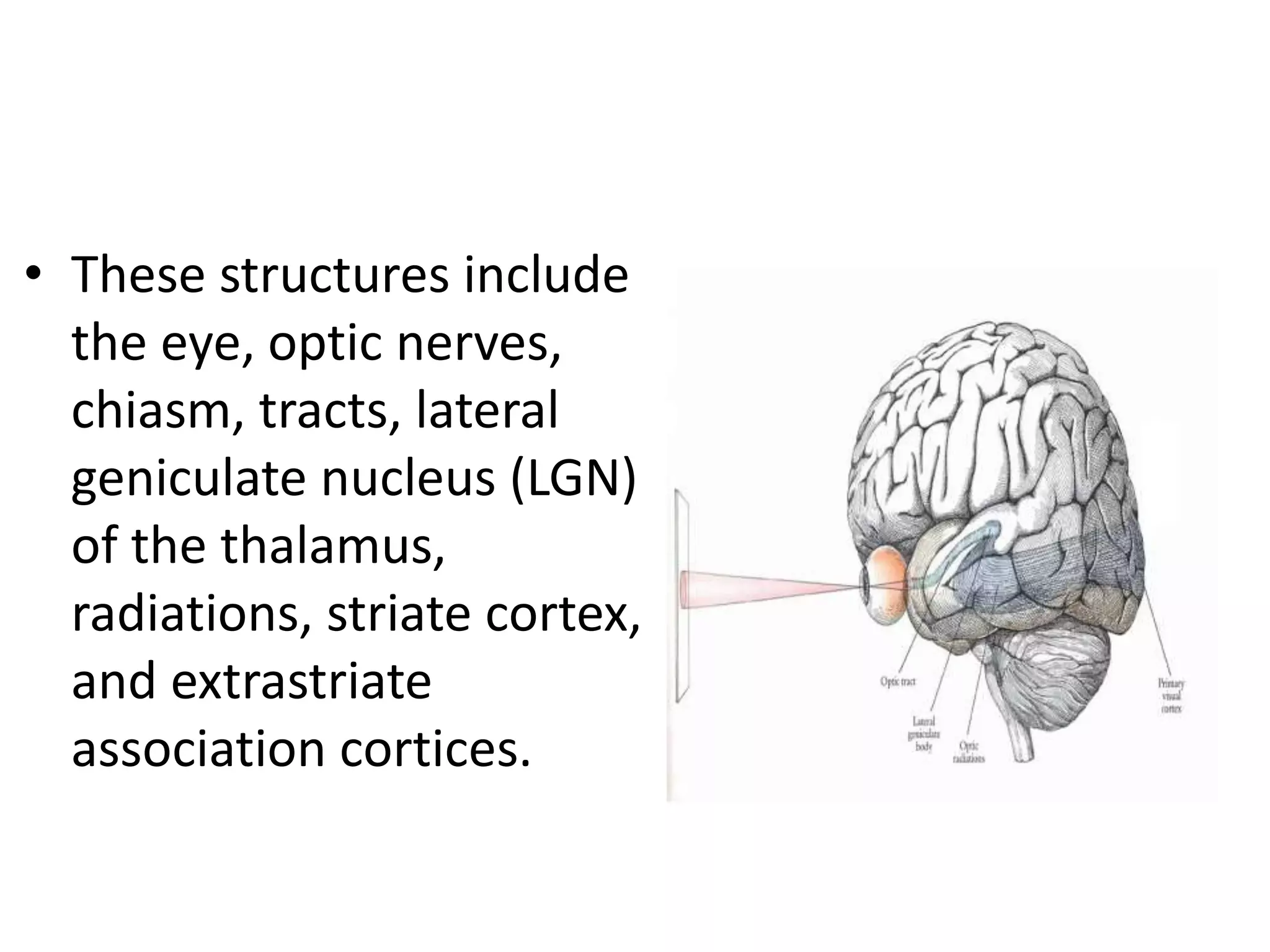
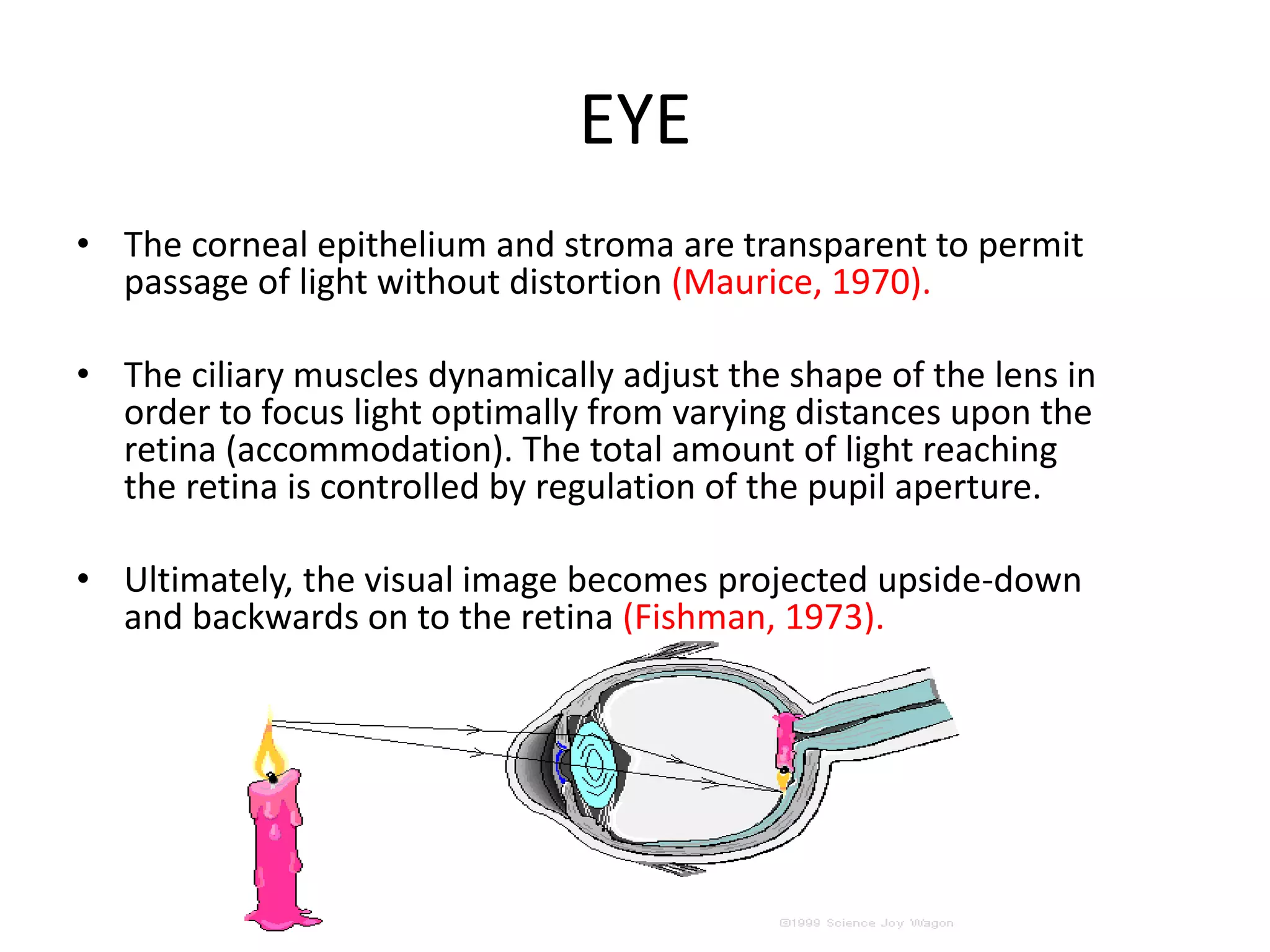
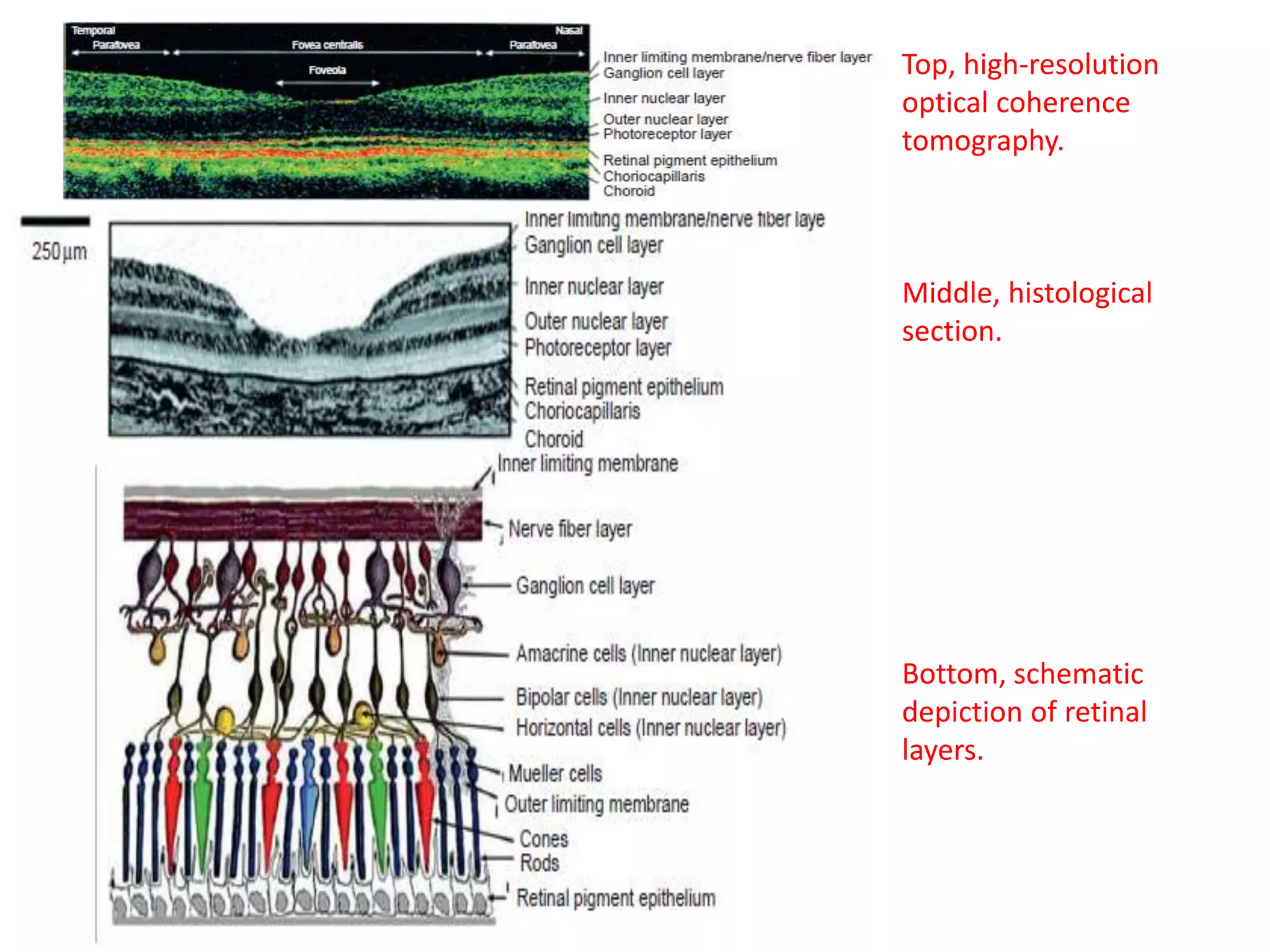
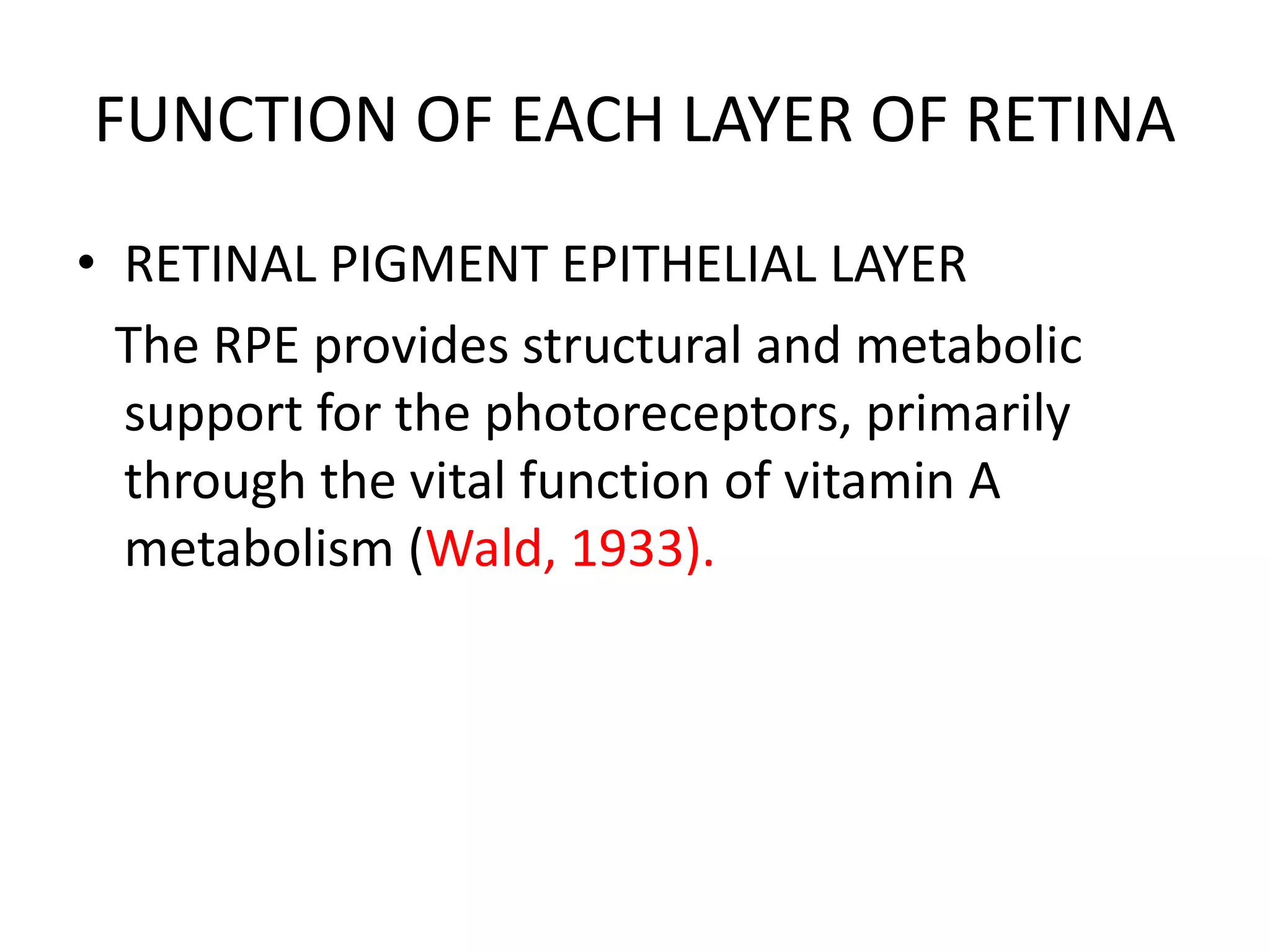
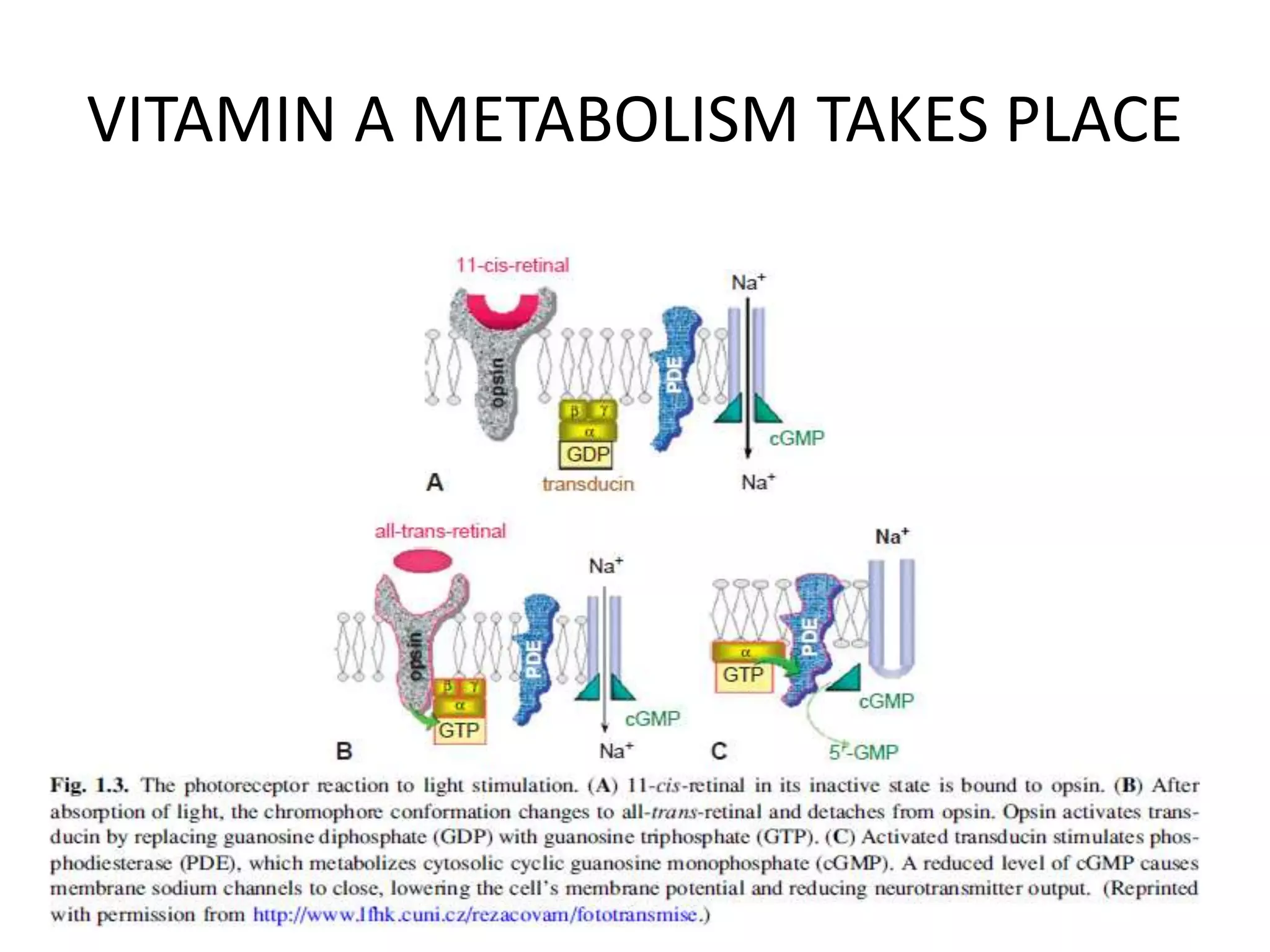
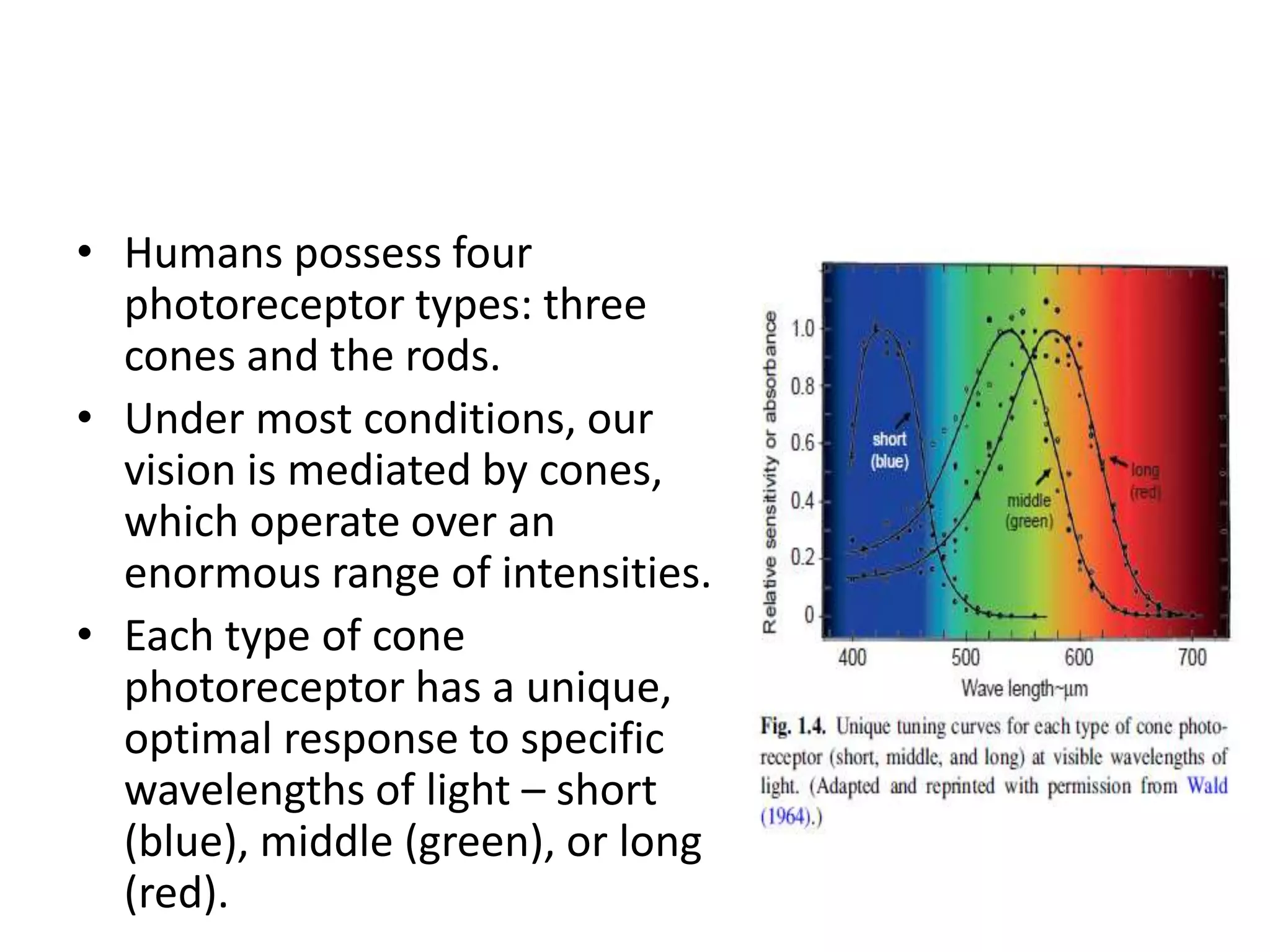
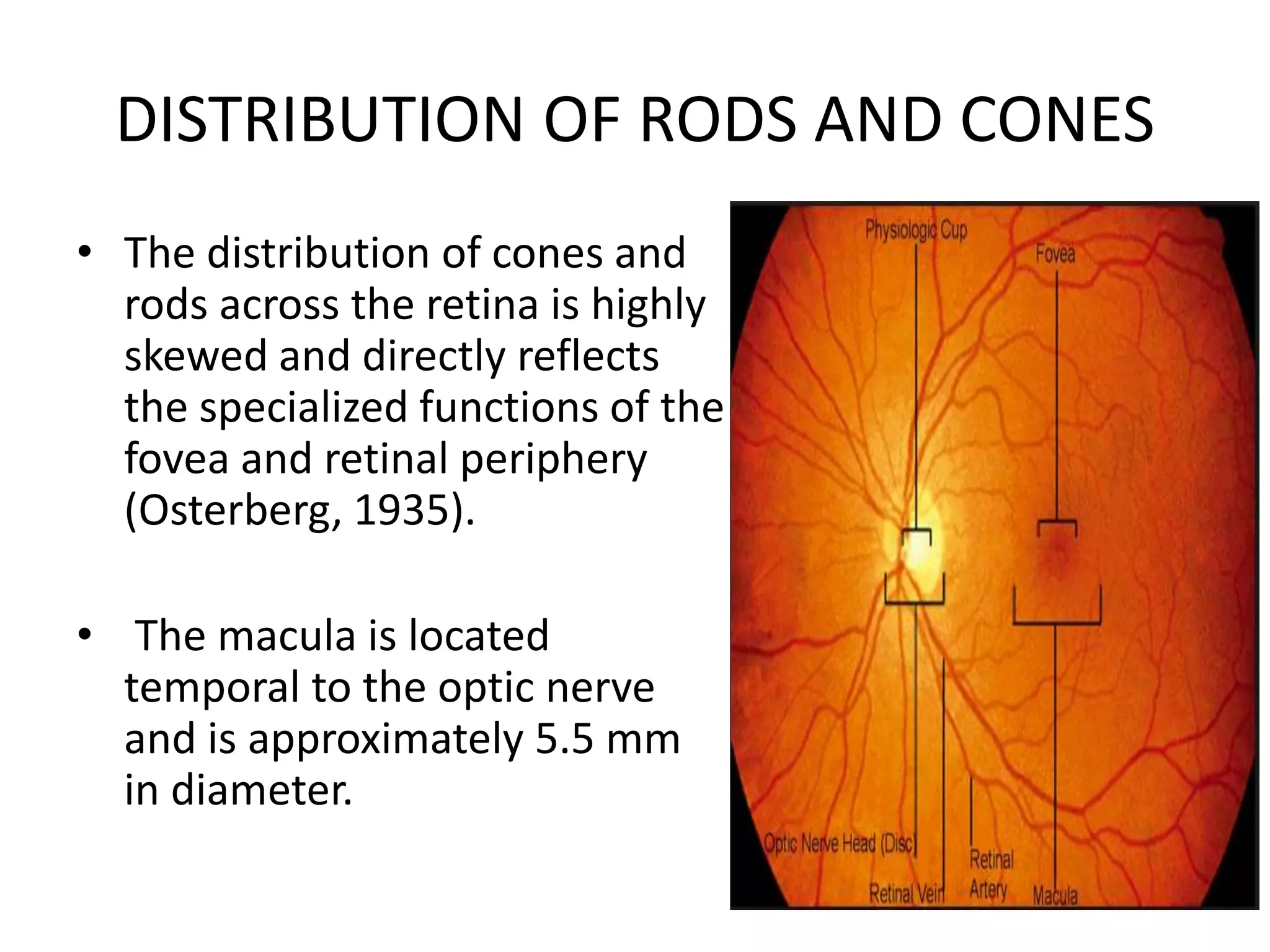
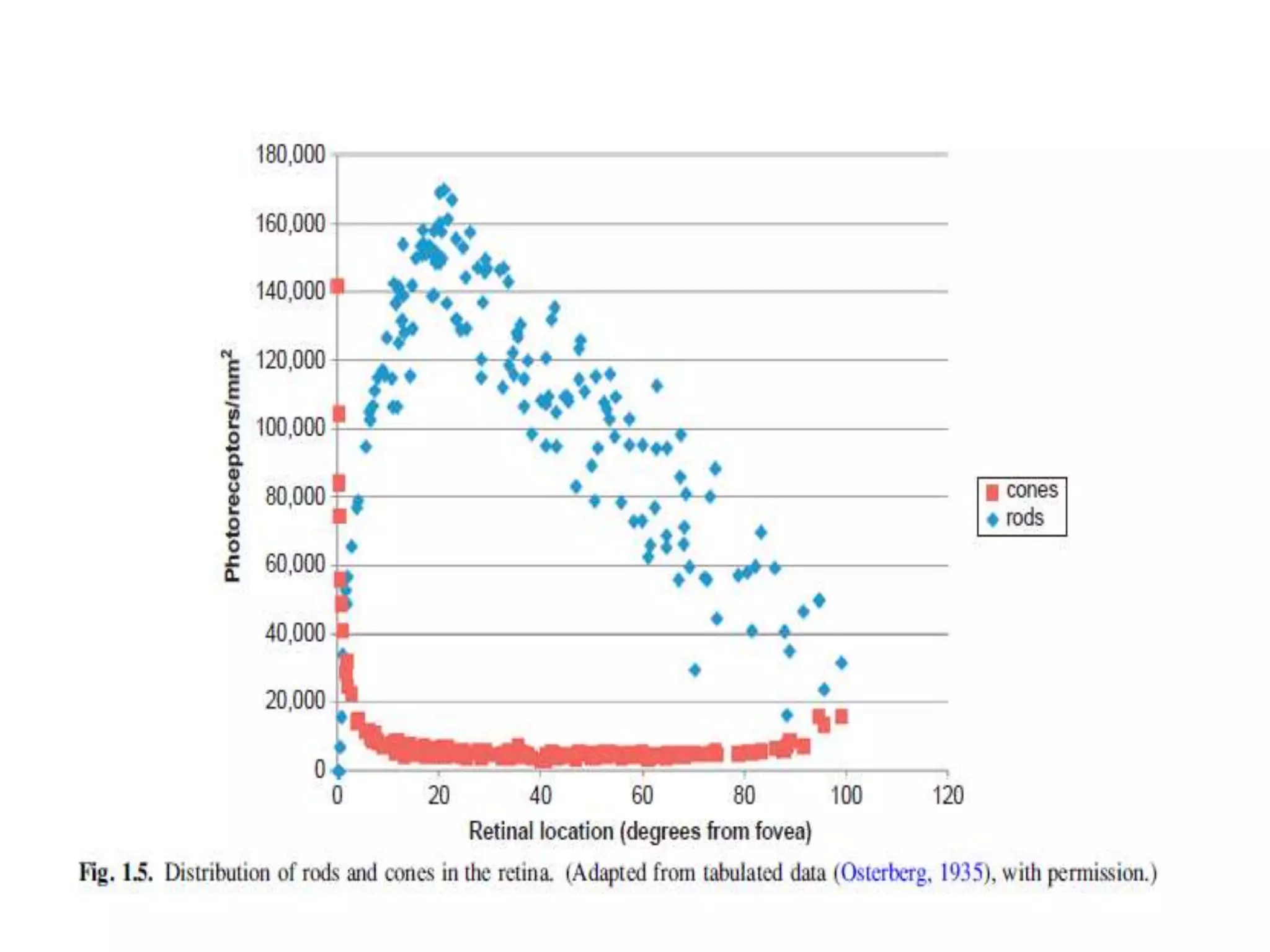
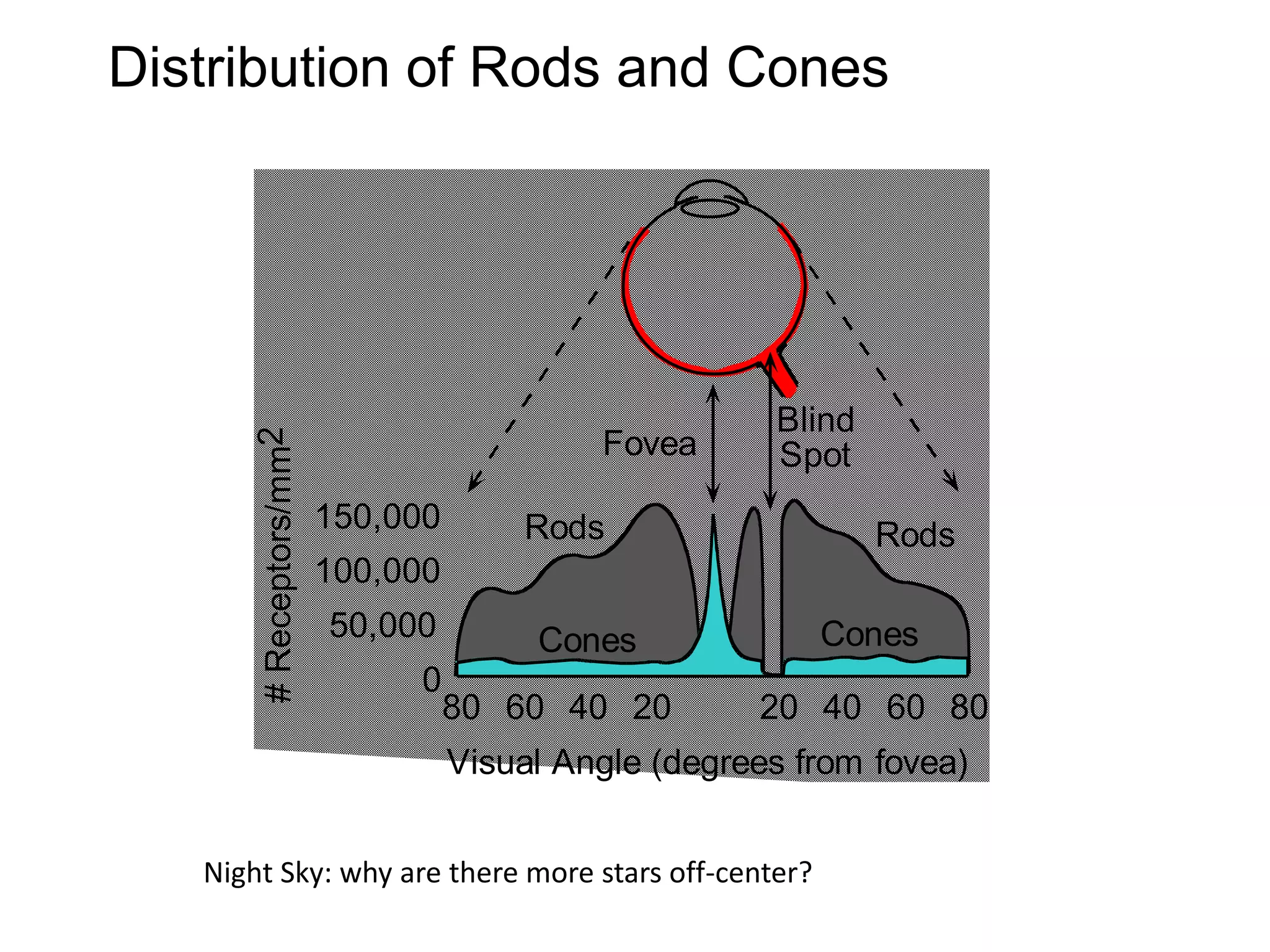
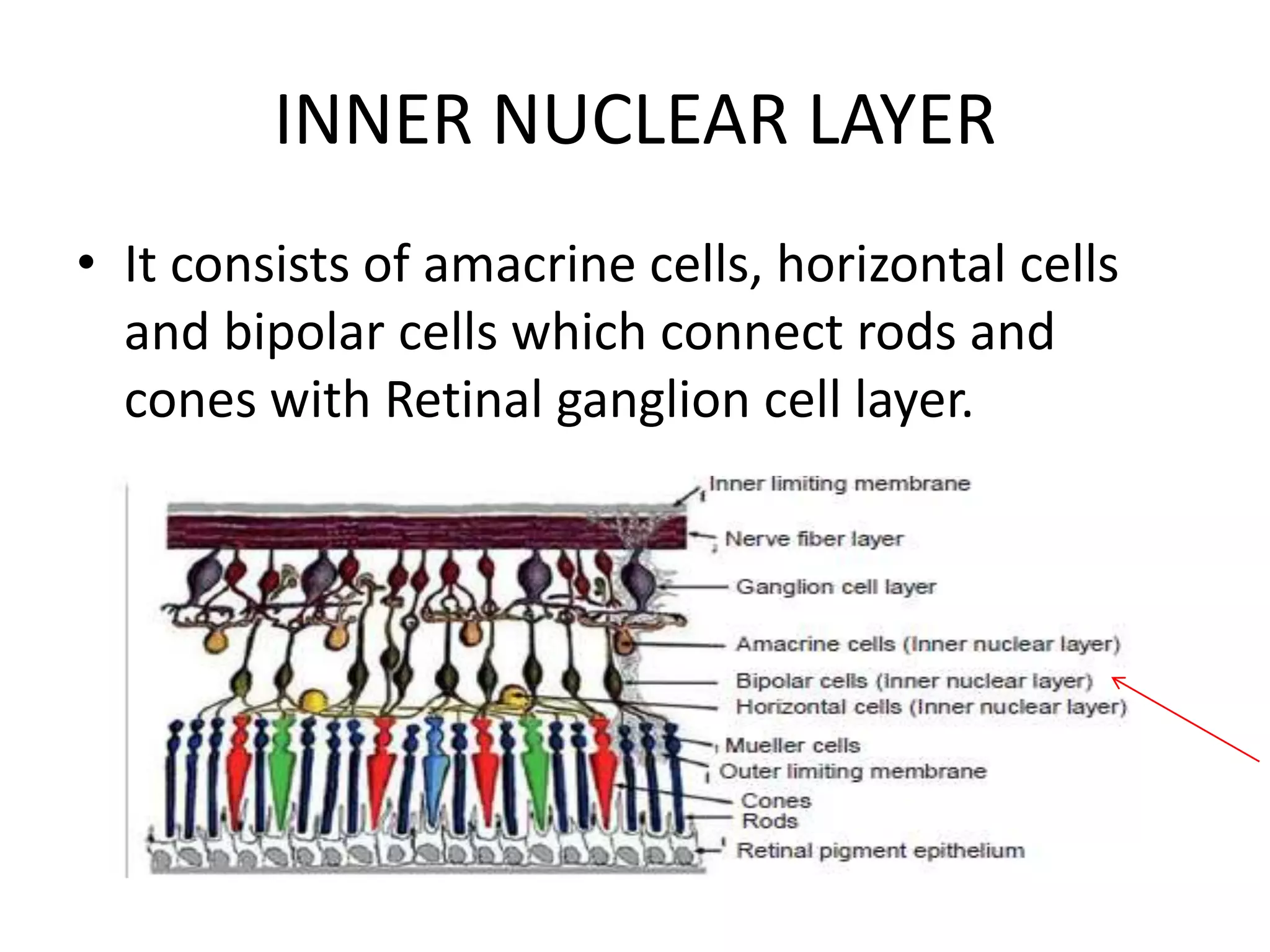
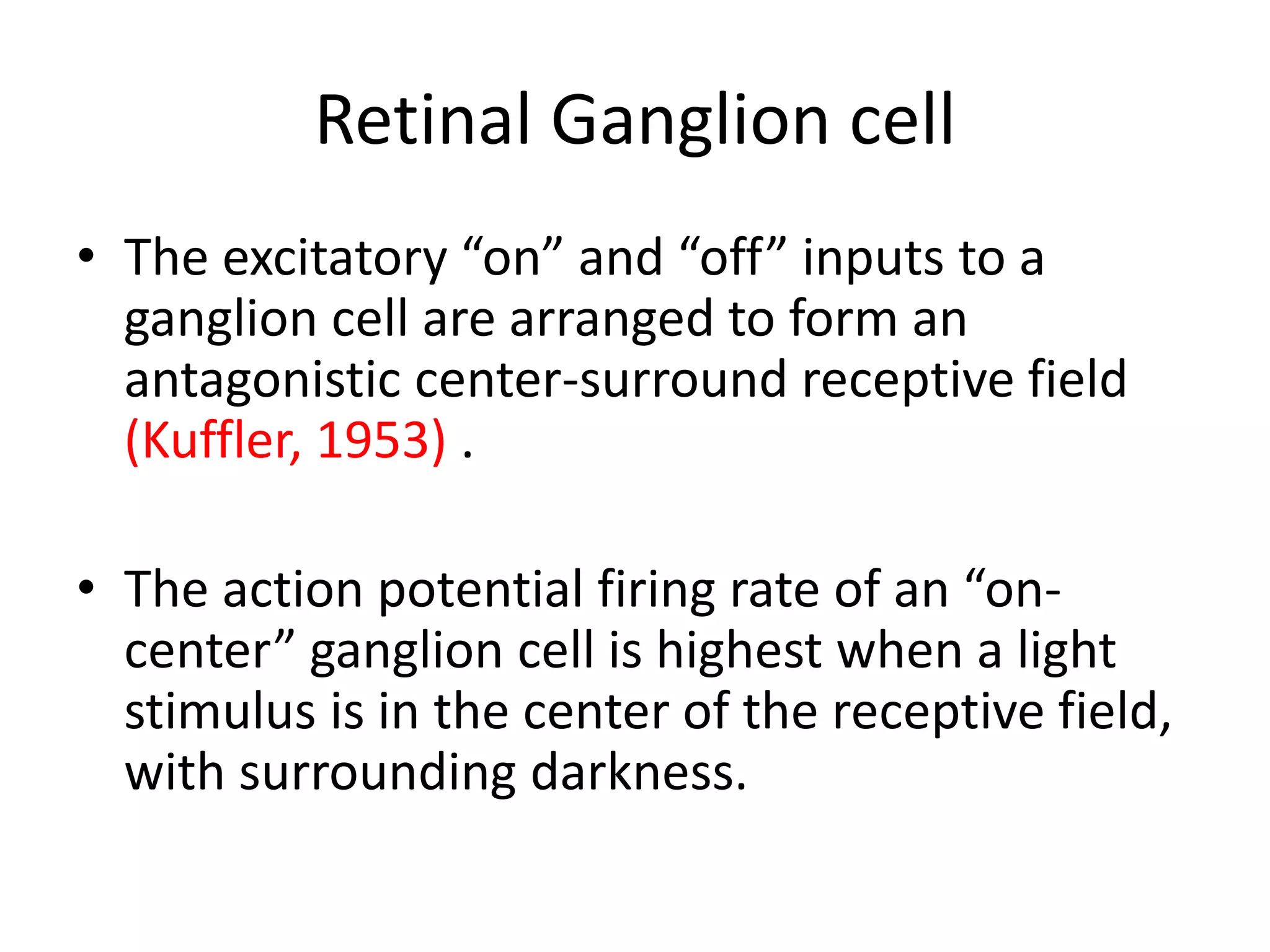
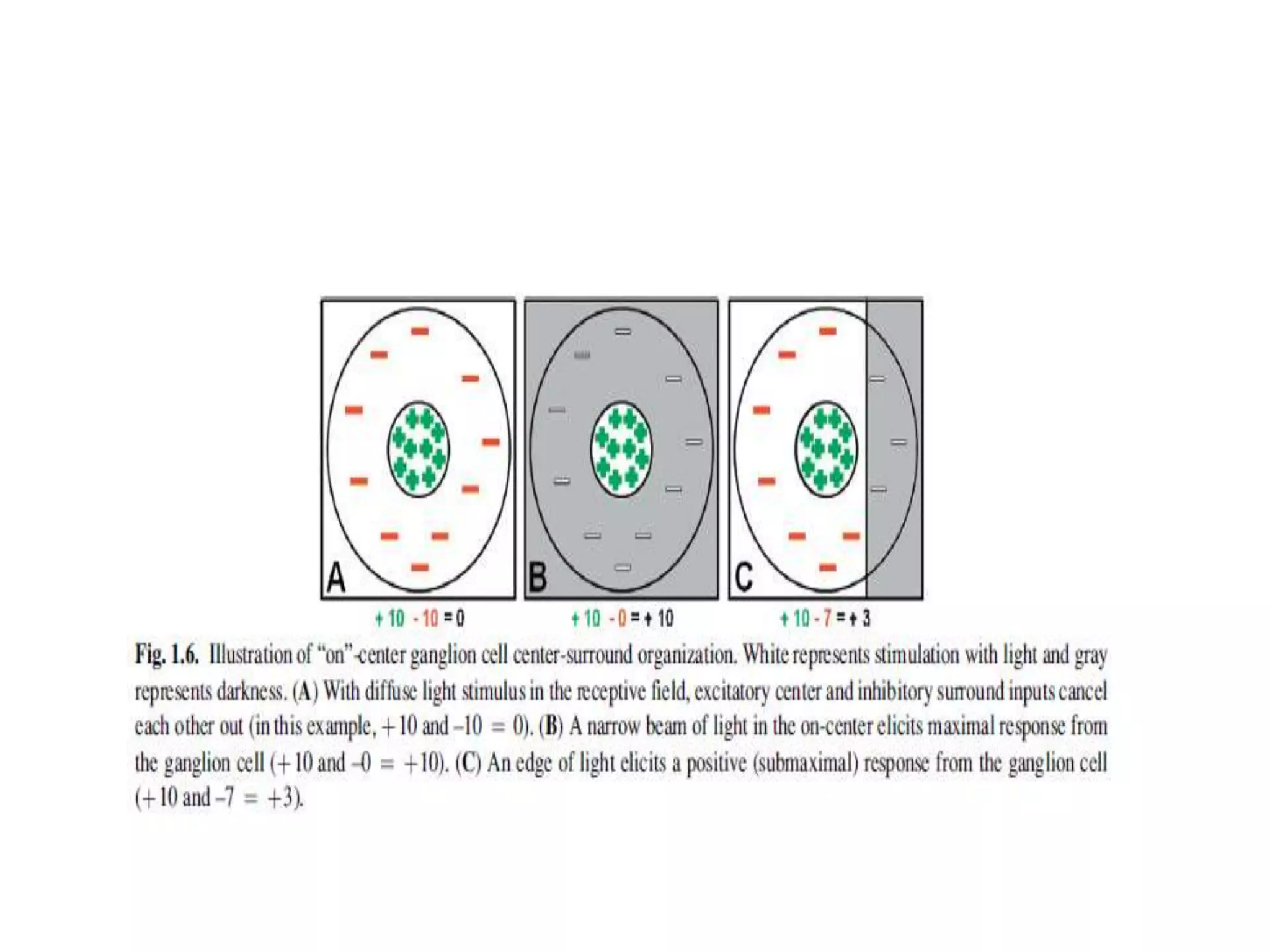
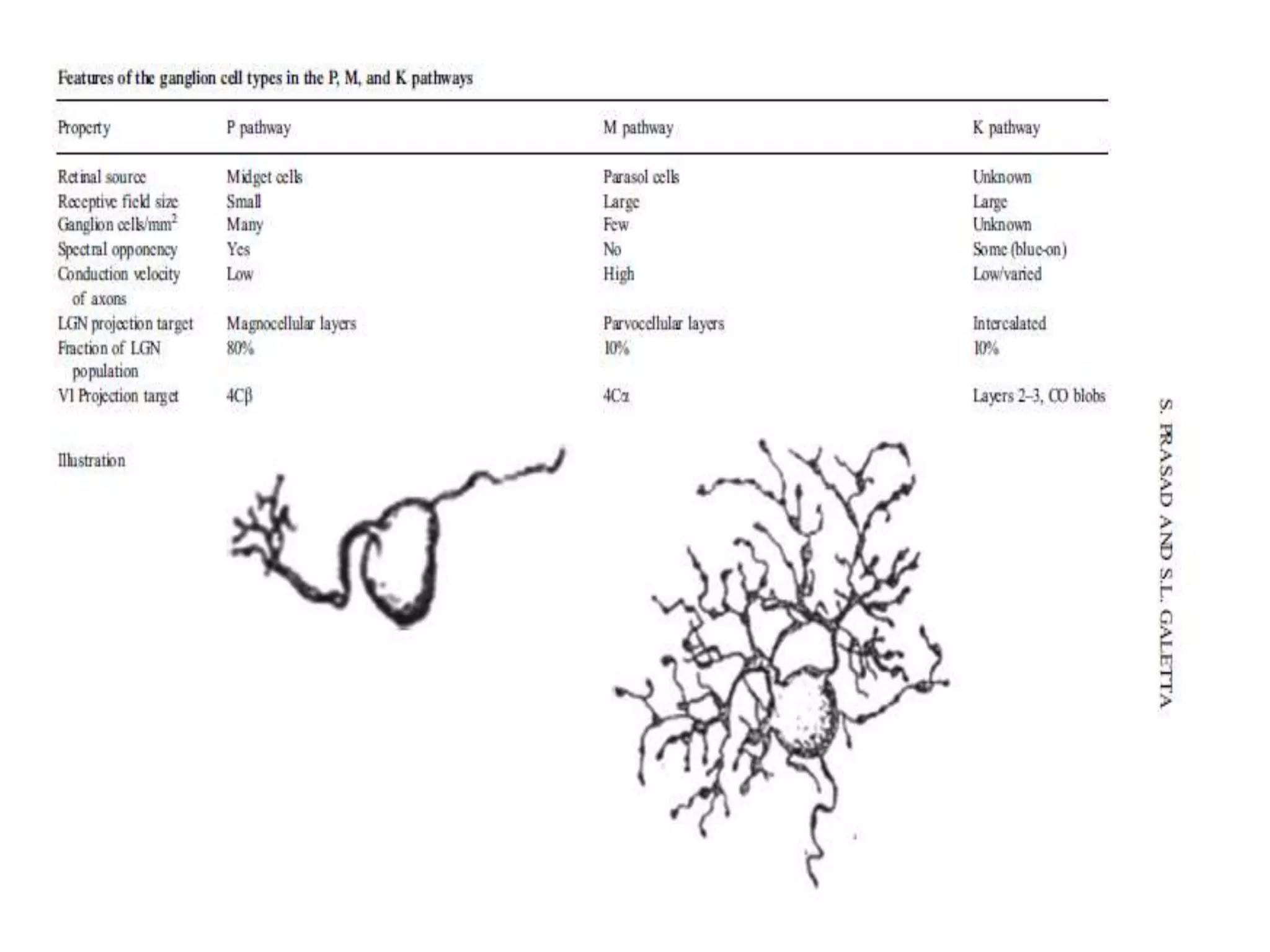
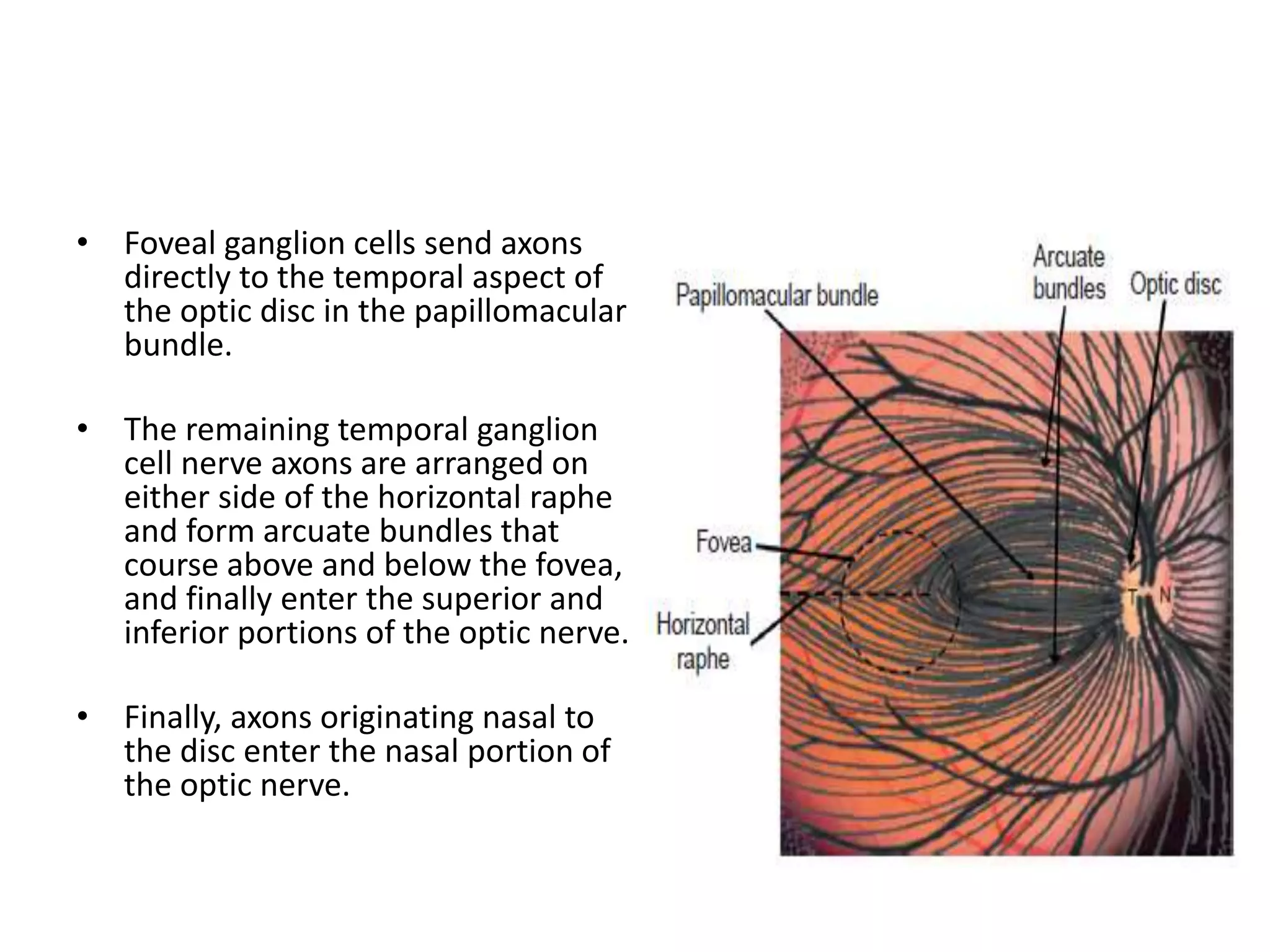
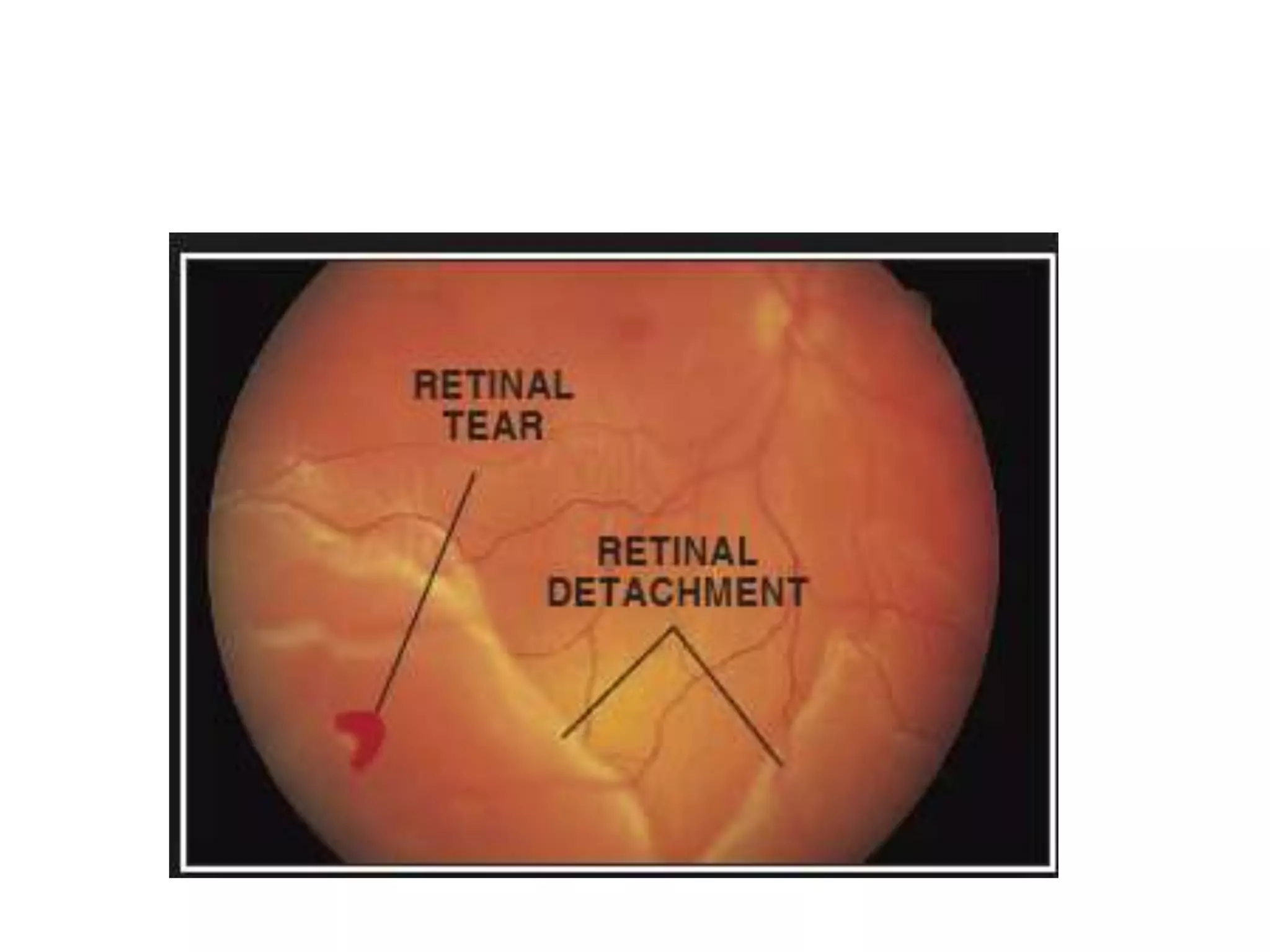
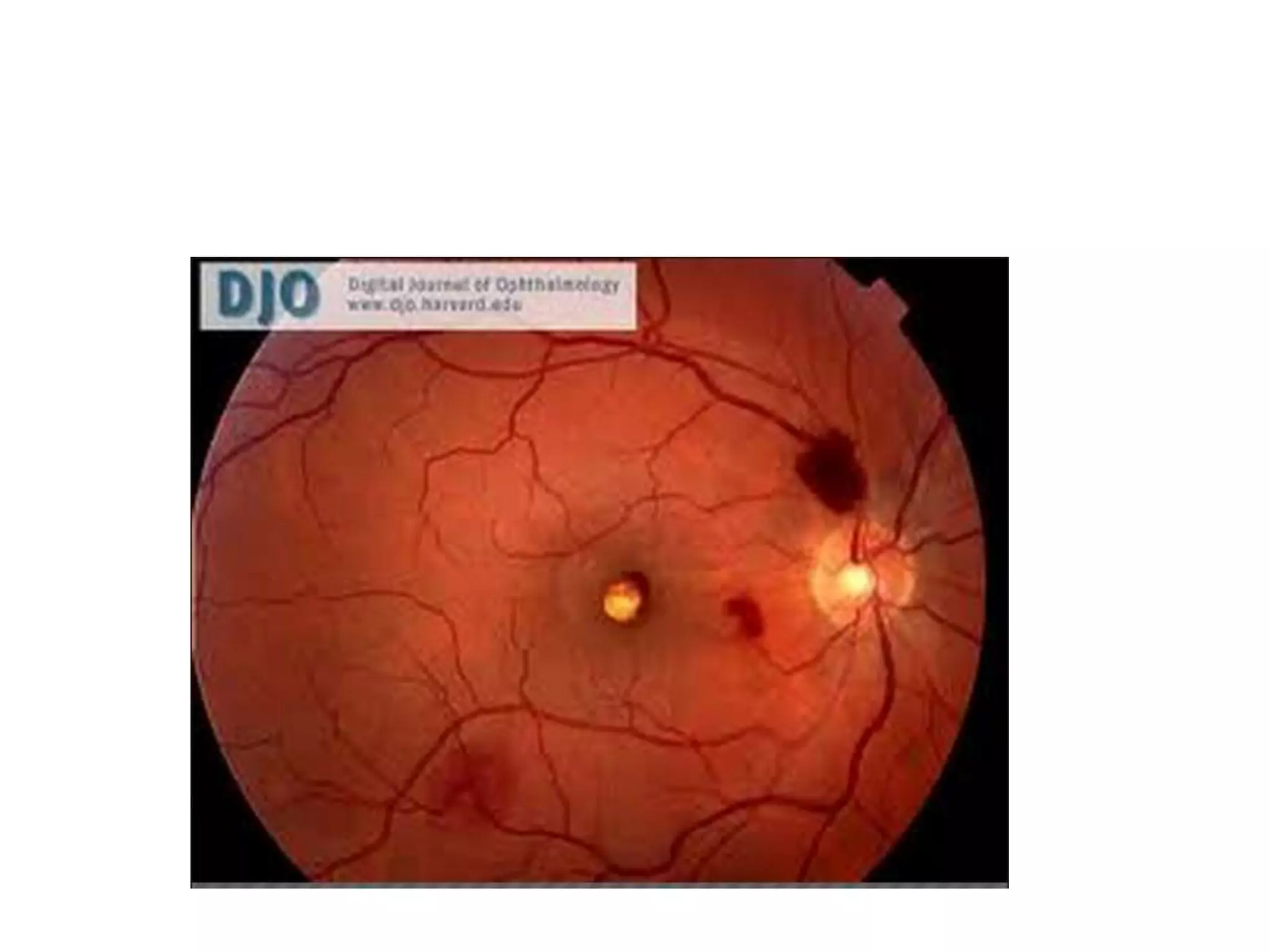
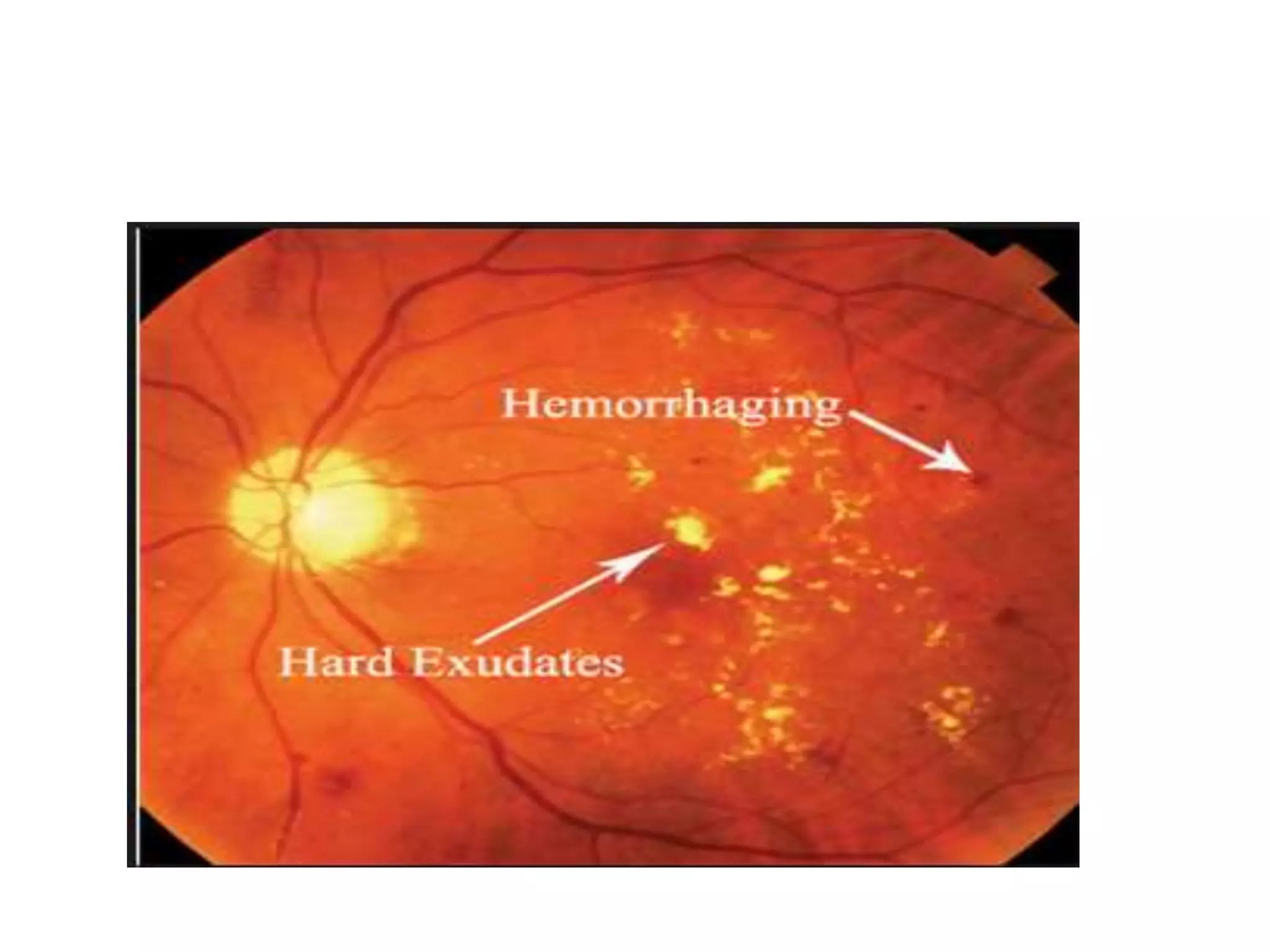
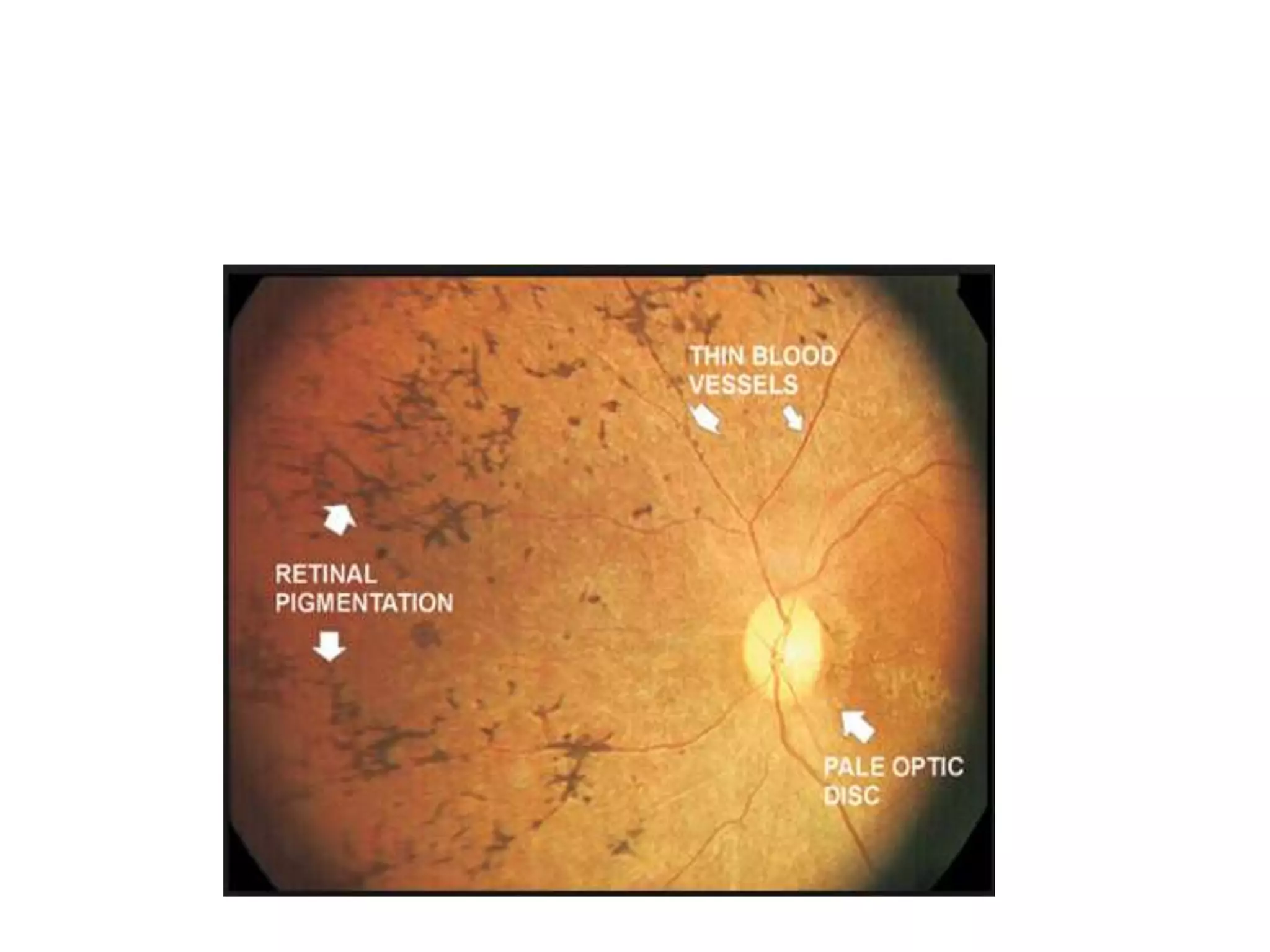
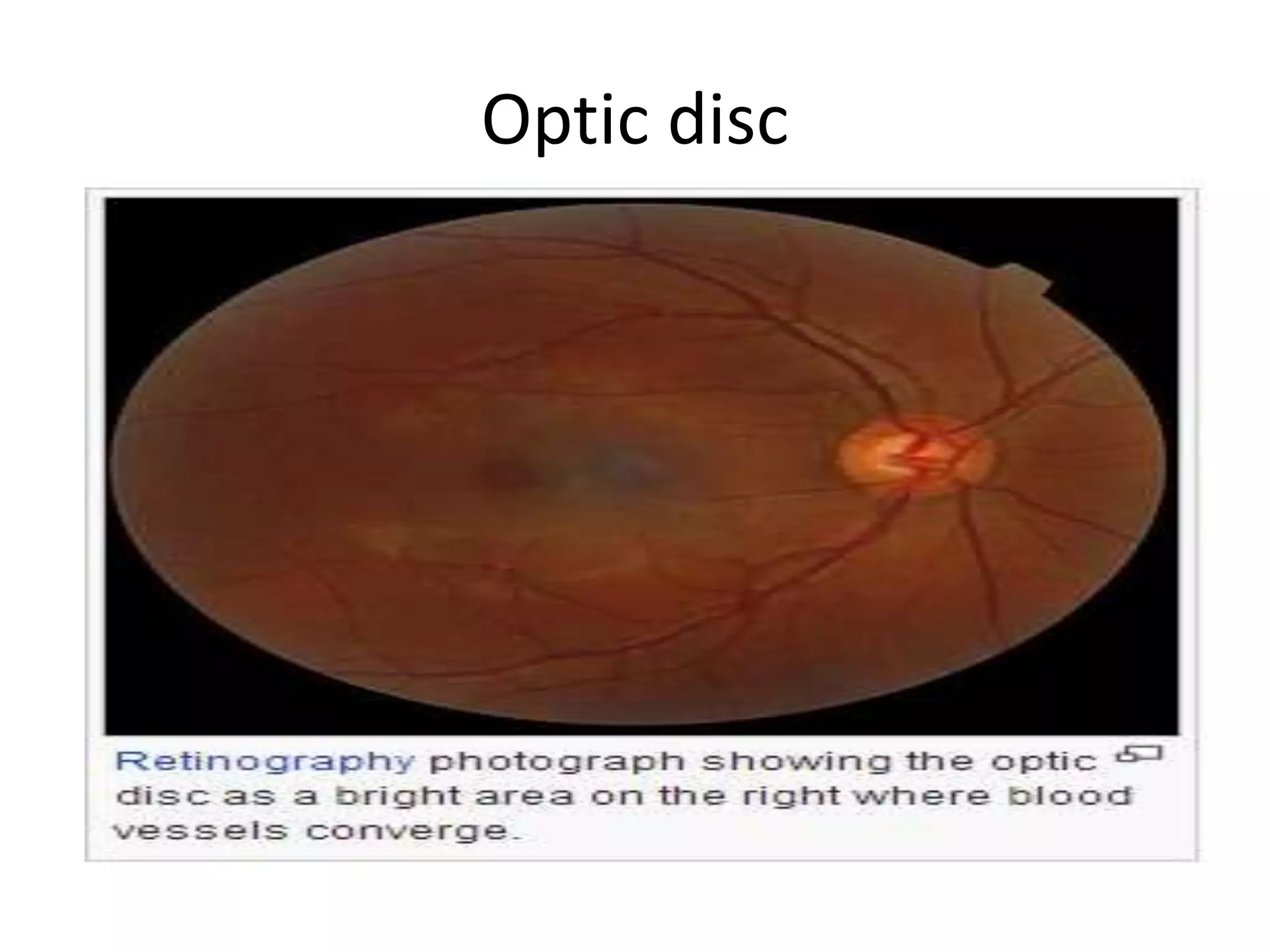
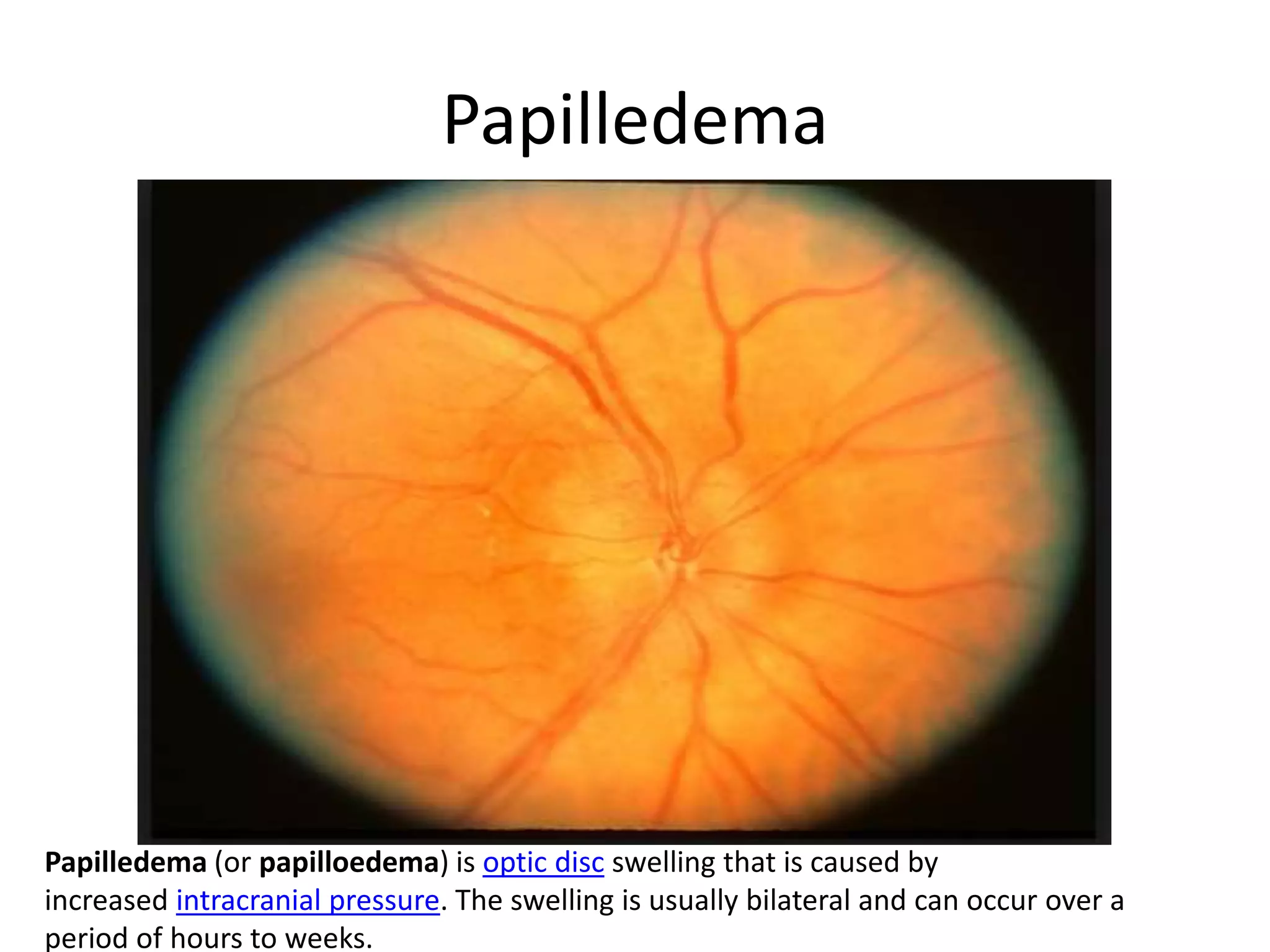
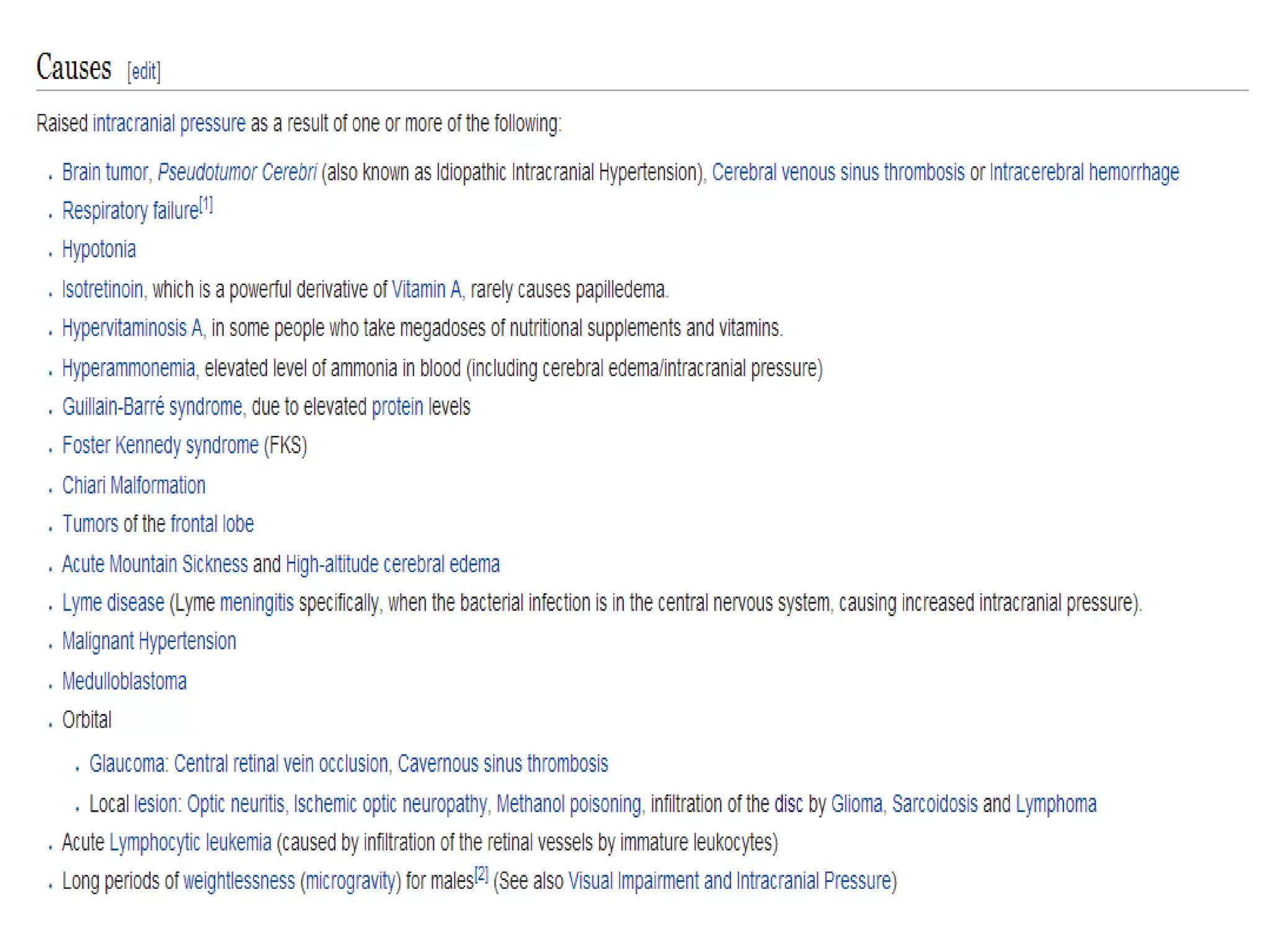
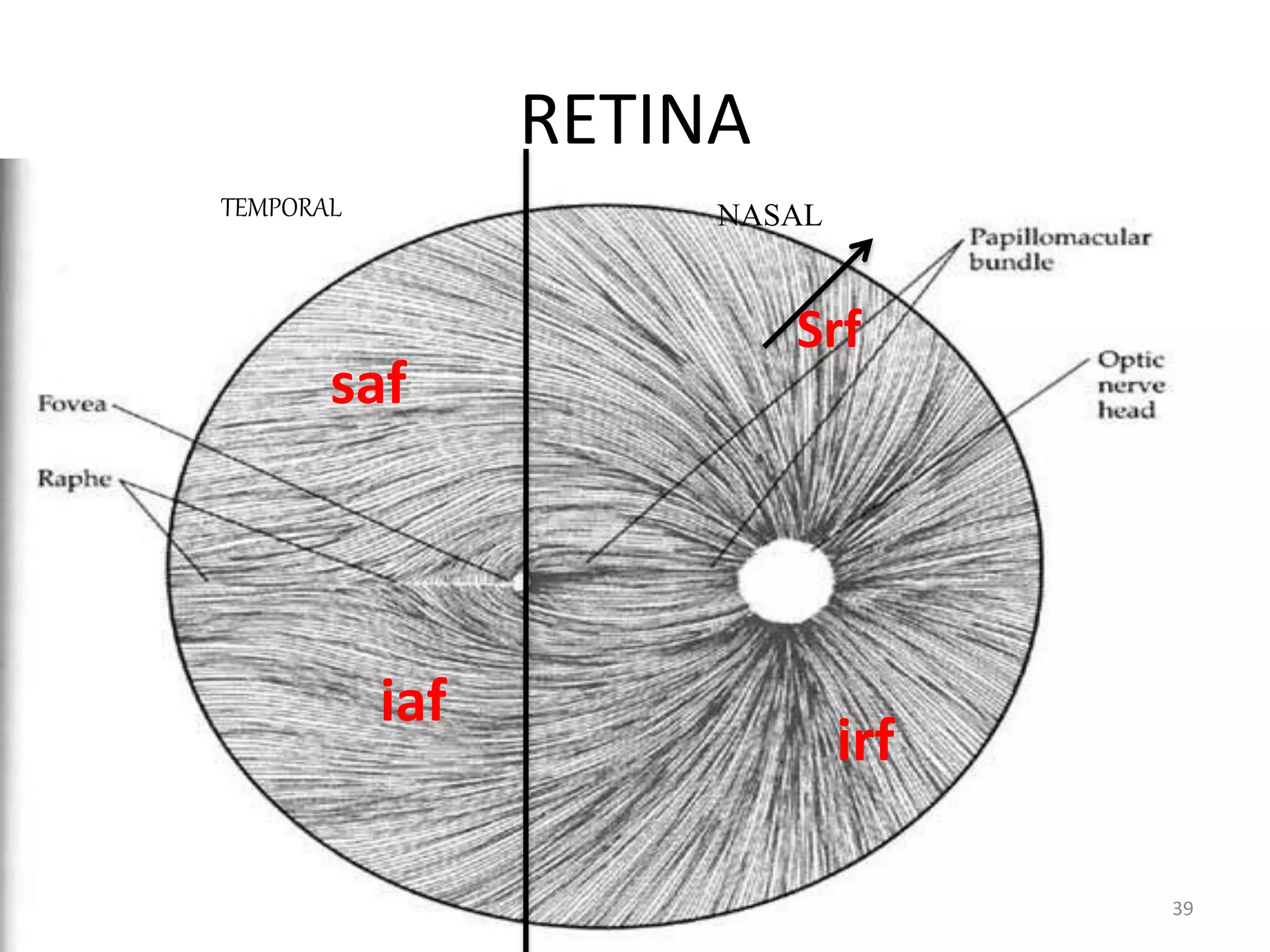
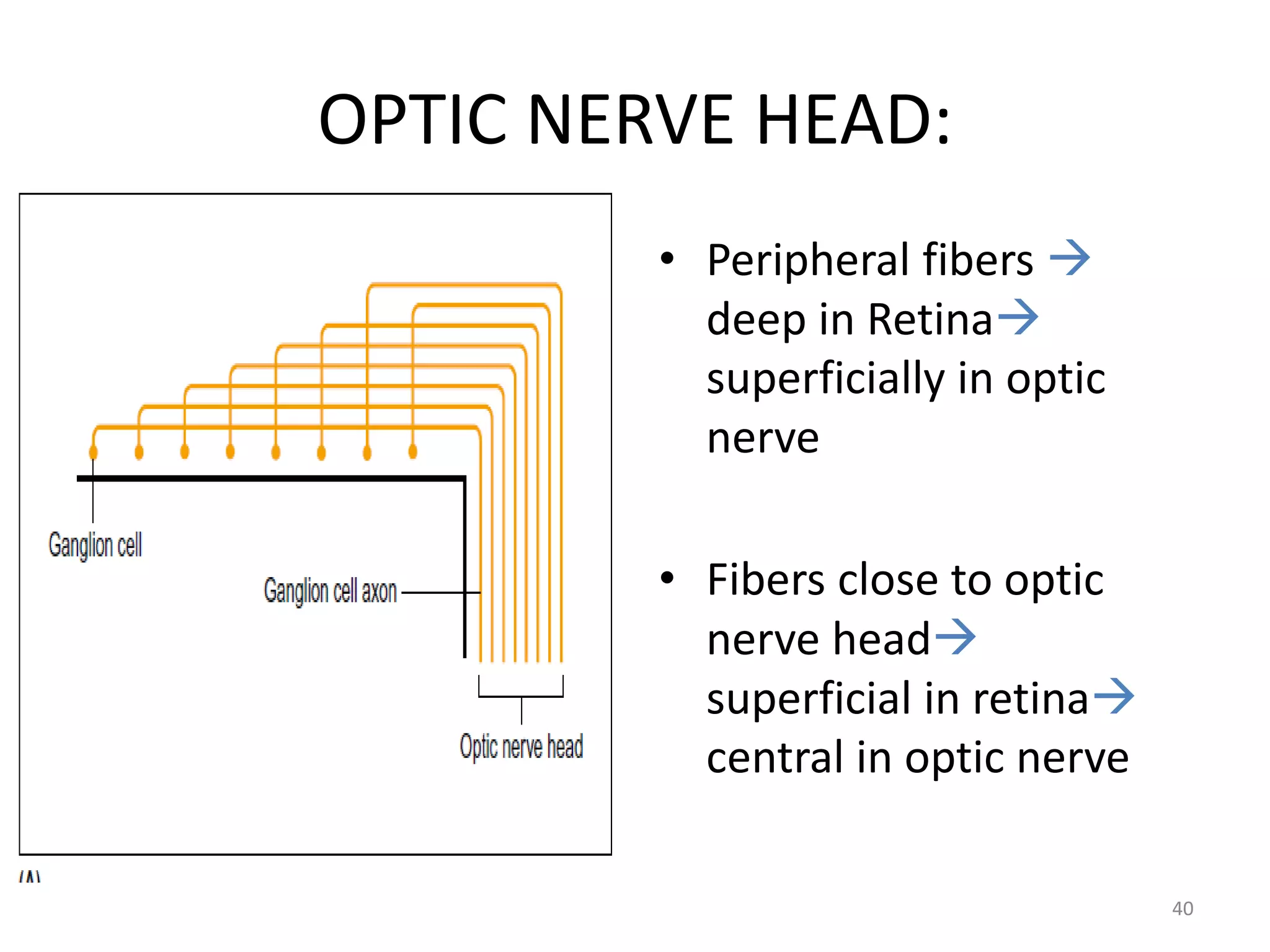
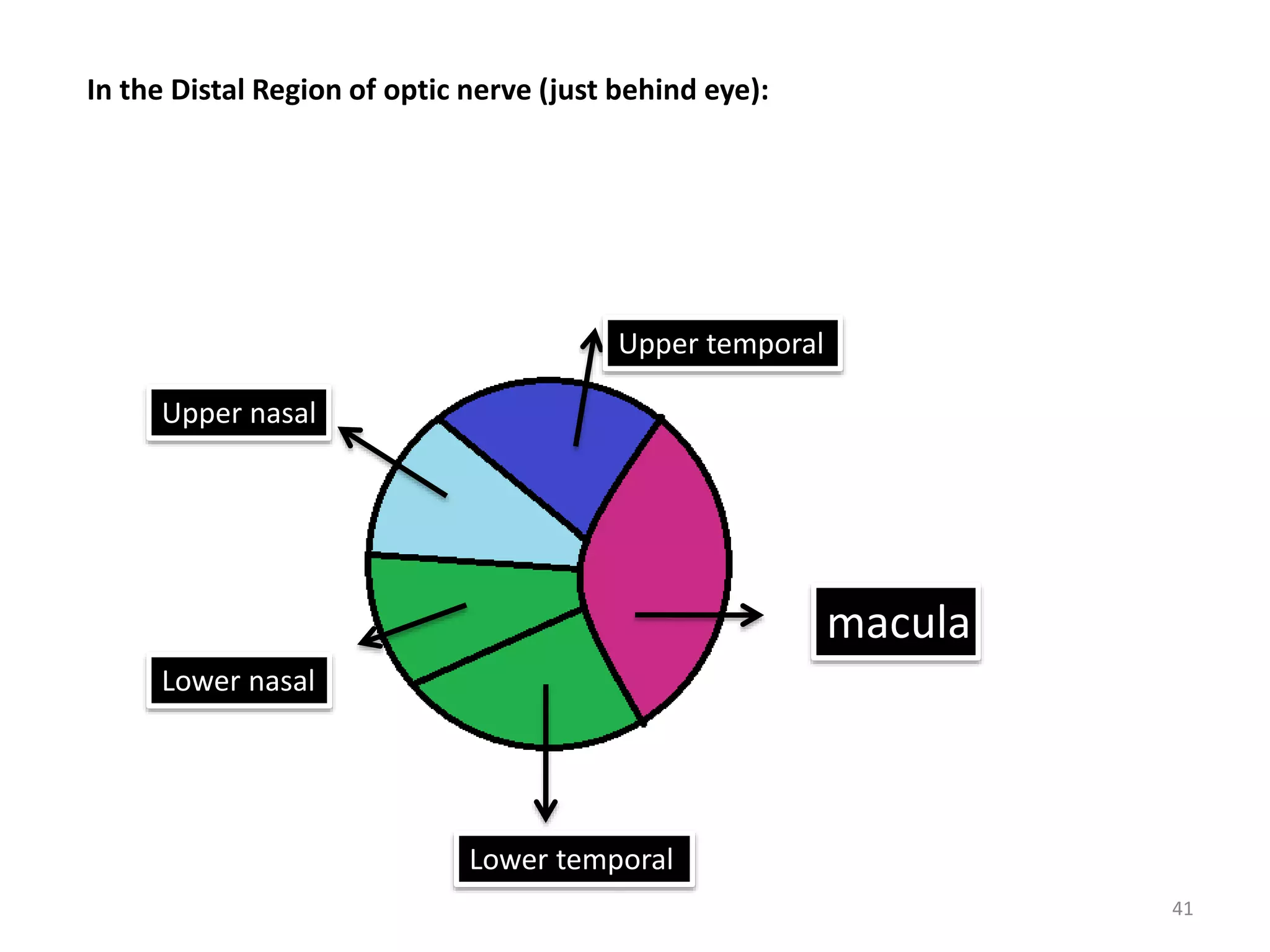
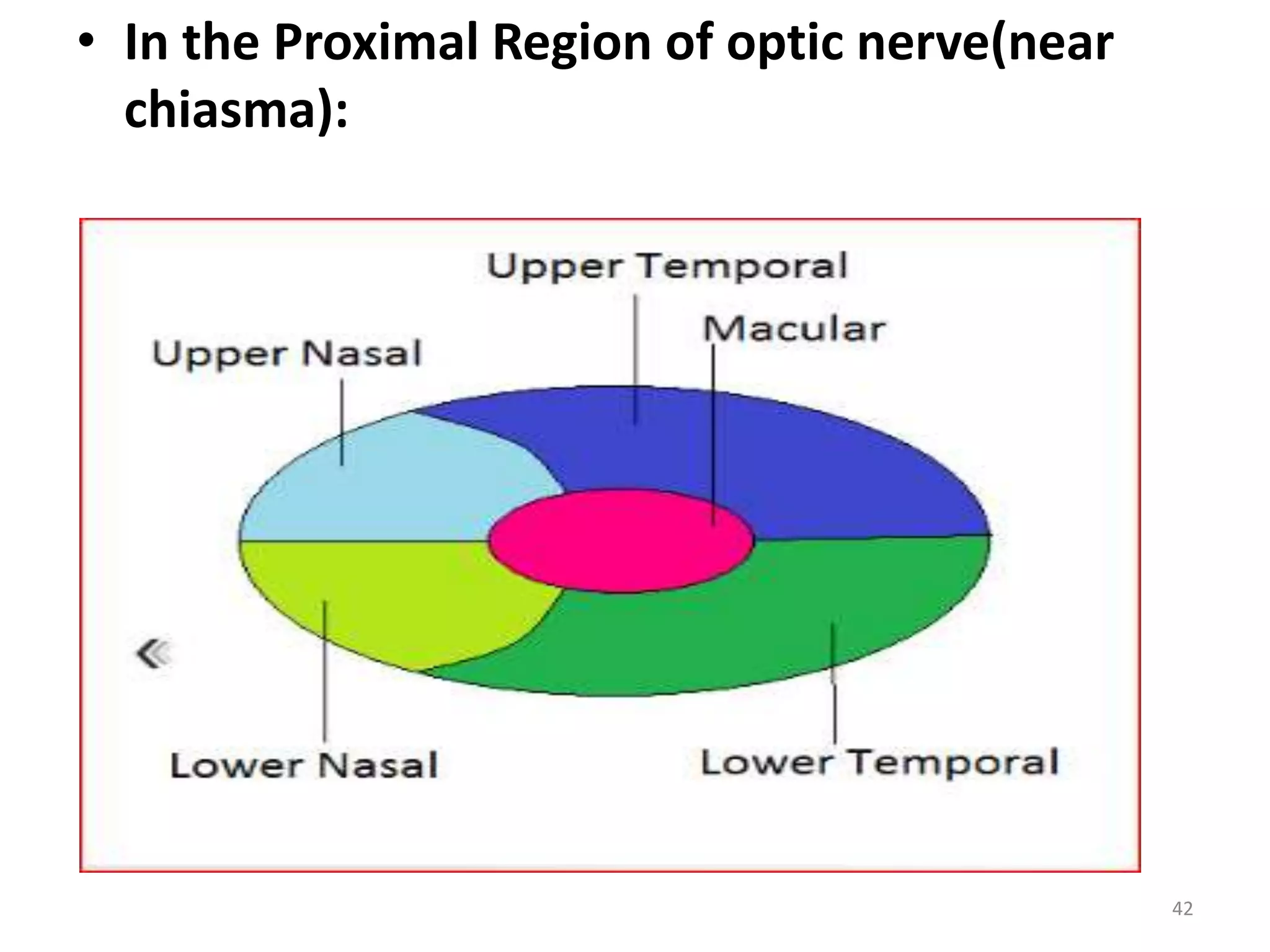
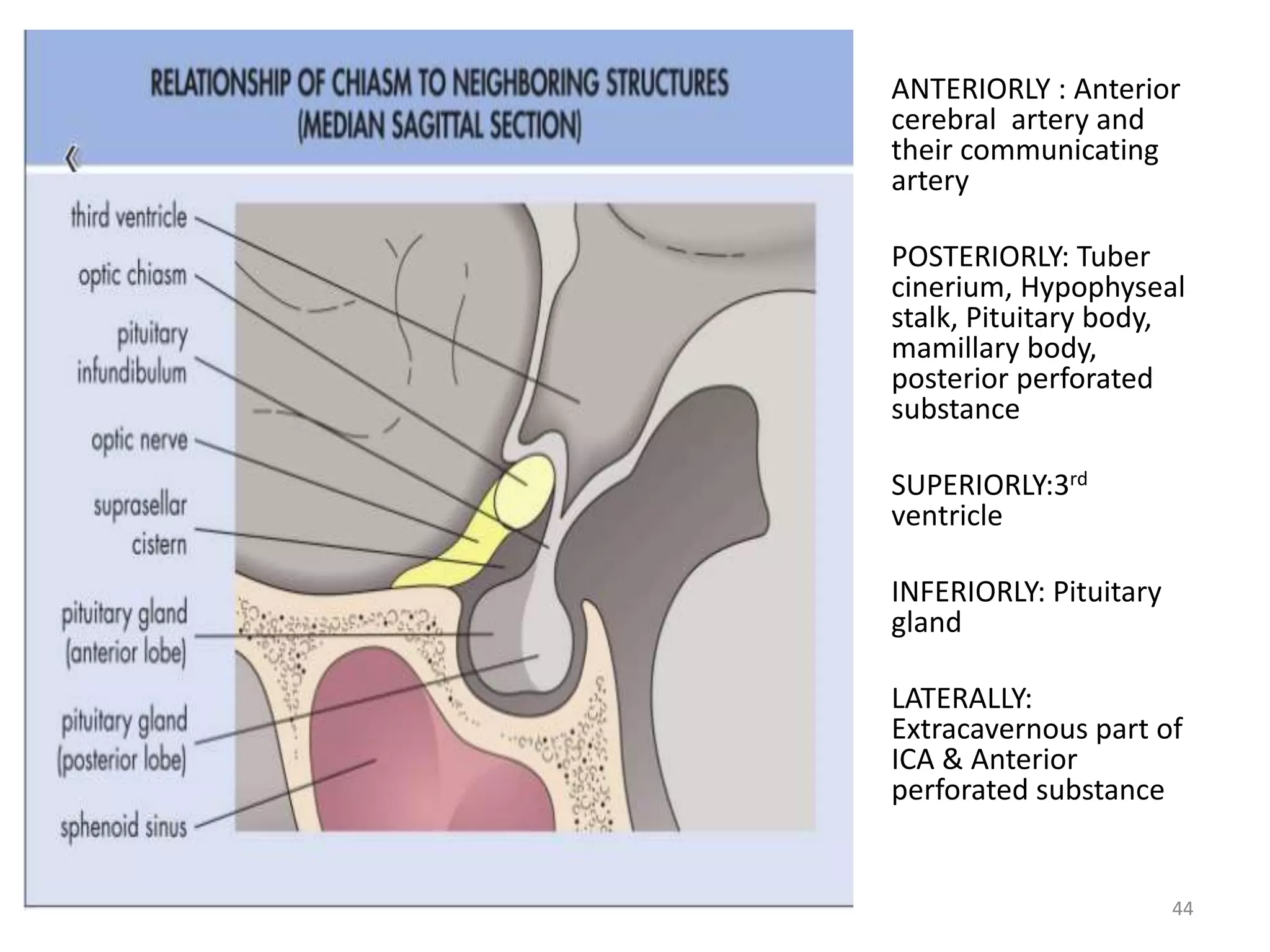
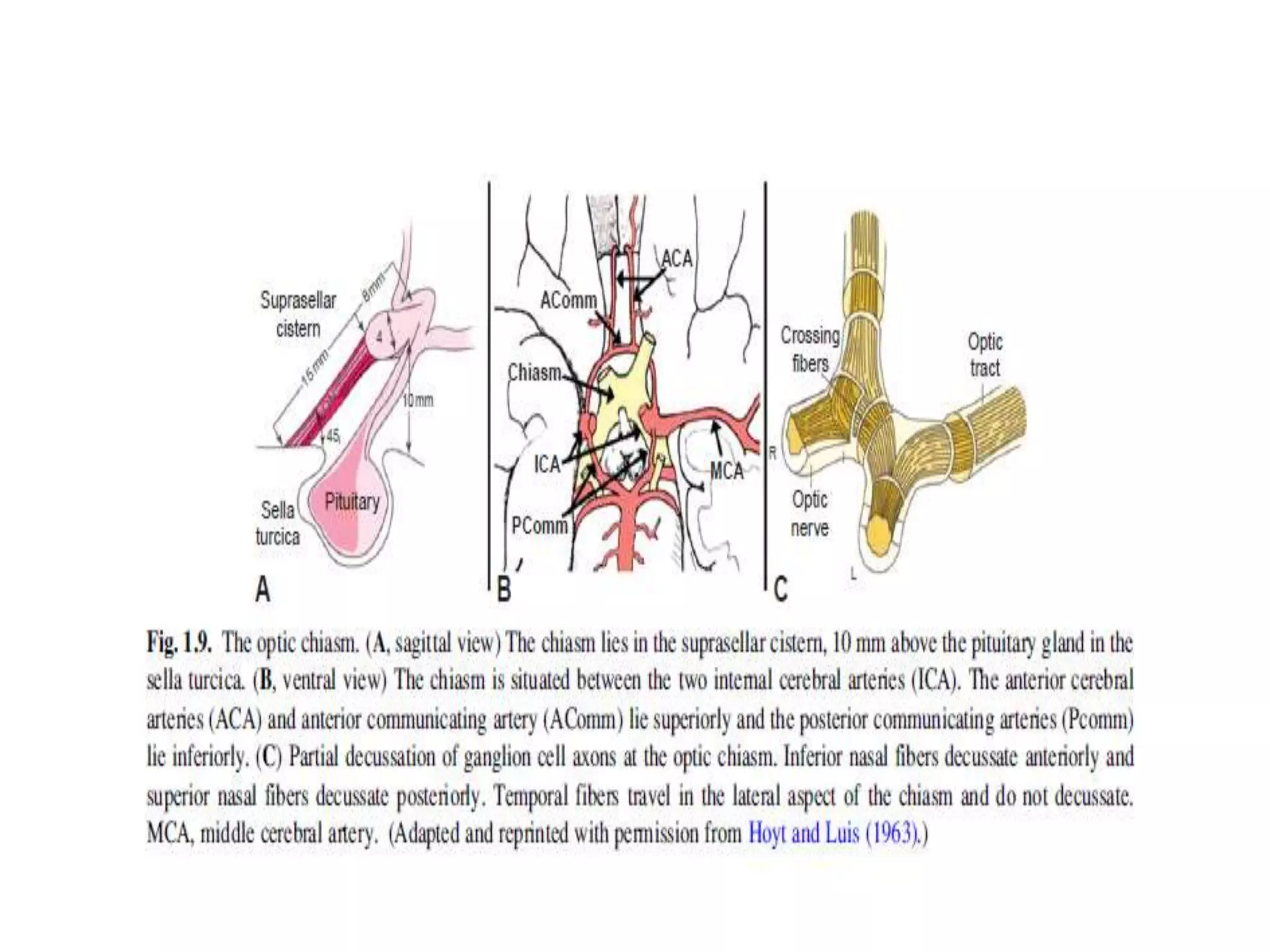
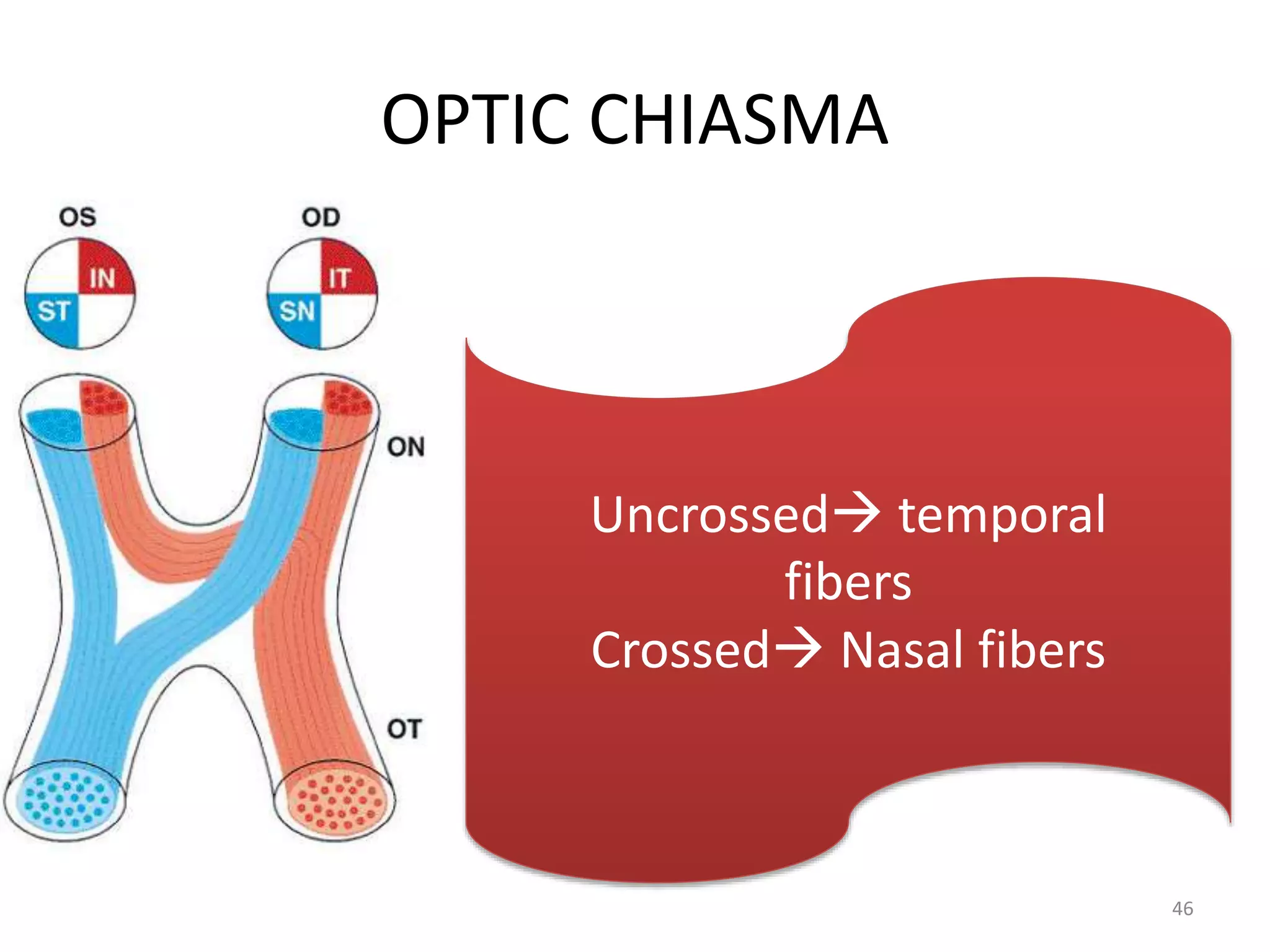
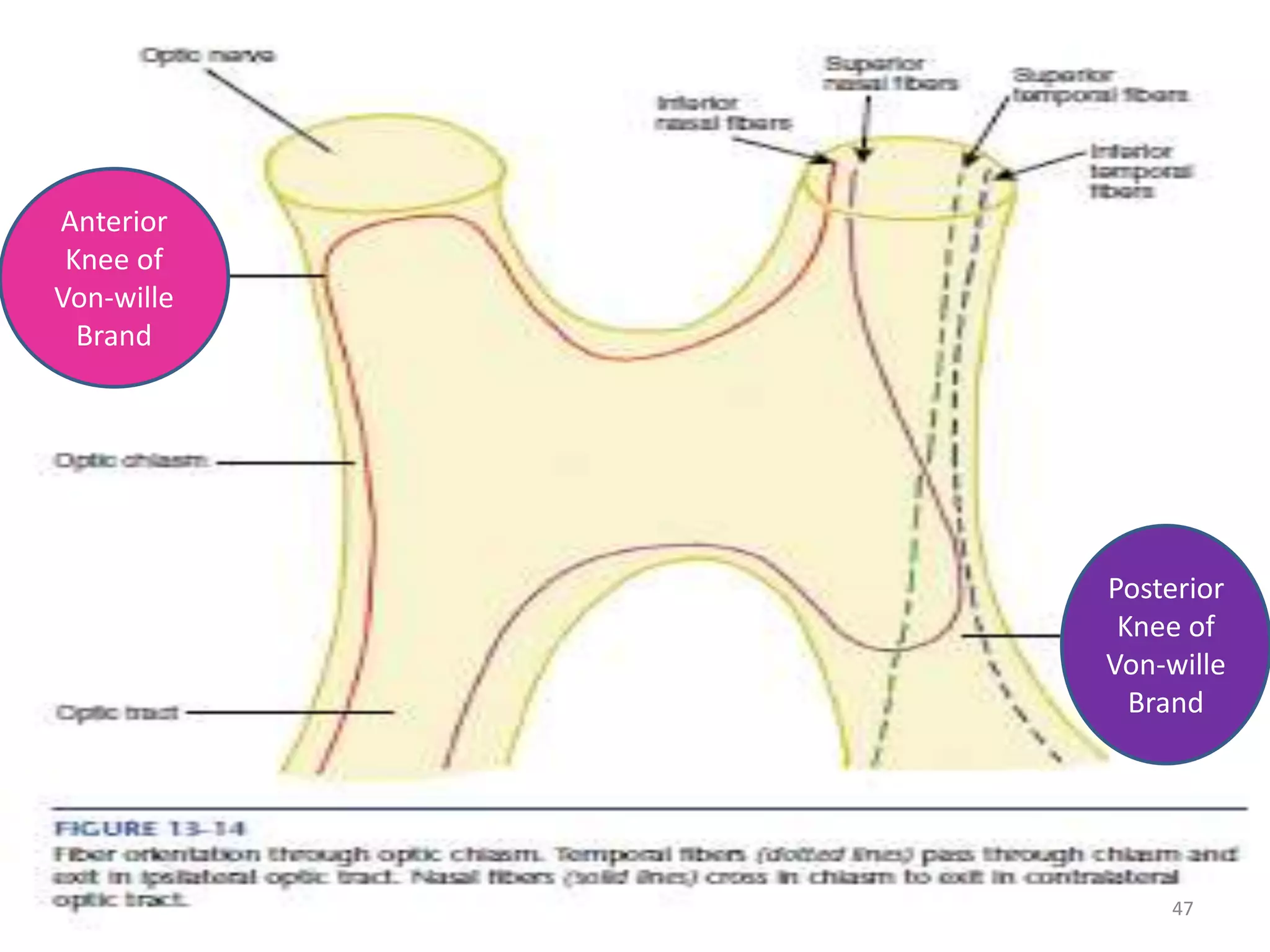
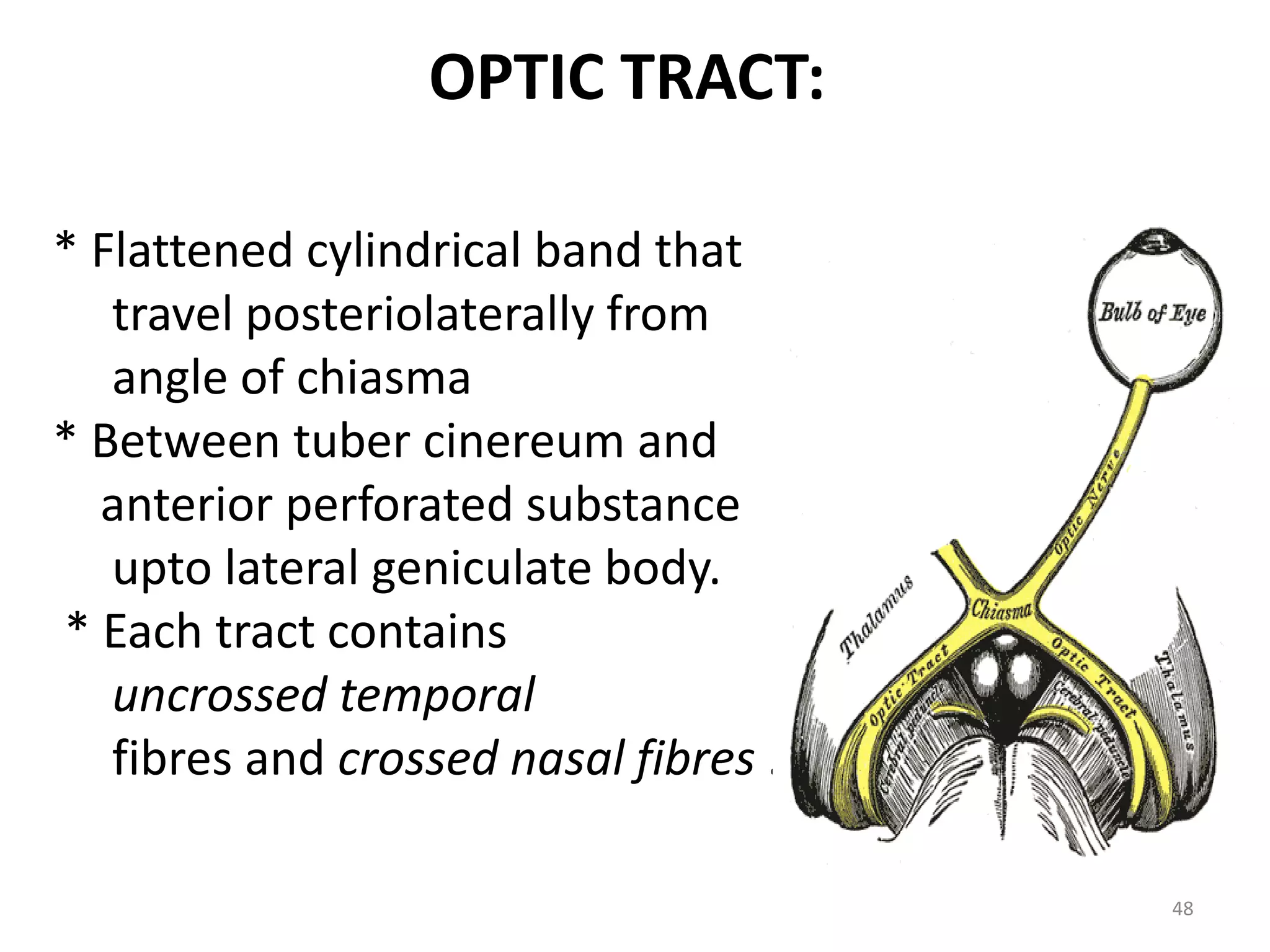
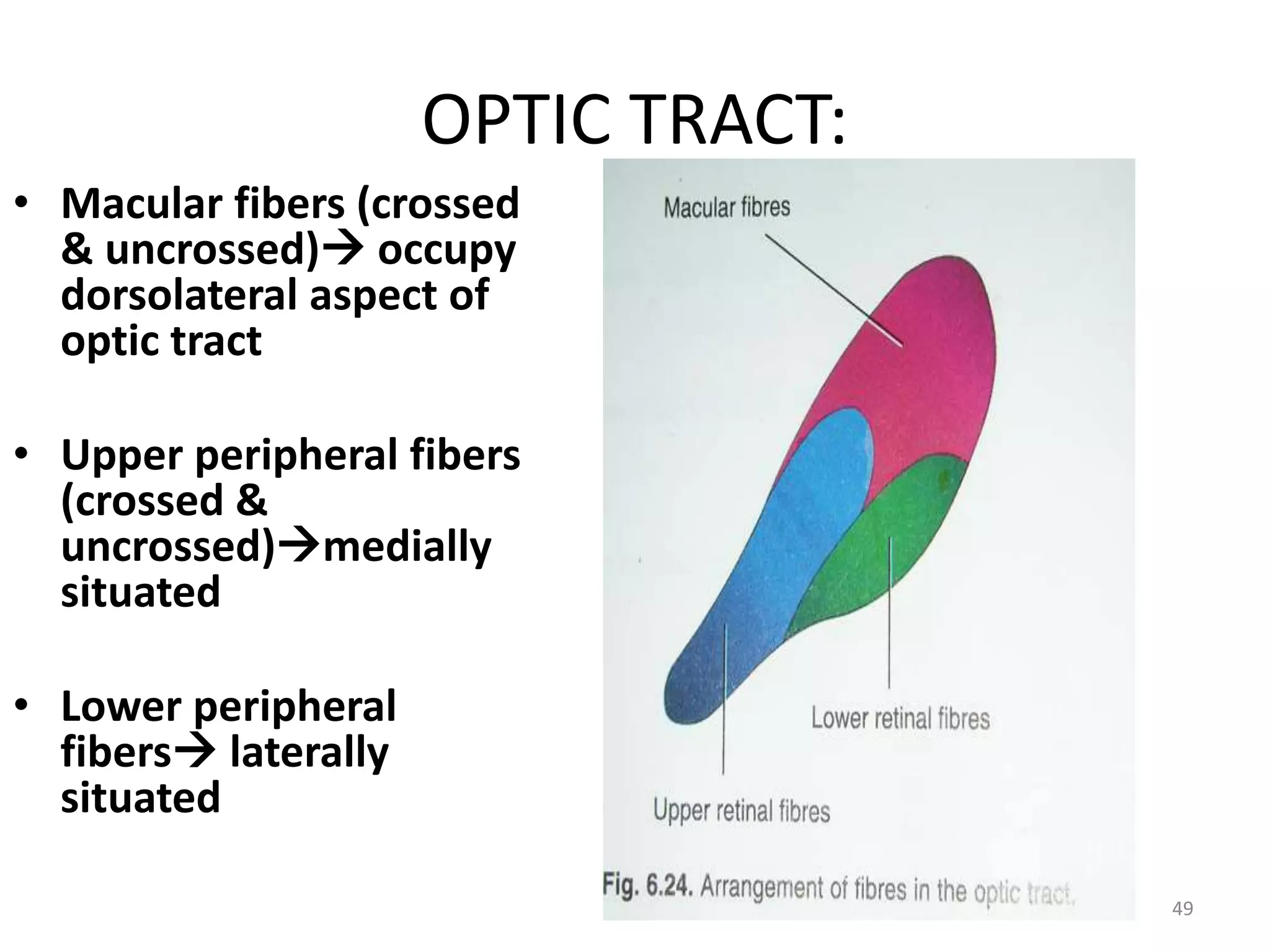
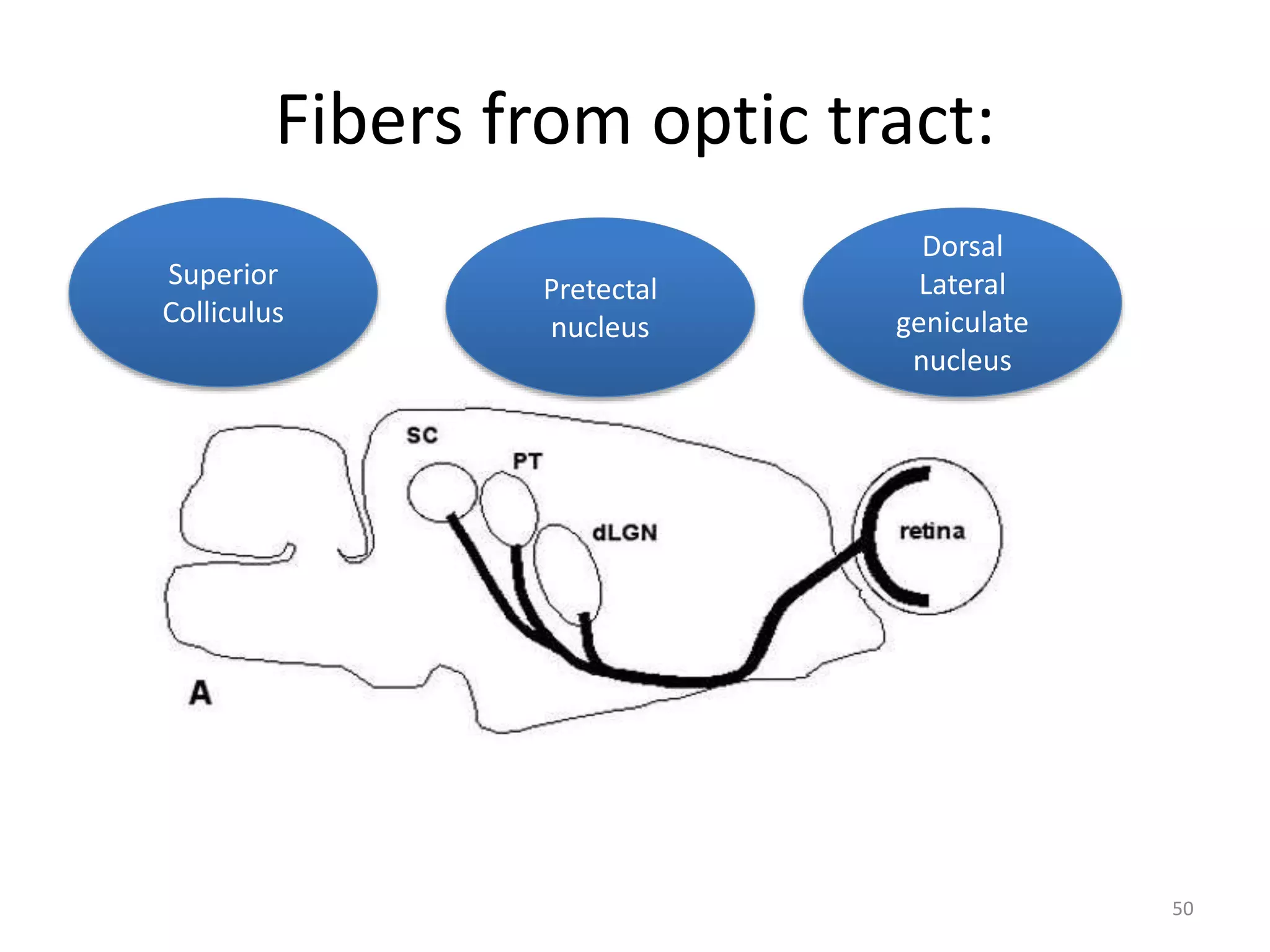
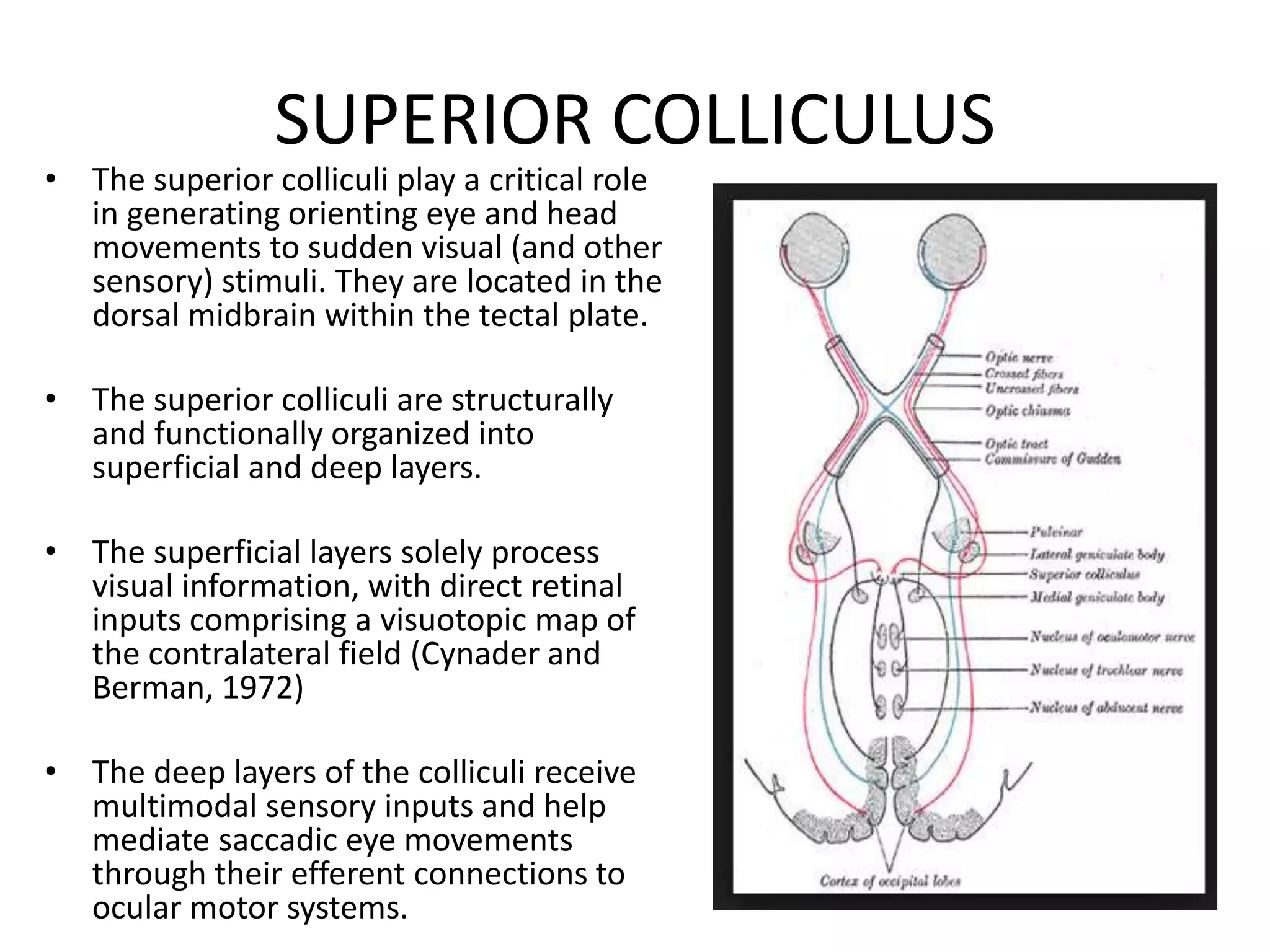
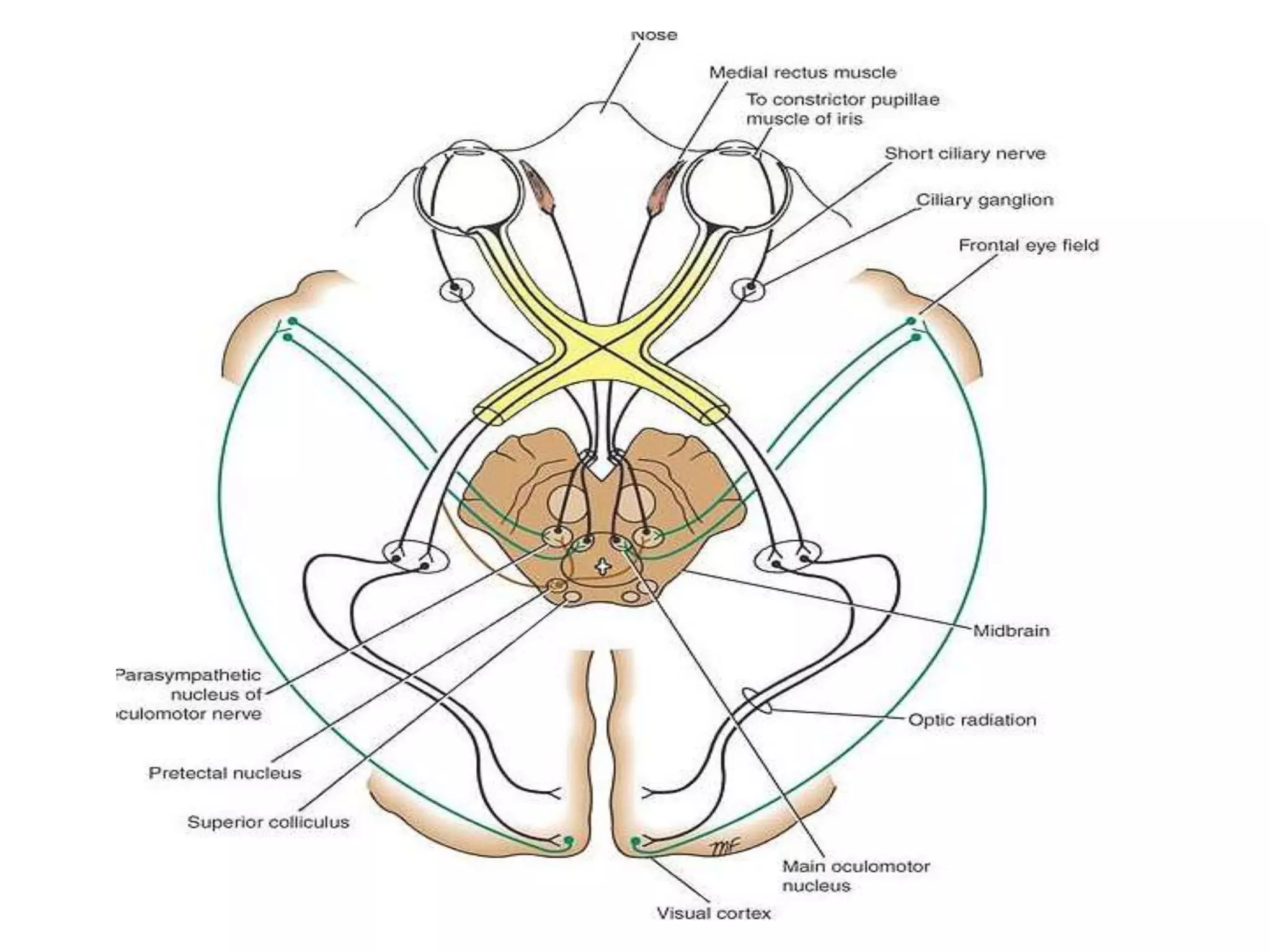
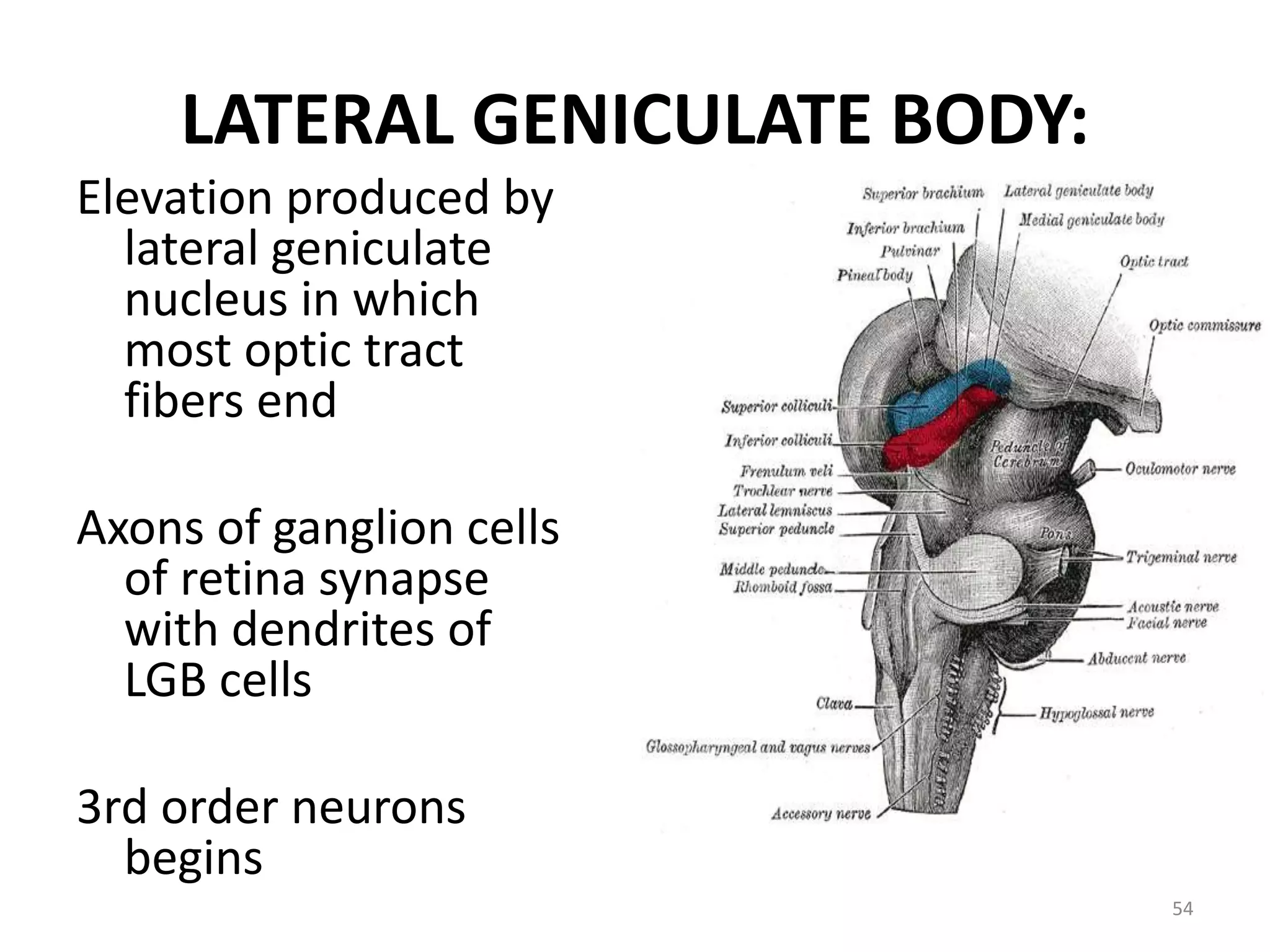
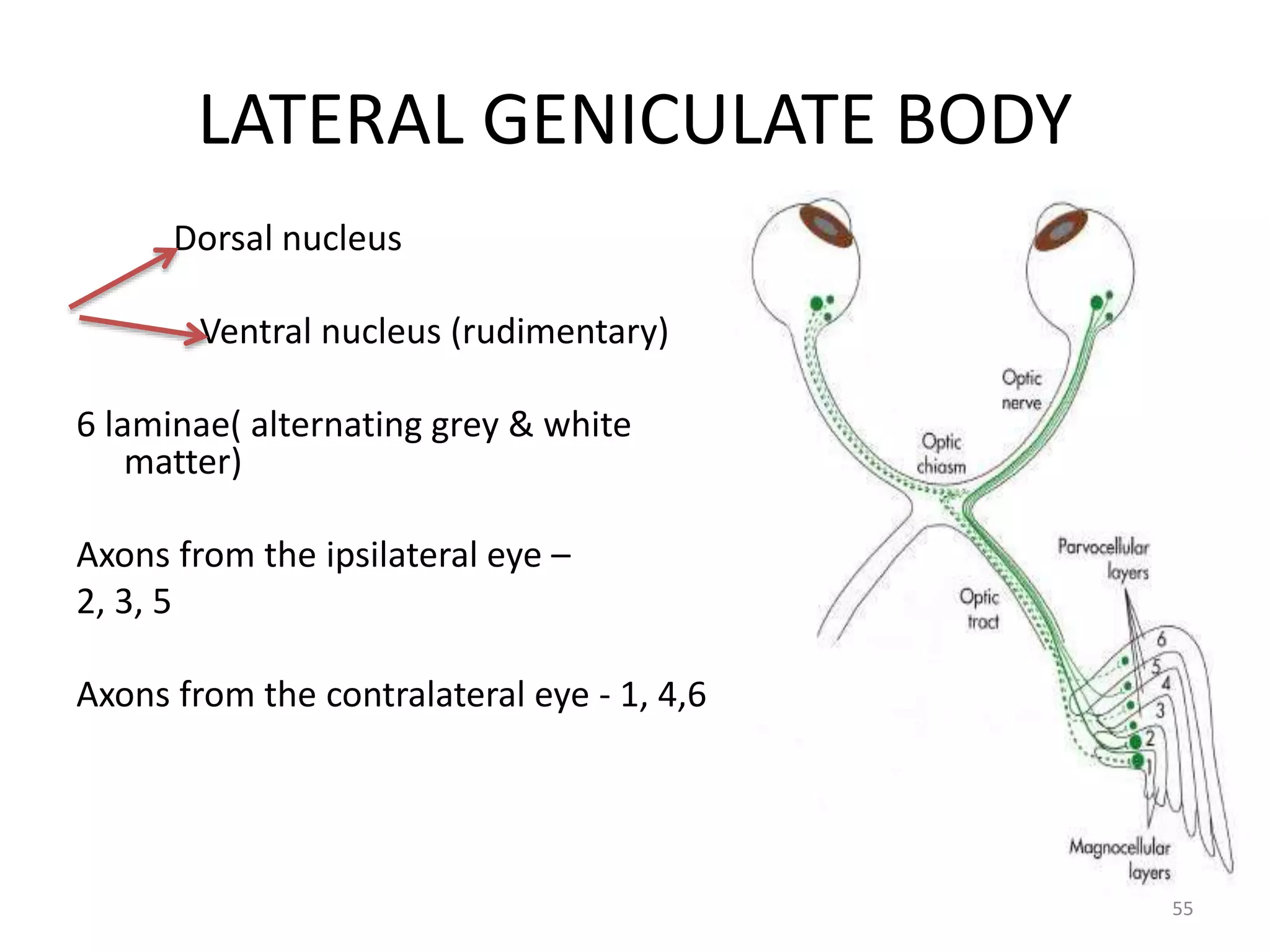
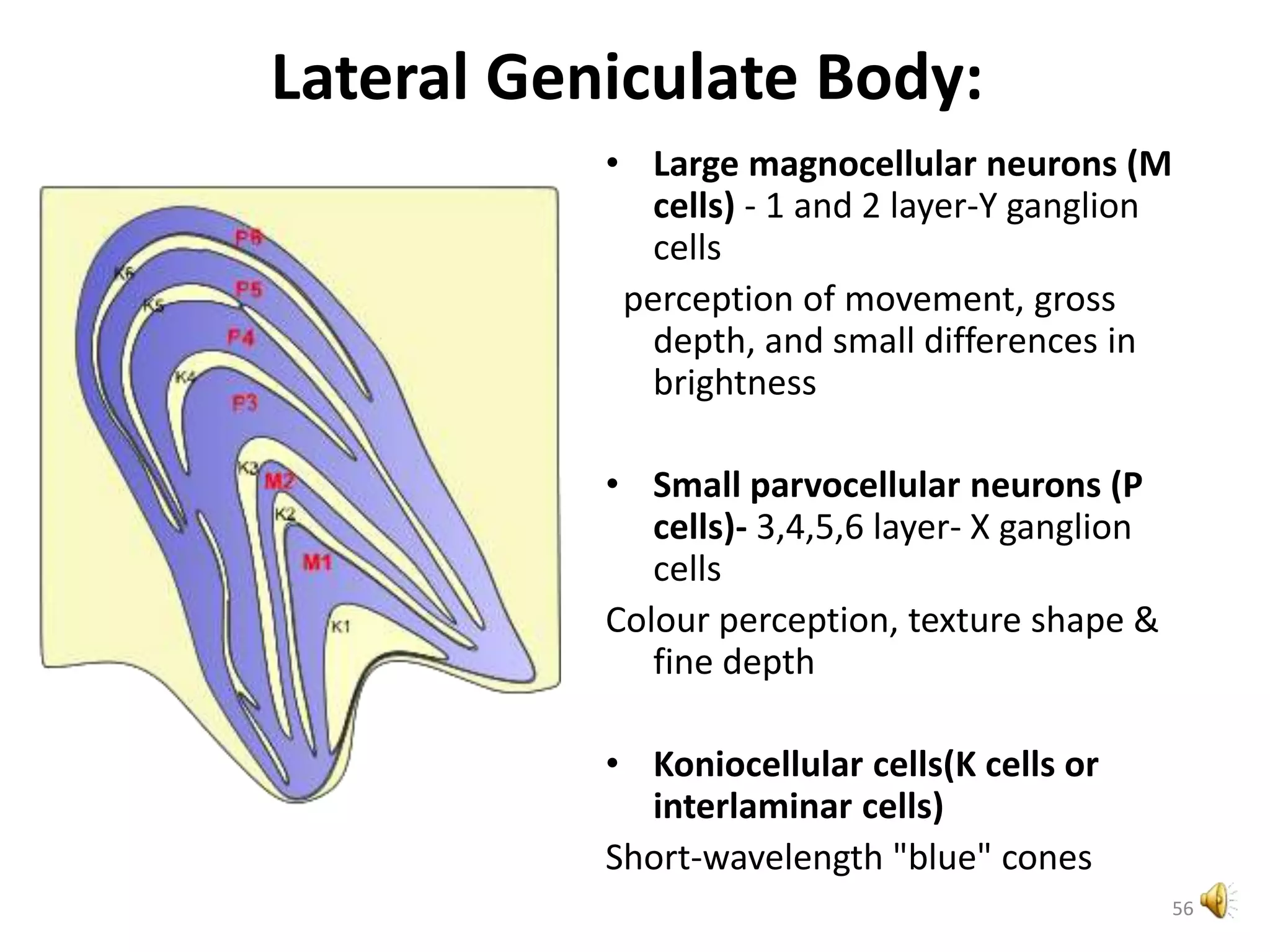
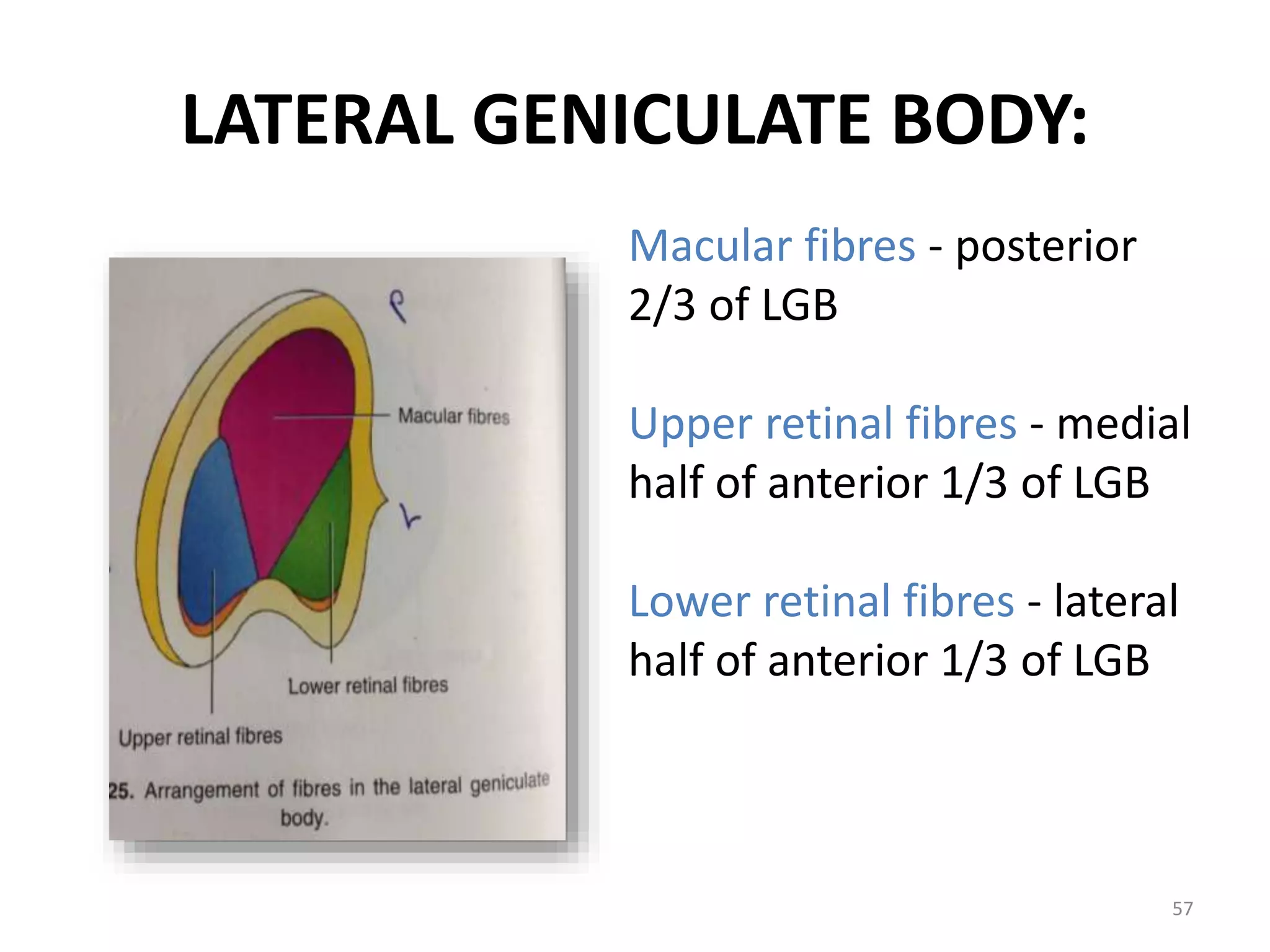
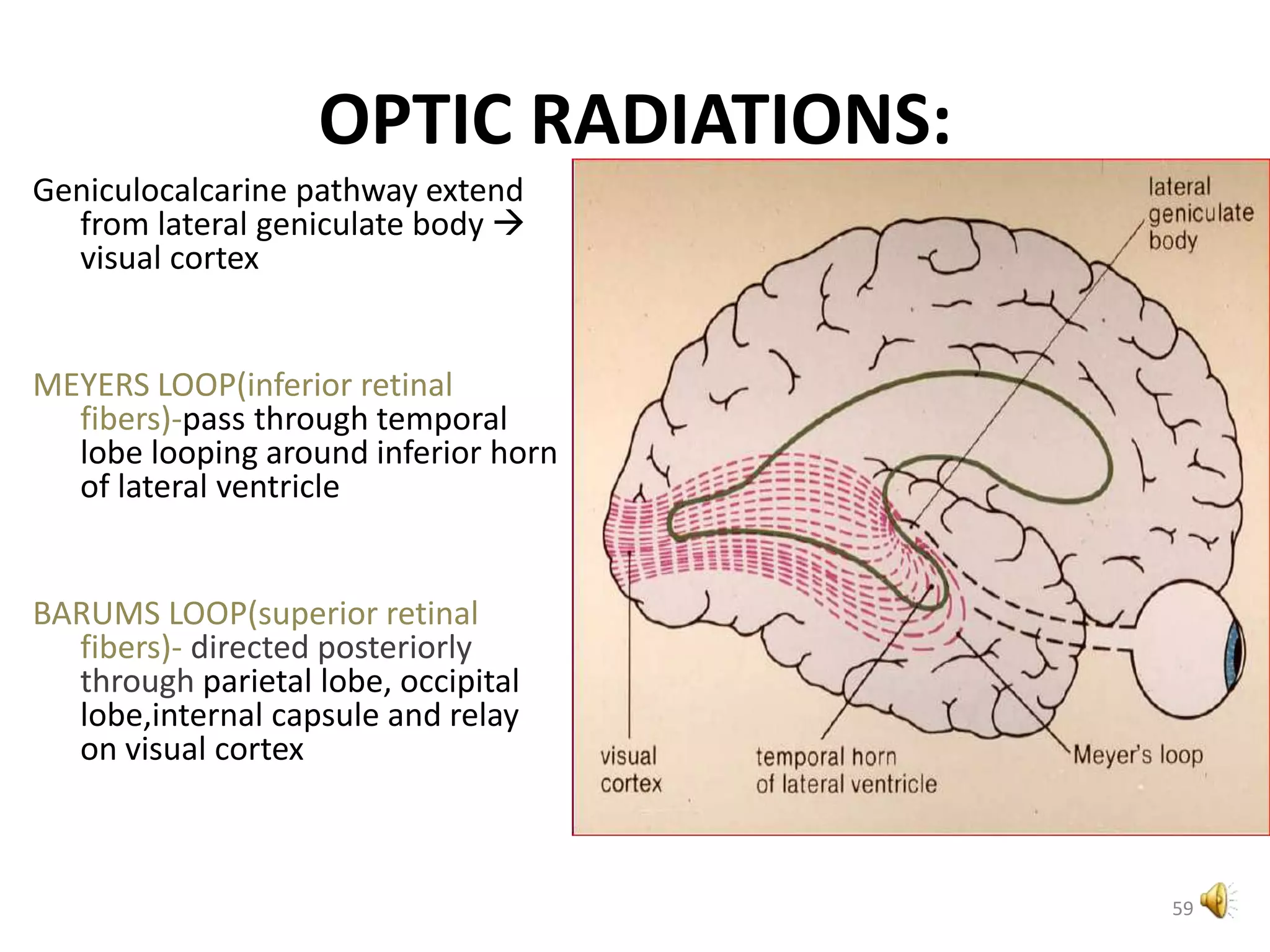
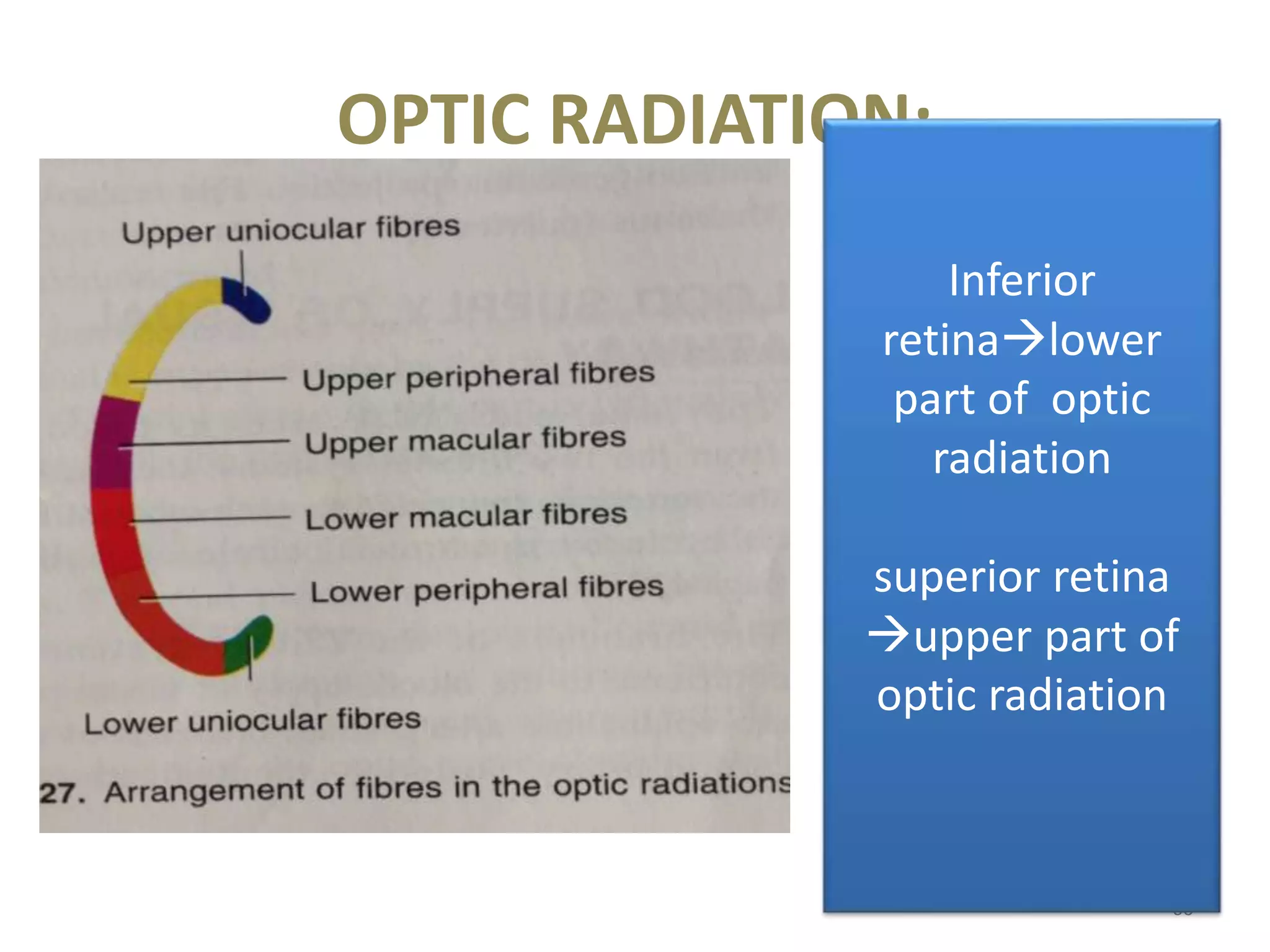
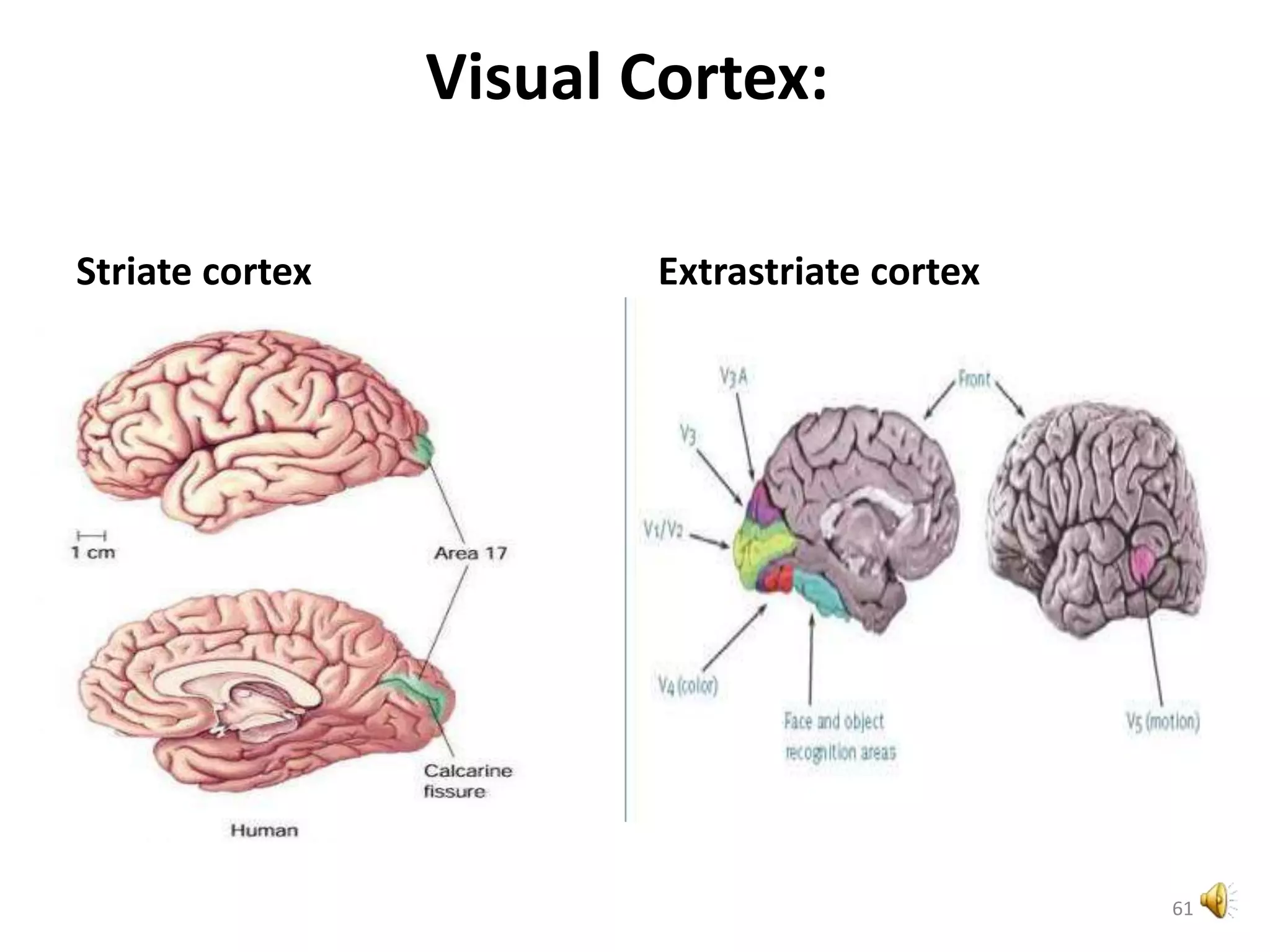
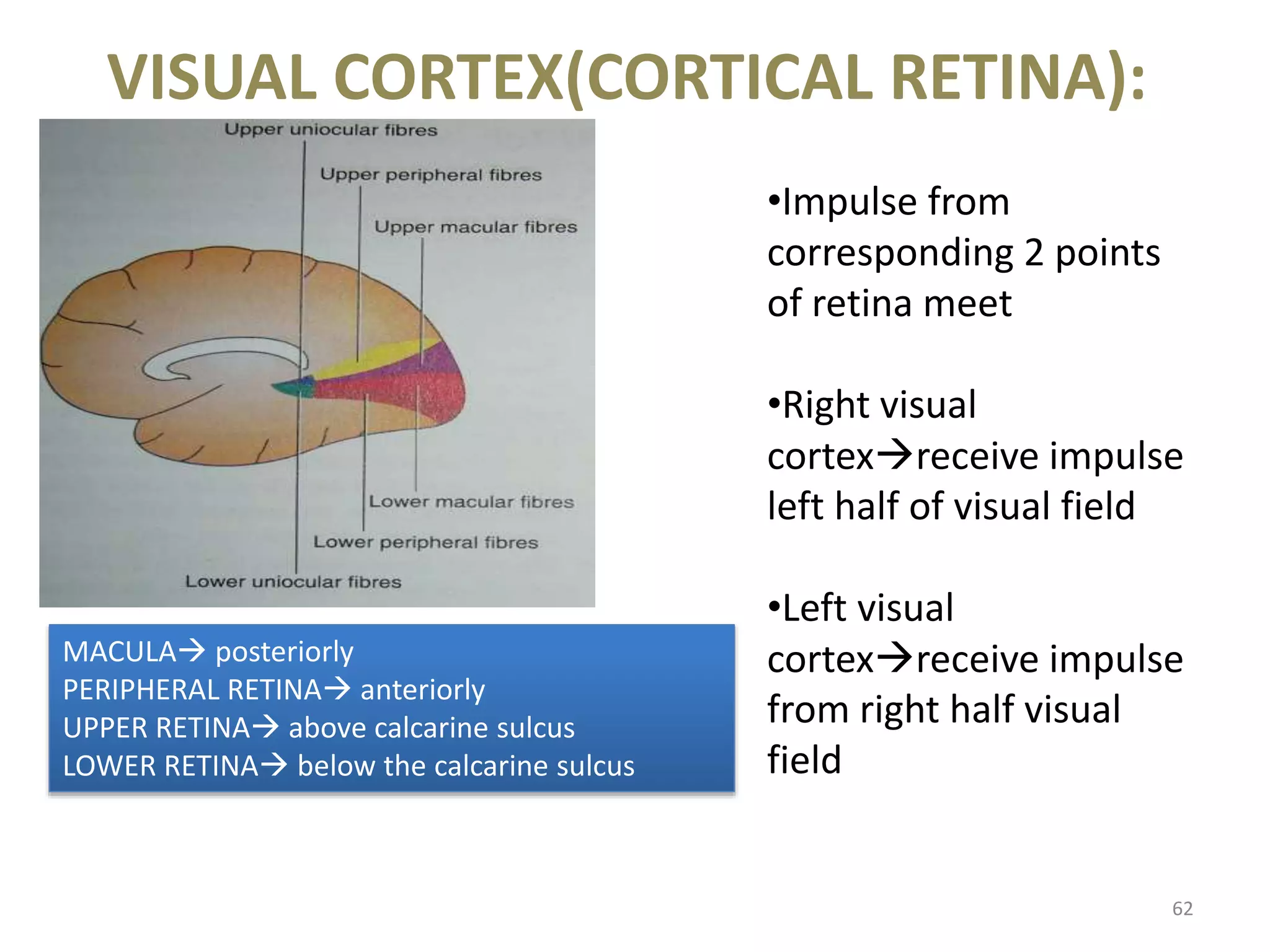
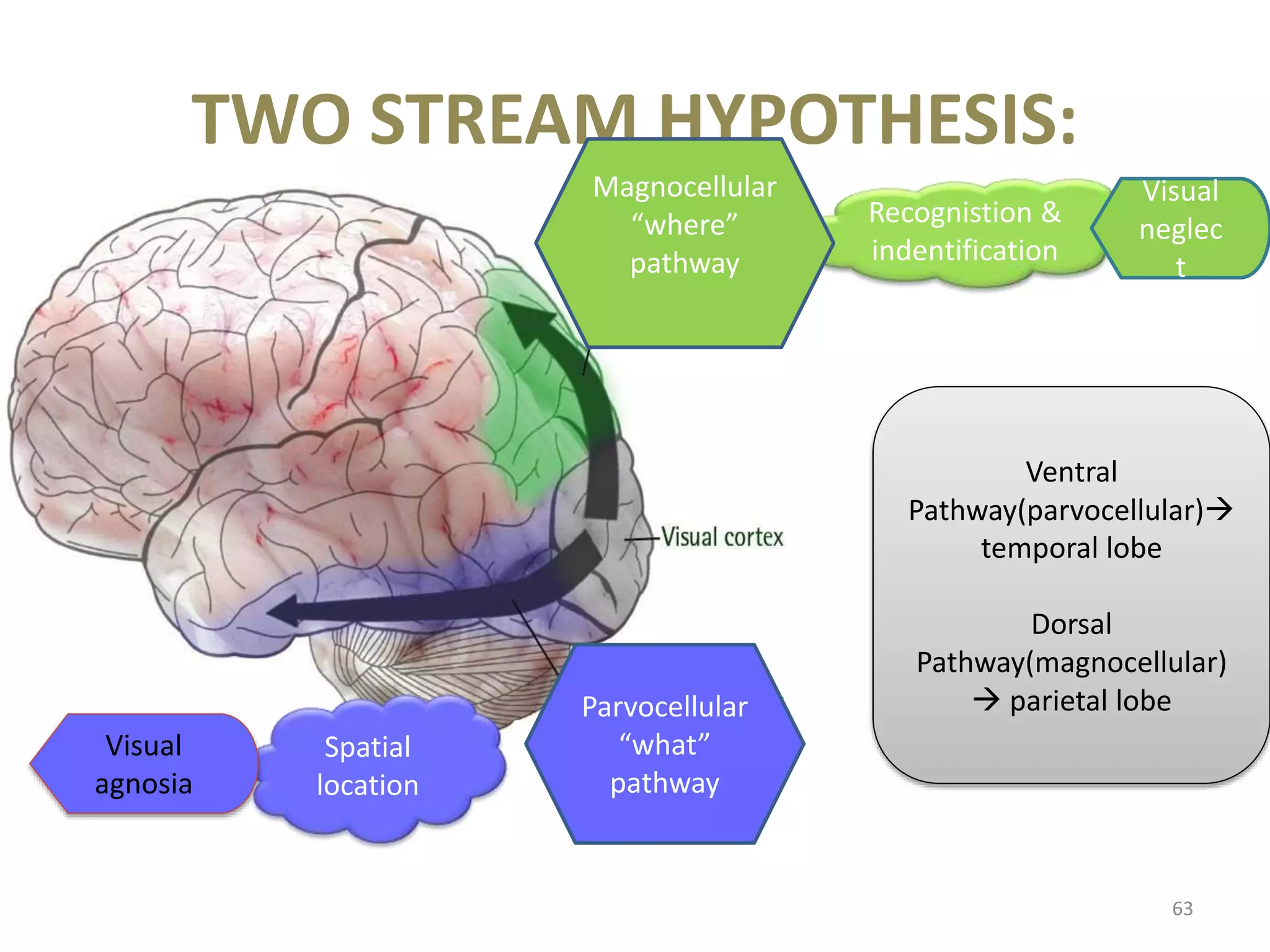
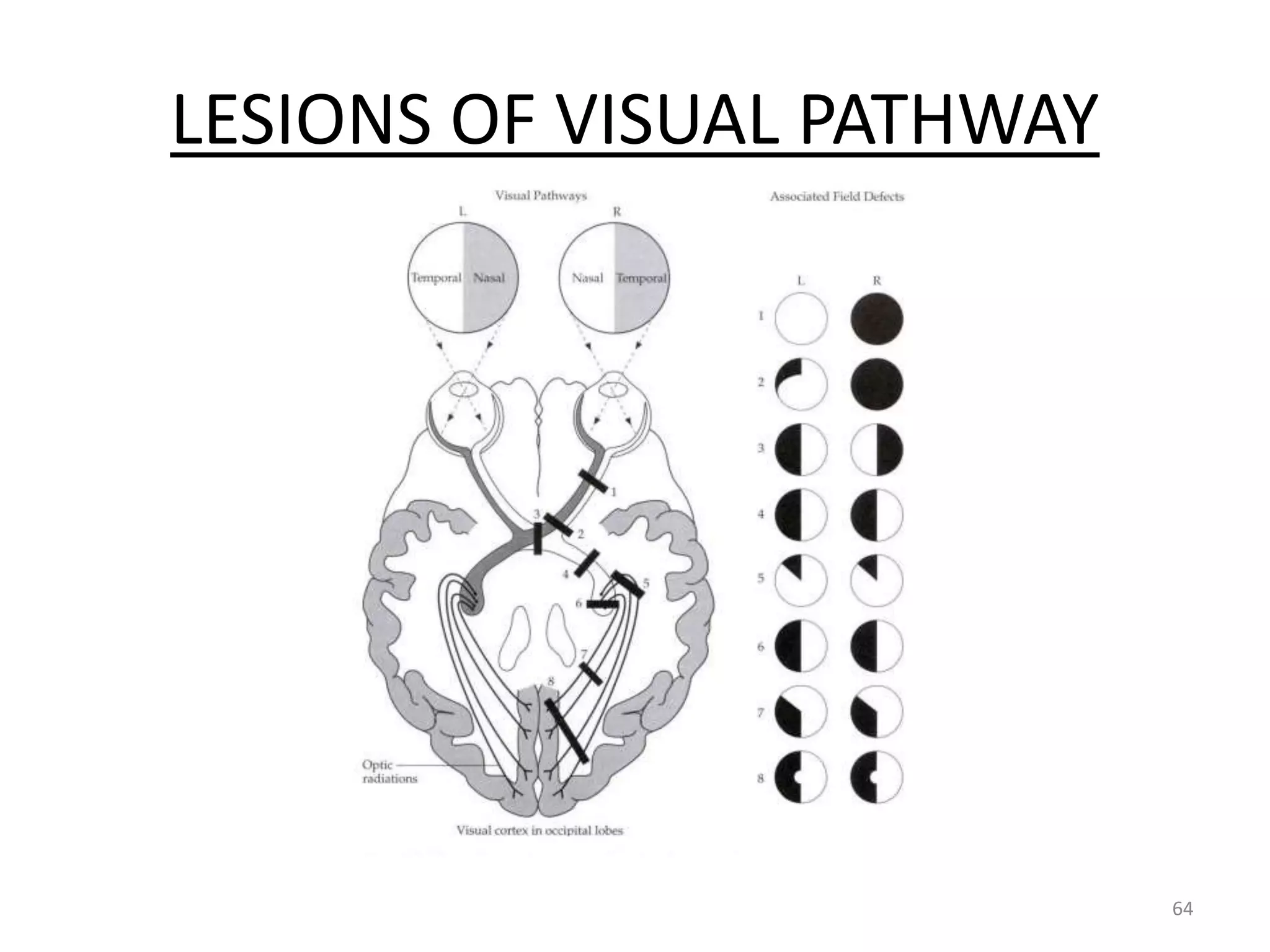
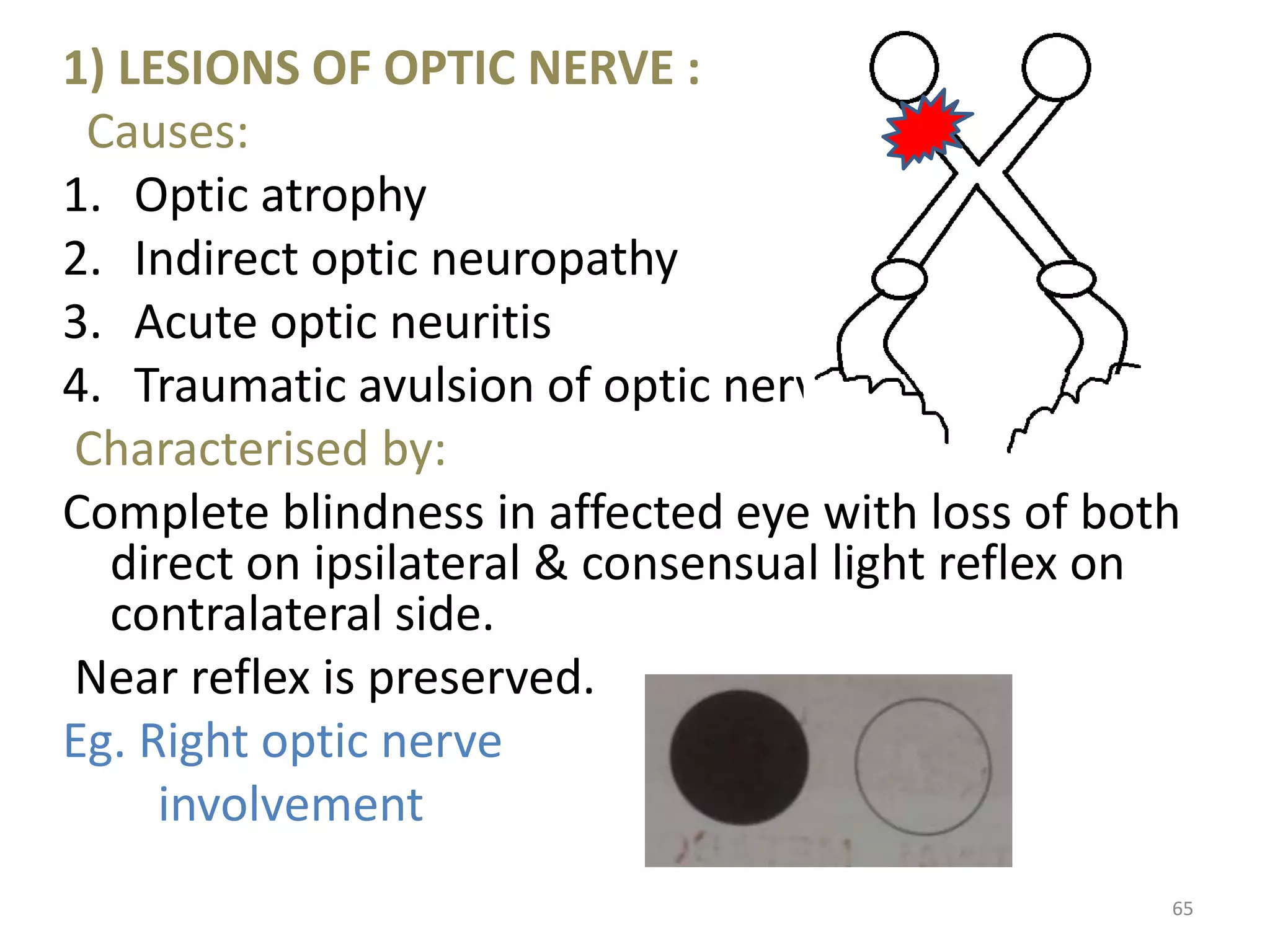
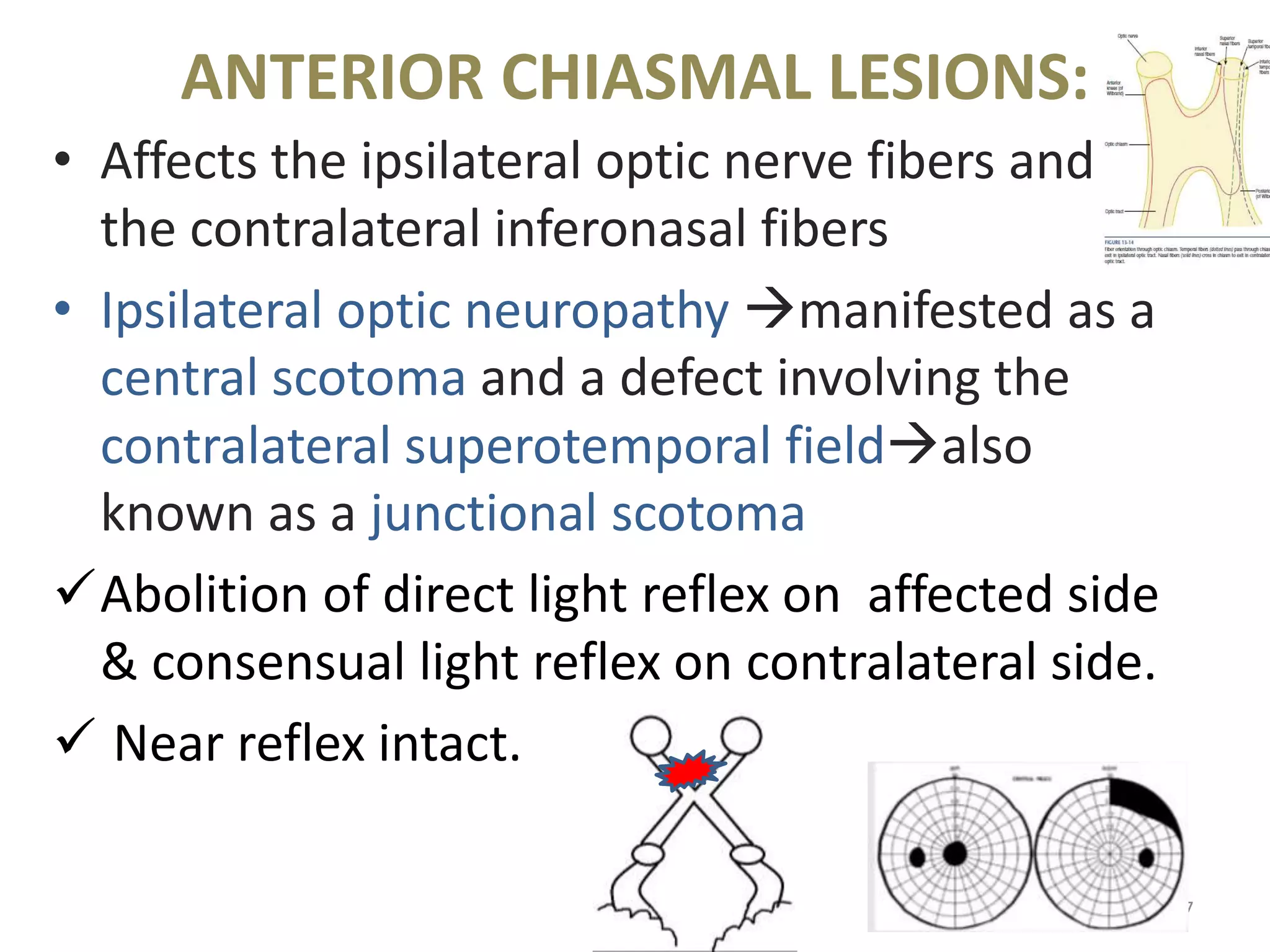
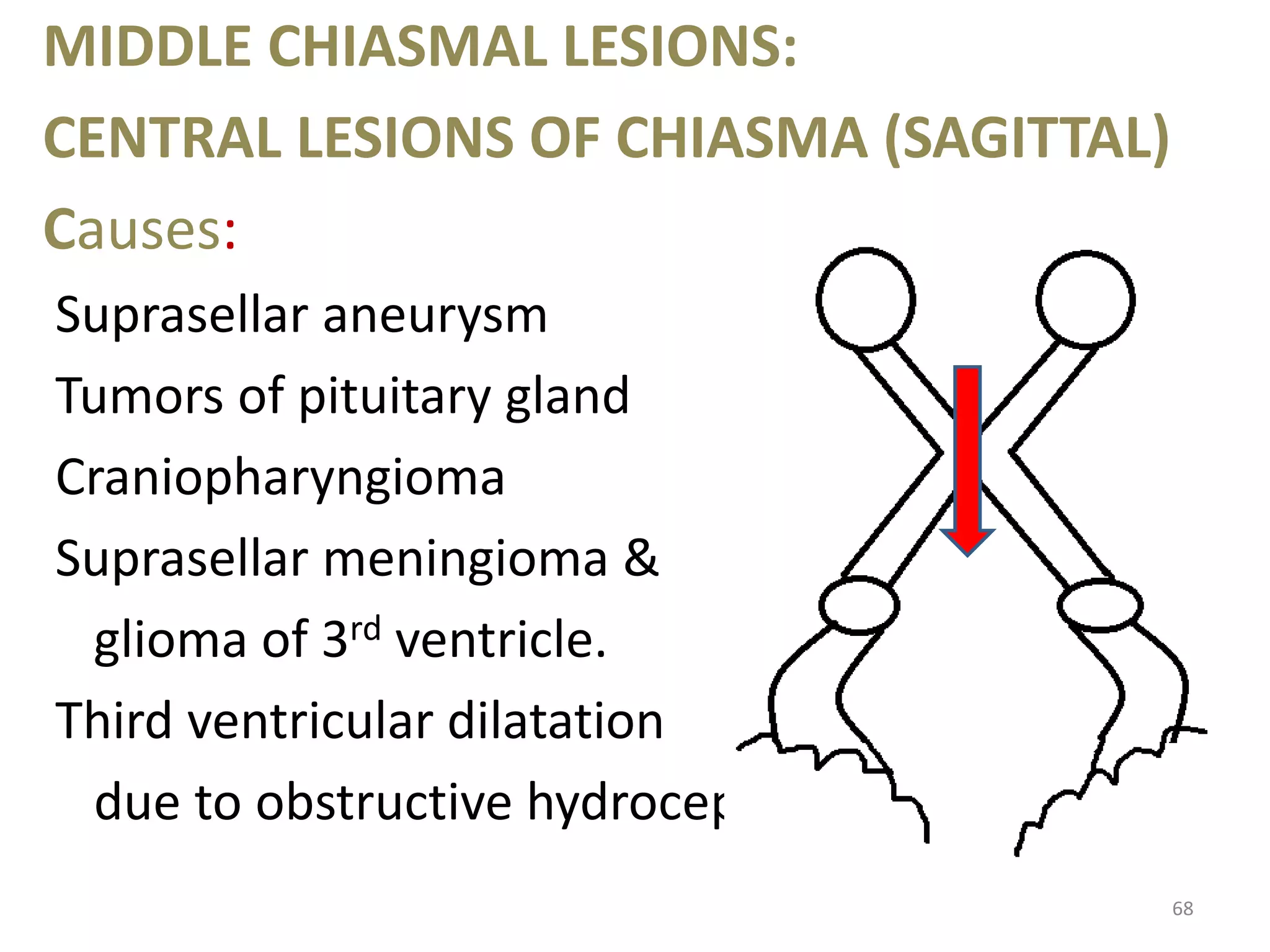
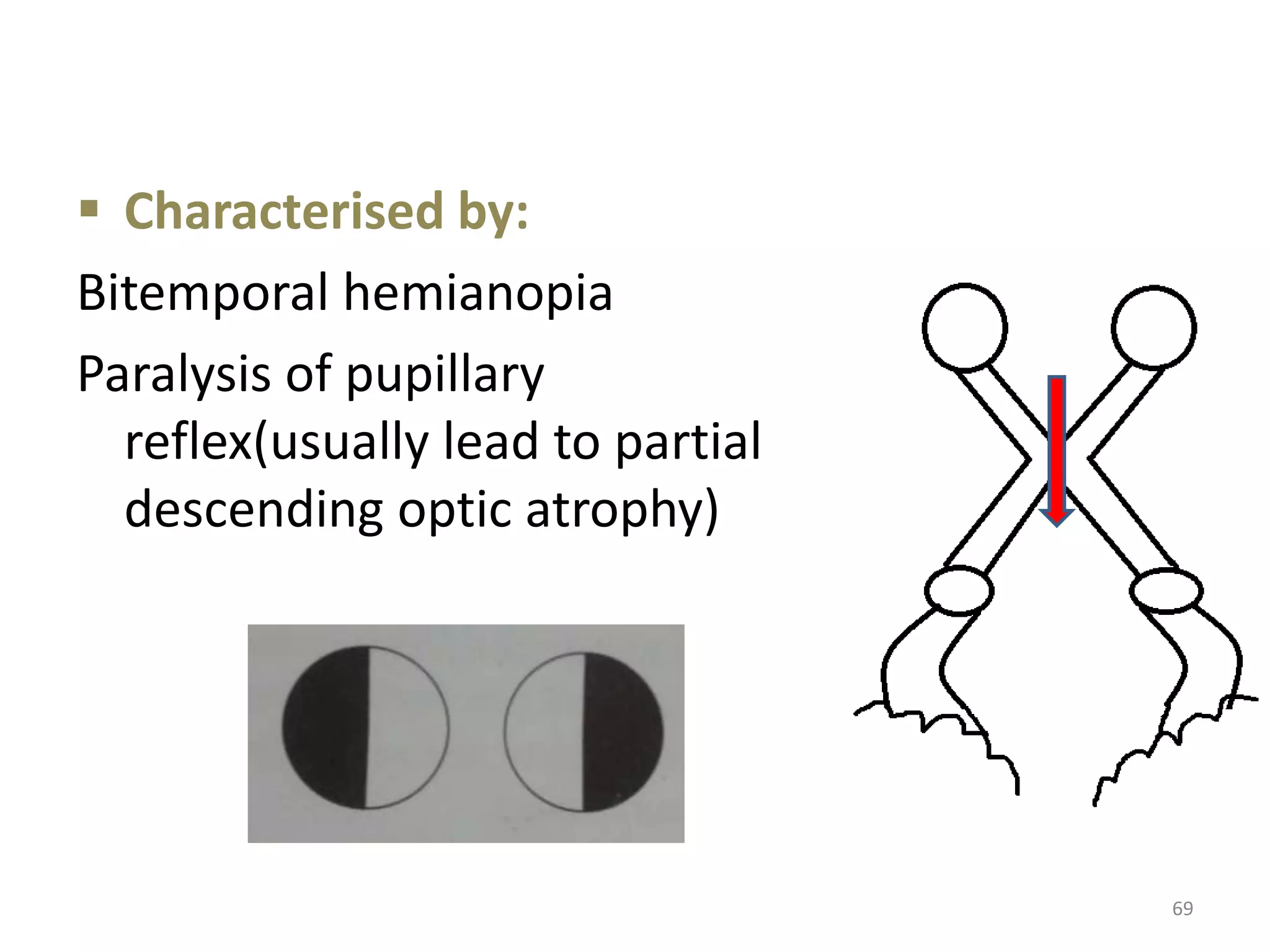
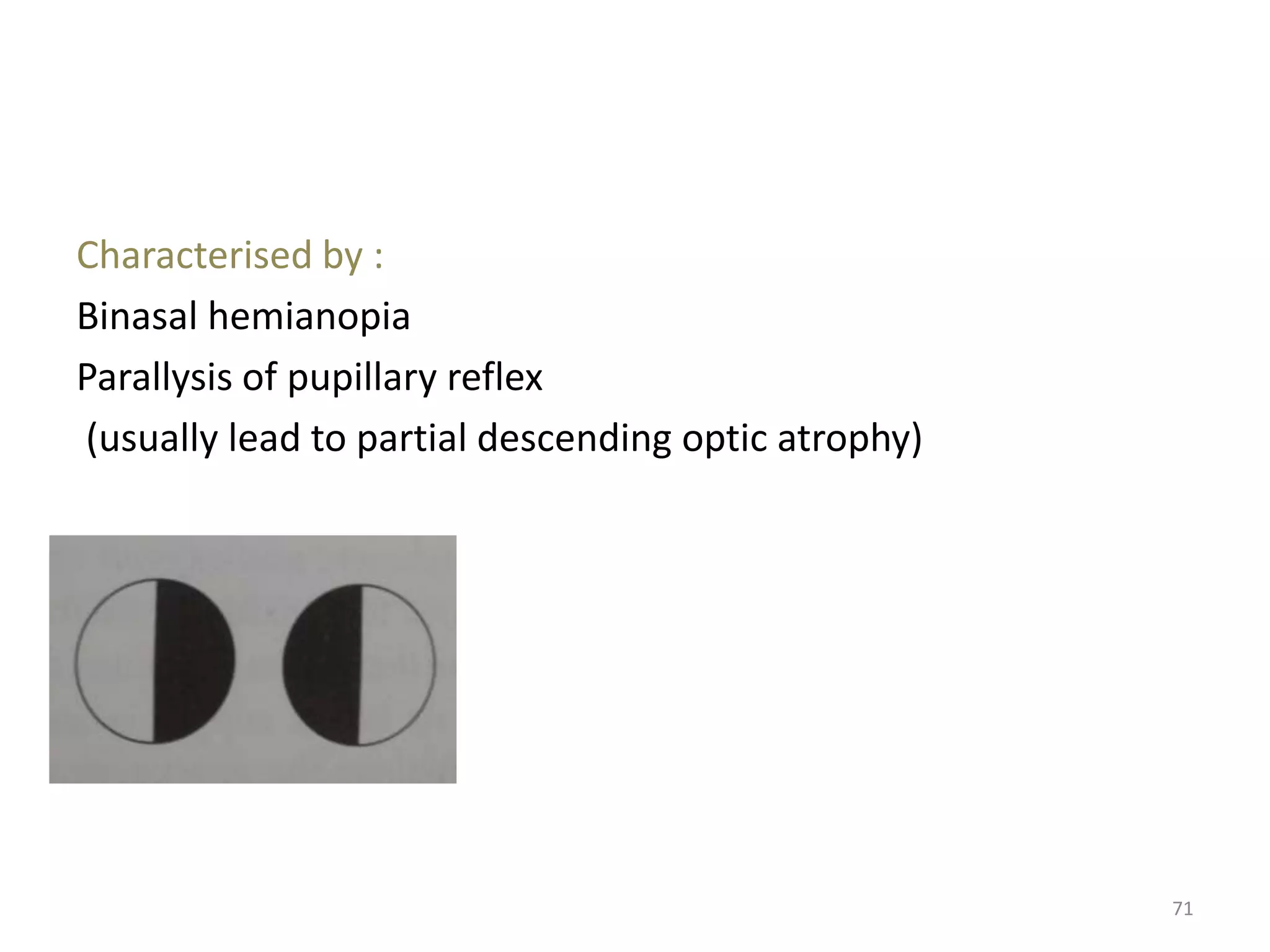
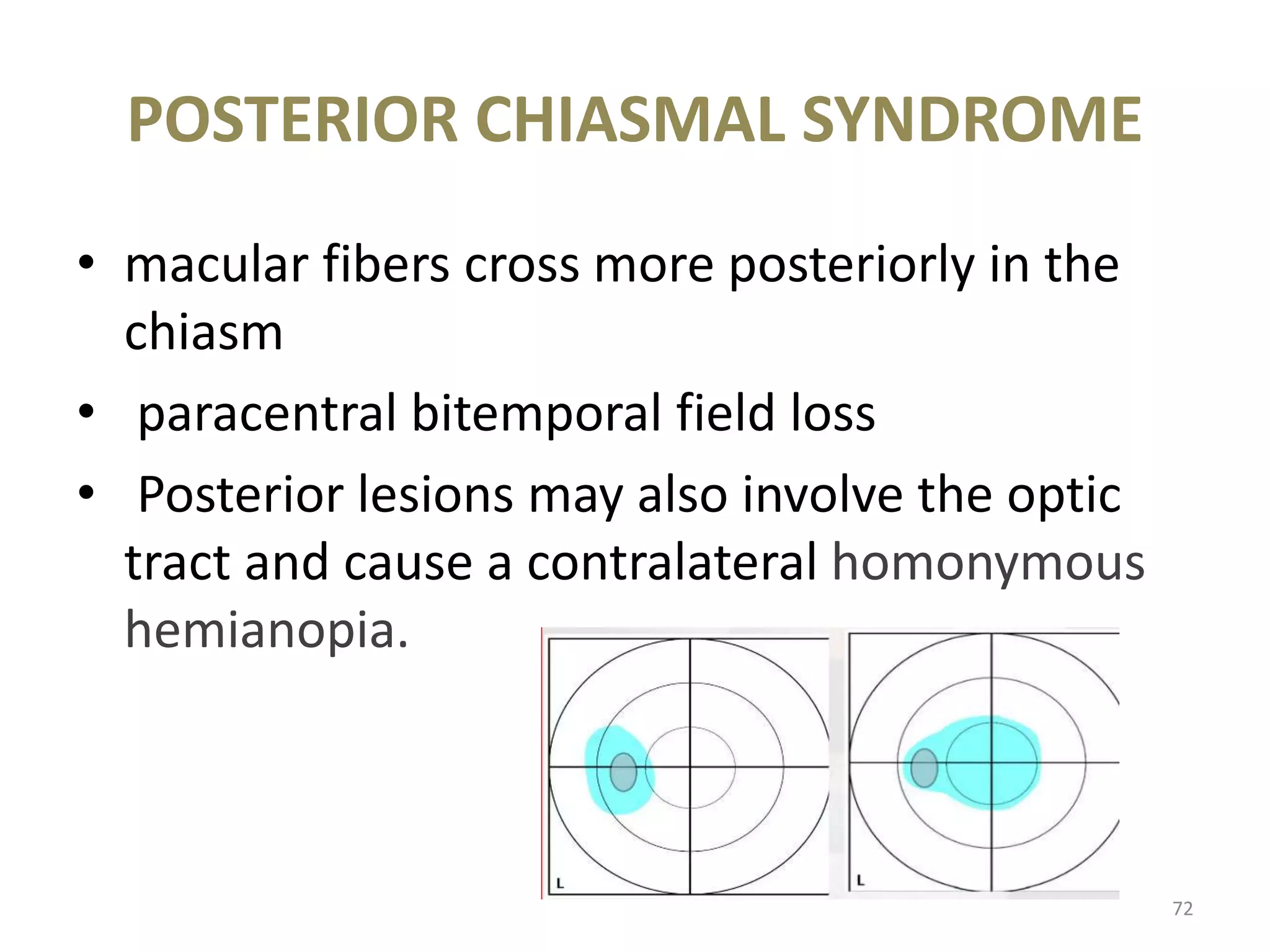
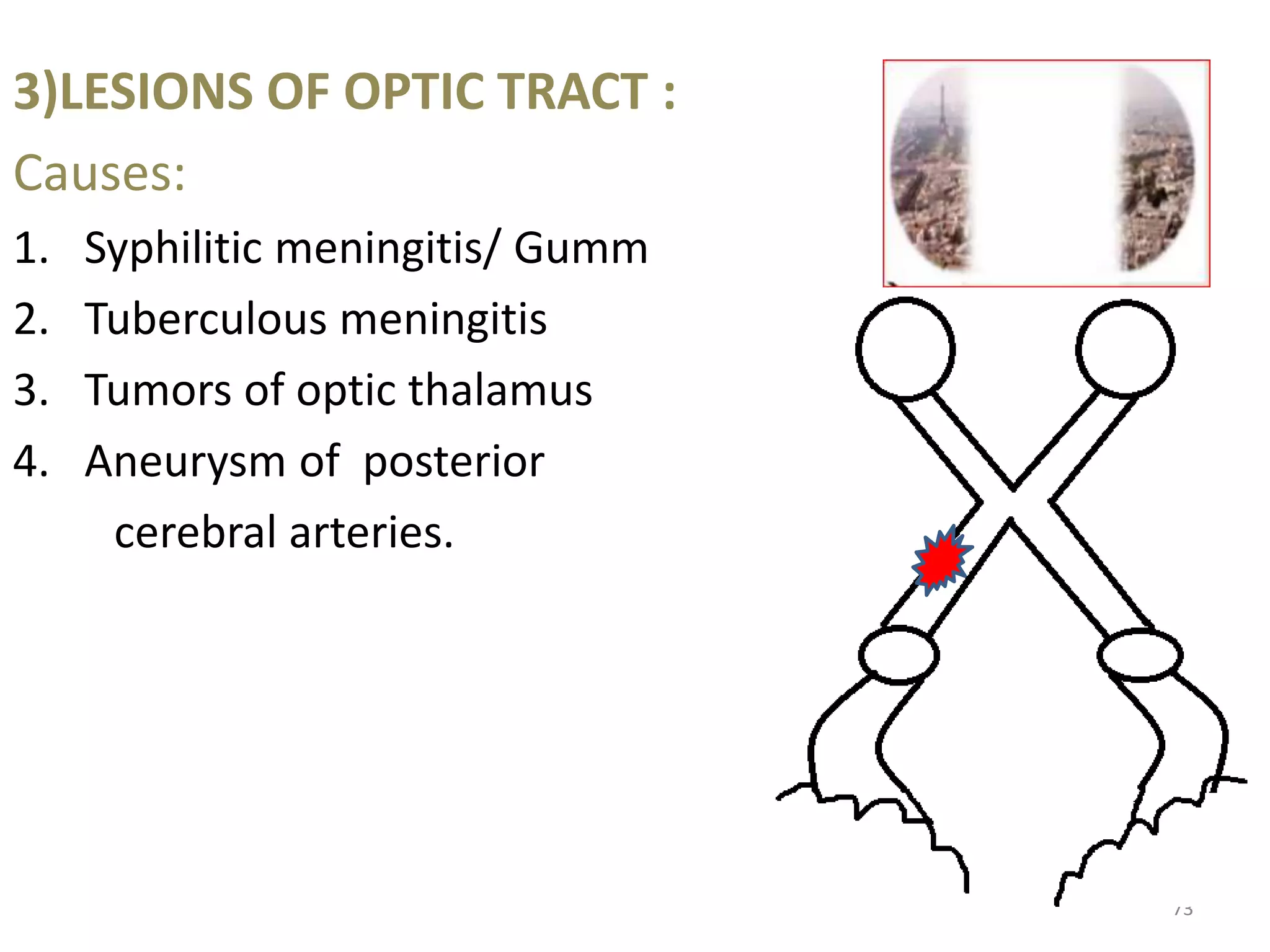
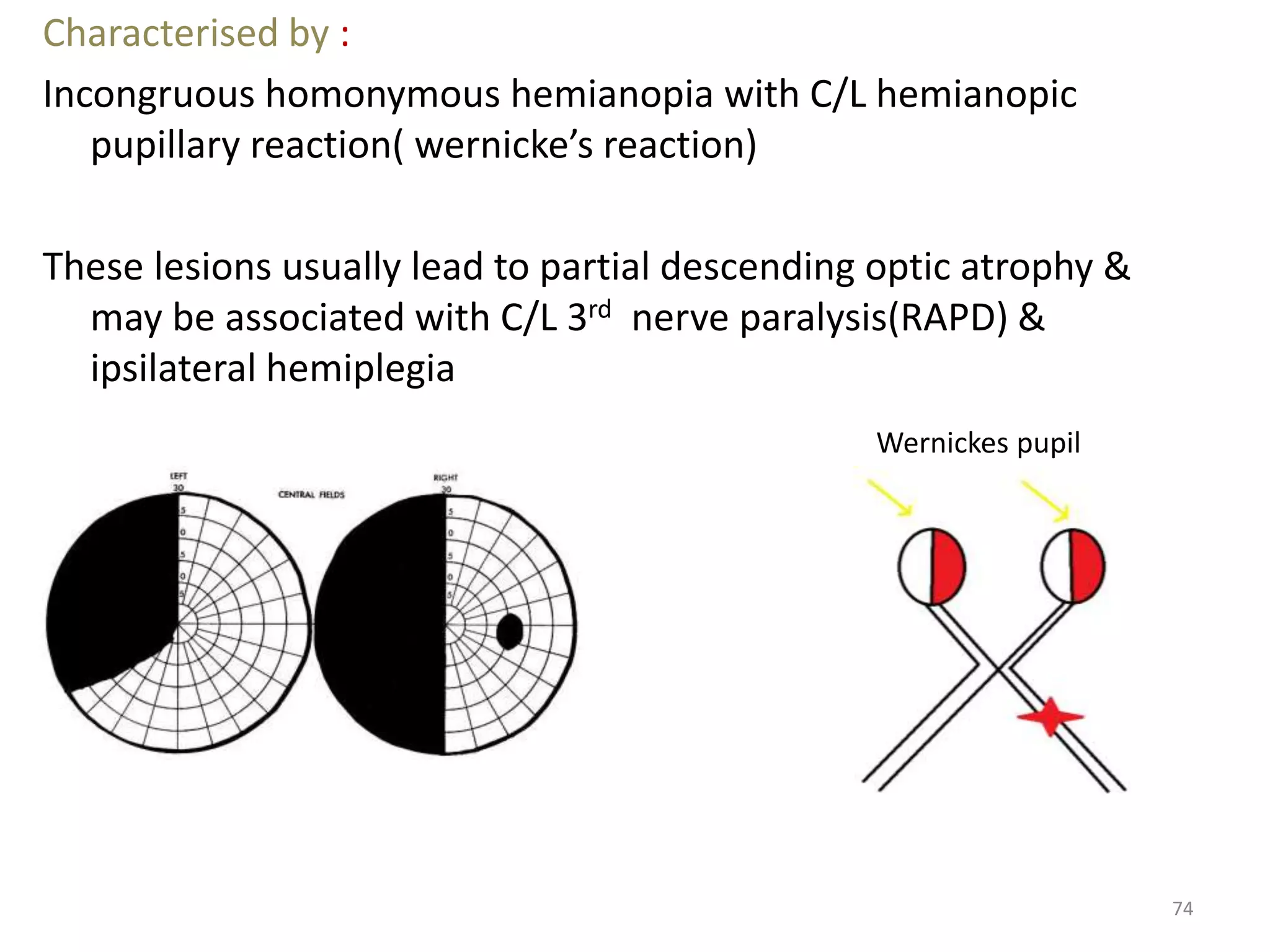
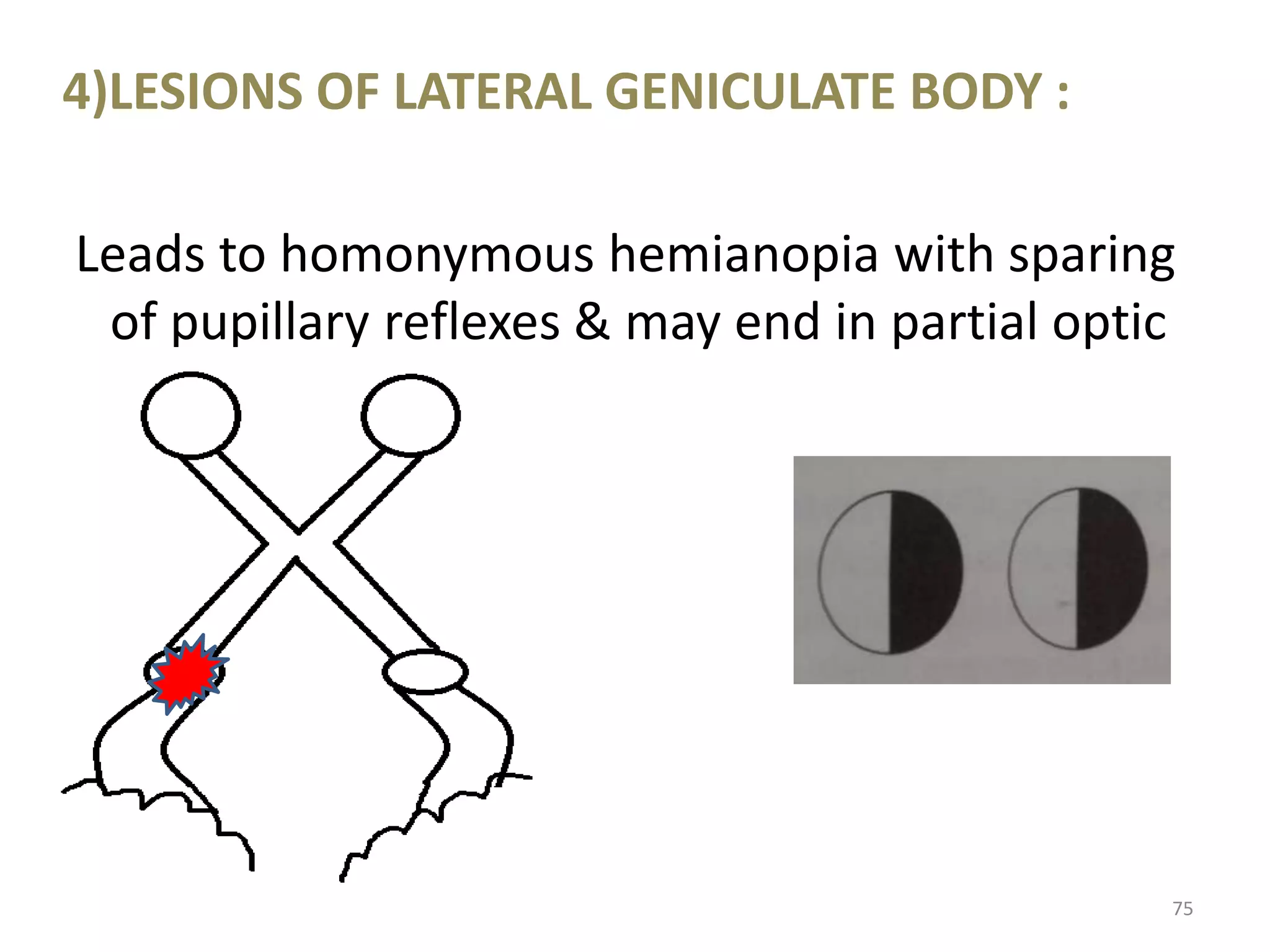
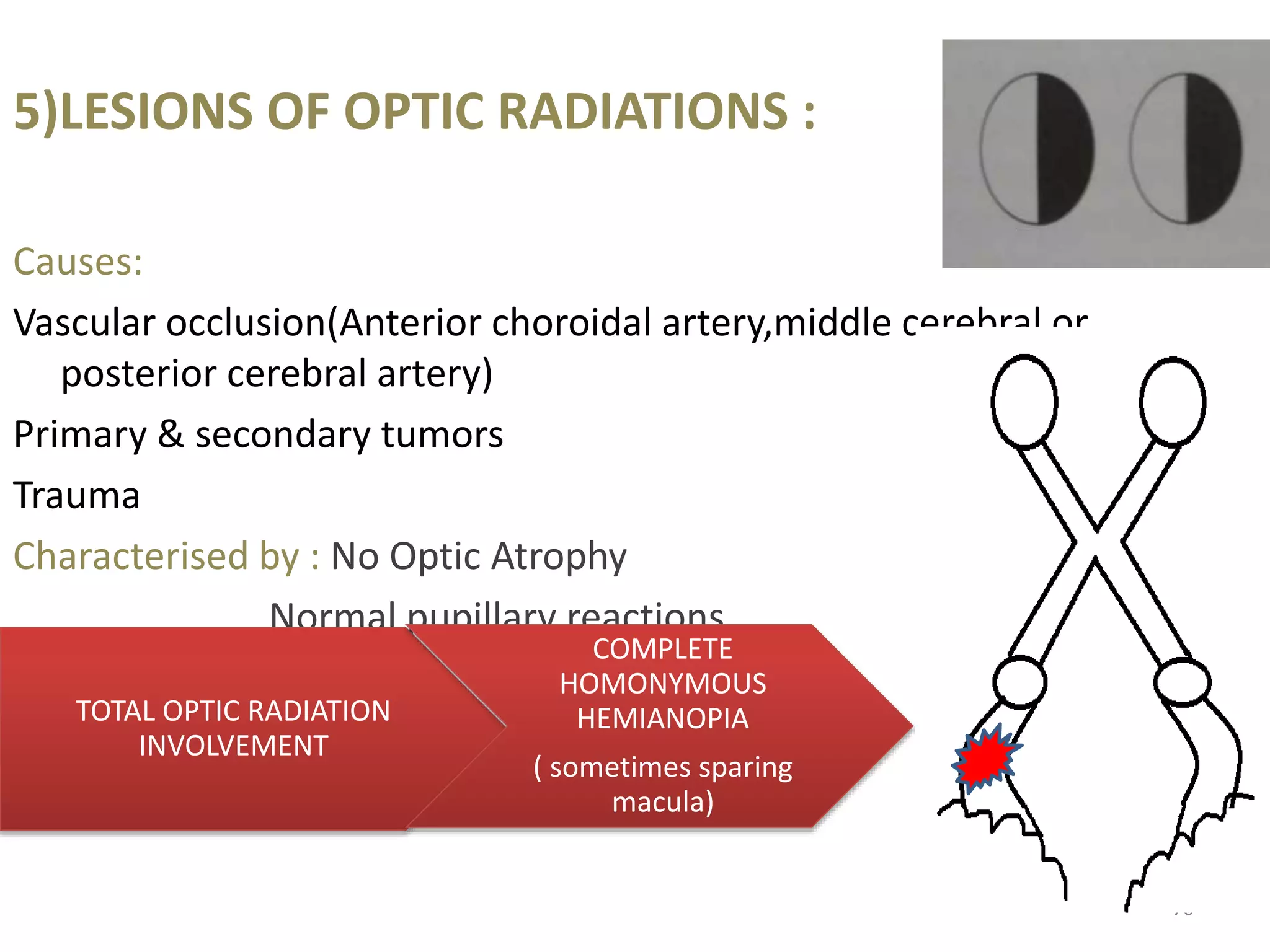
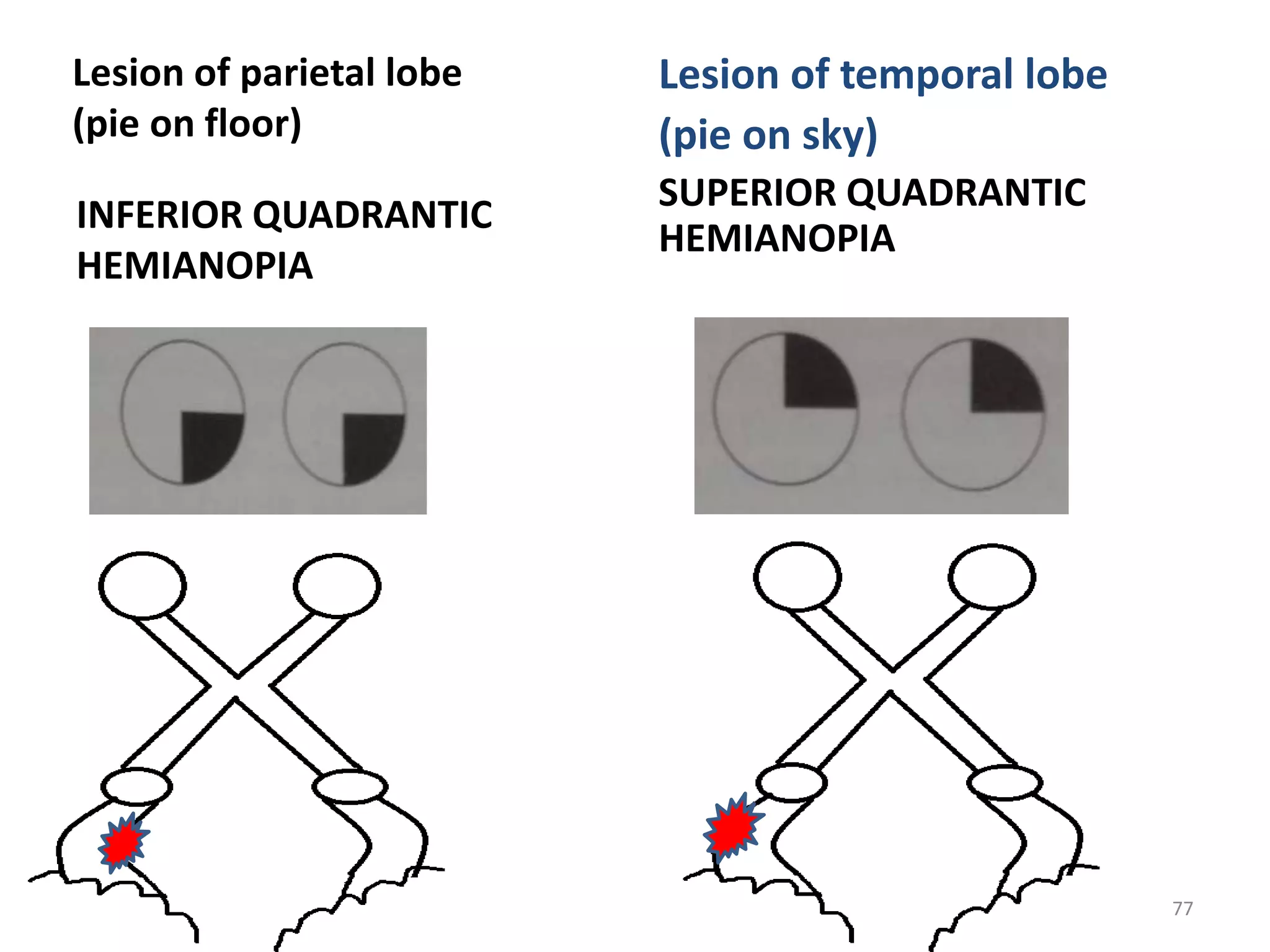
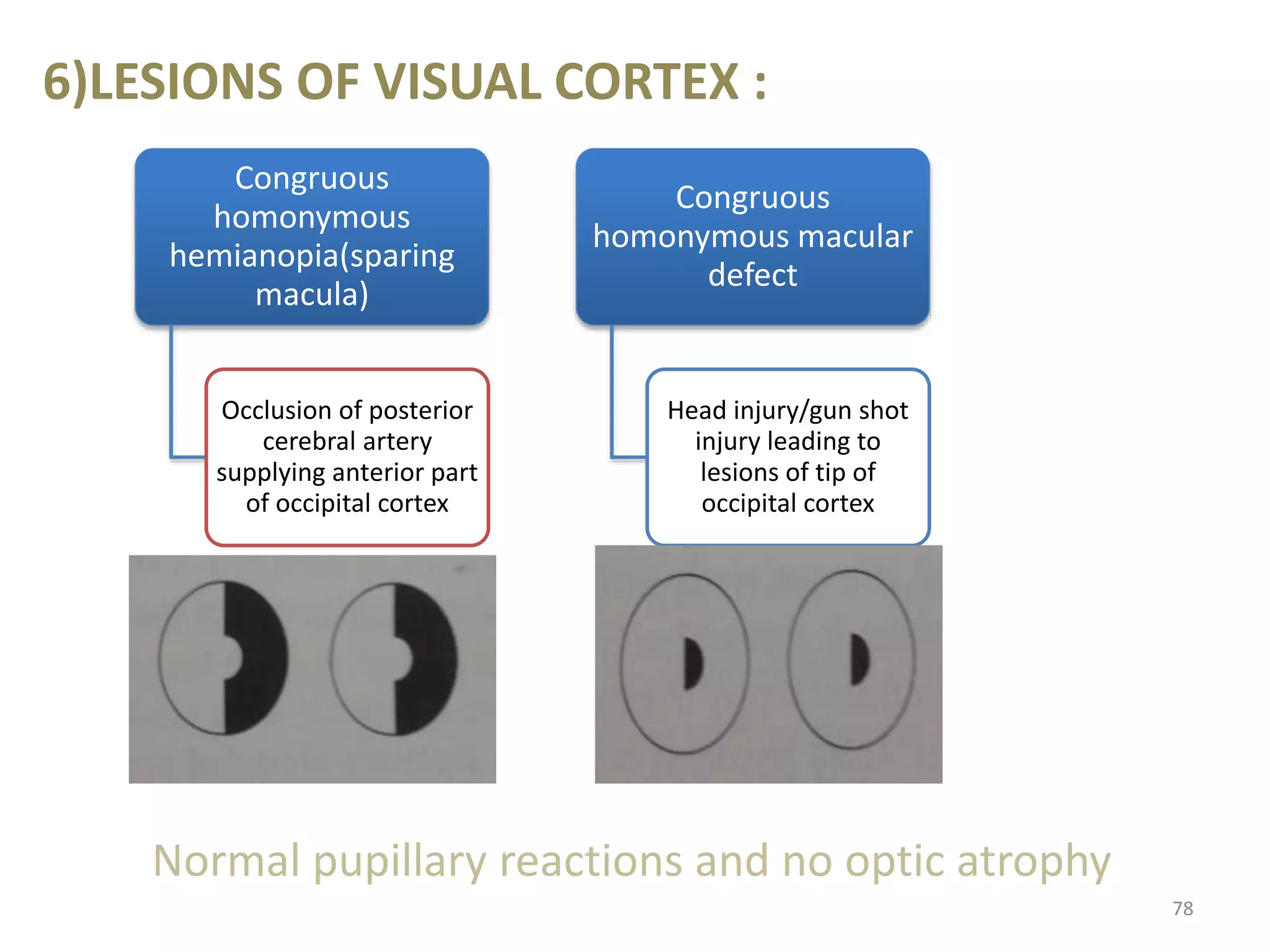
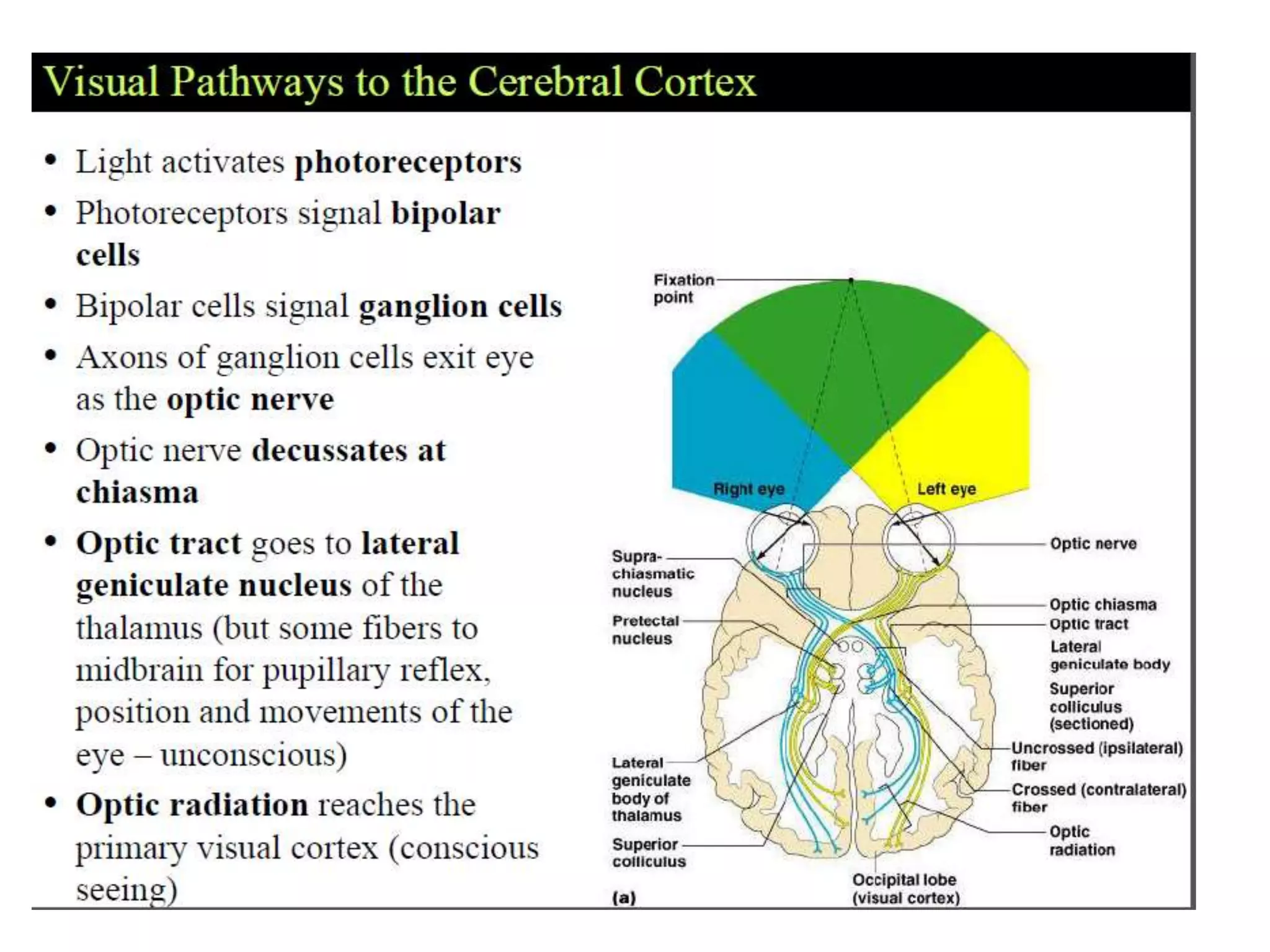
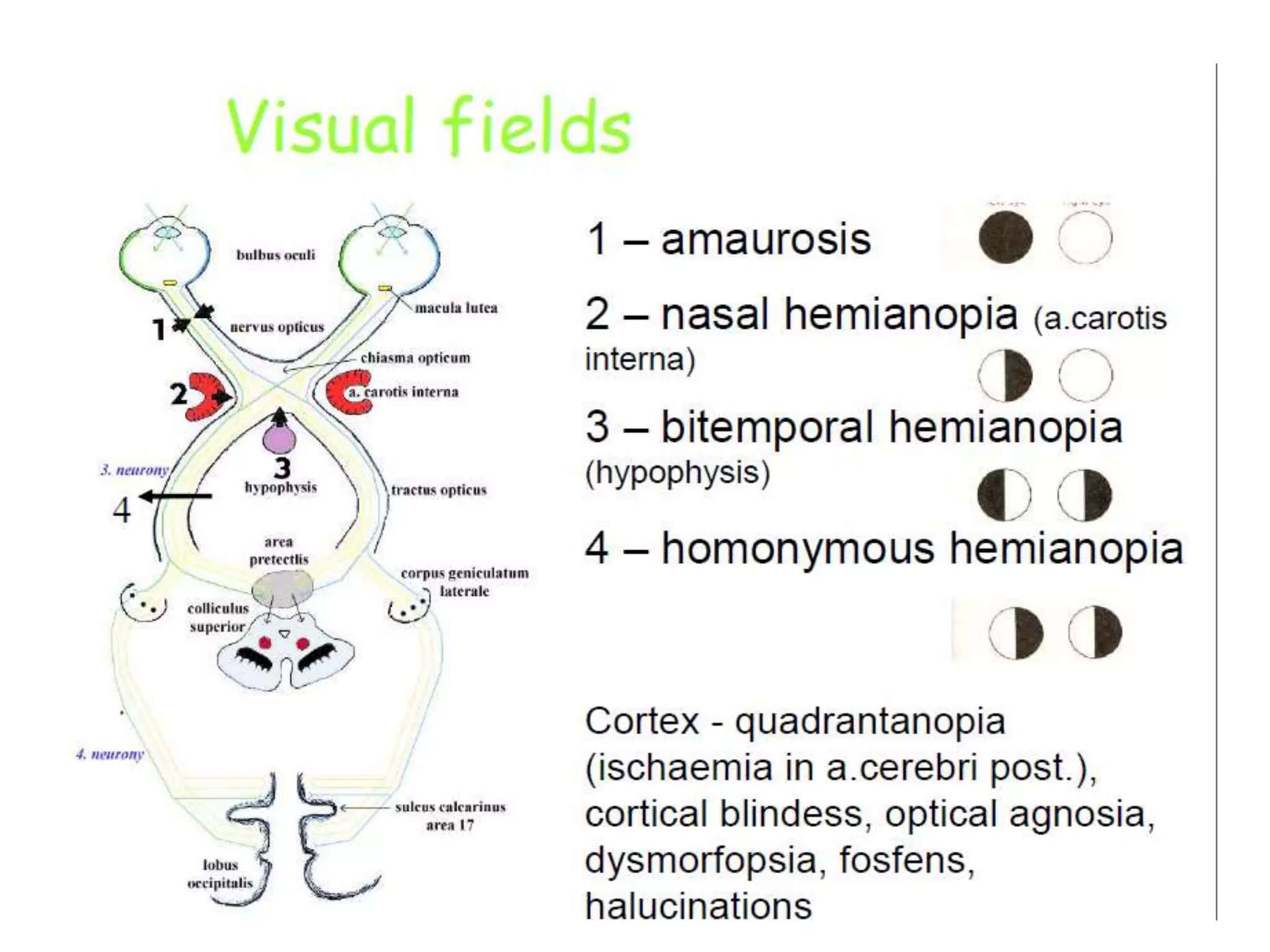
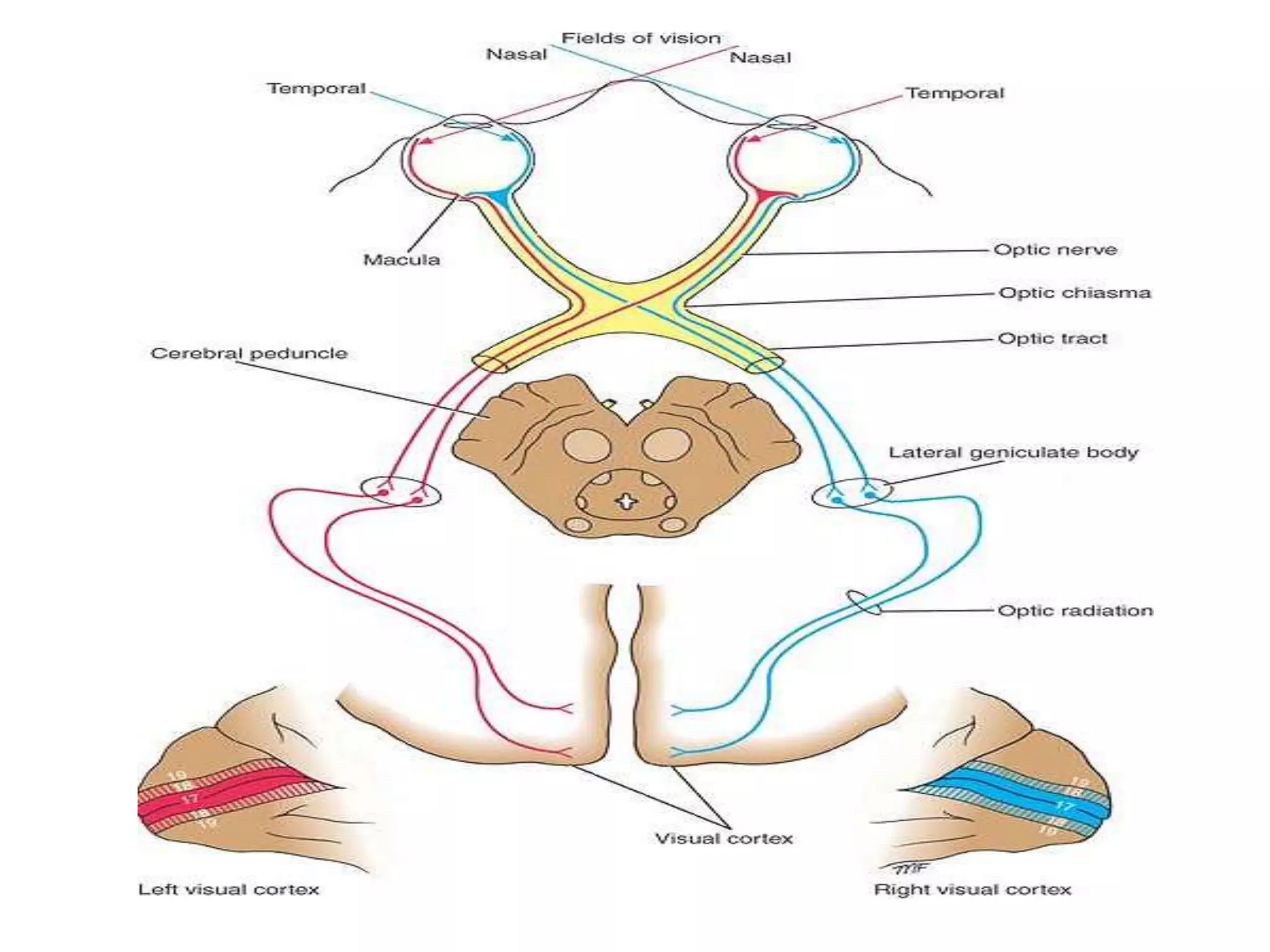
This document provides an overview of the visual pathway from the eye to the primary visual cortex. It describes the key structures and cell types involved including the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus, optic radiations, and striate cortex. The retina contains rods and cones that convert light signals to neural signals relayed by the optic nerve. The optic chiasm allows for decussation of fibers so that the left visual field is processed in the right hemisphere and vice versa. The lateral geniculate nucleus acts as a relay station and contains magnocellular, parvocellular, and koniocellular cells before projections reach the primary visual cortex via the optic radiations