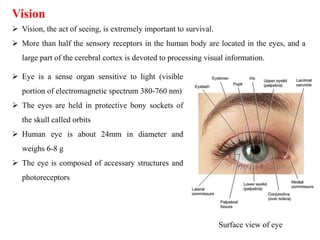
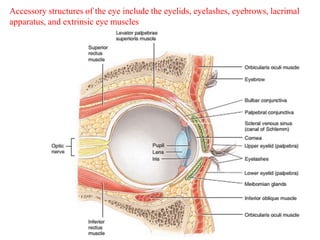
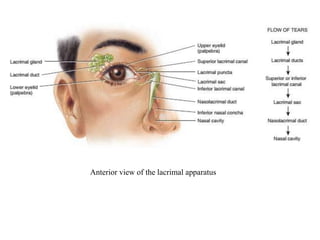
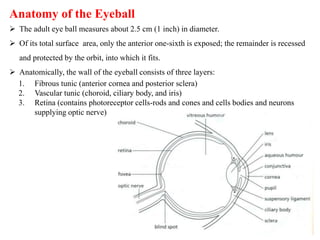
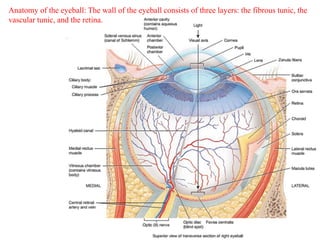
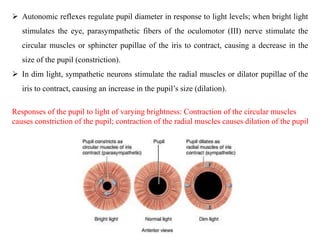
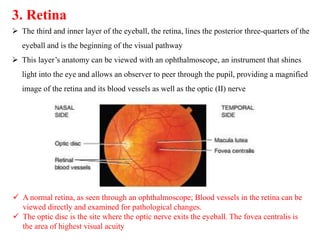
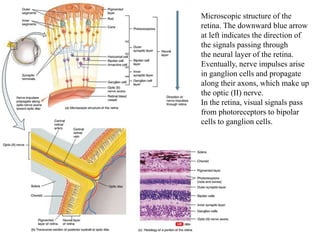
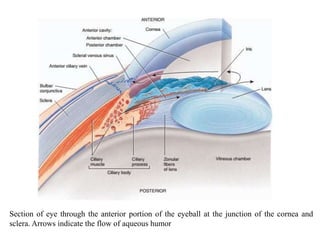
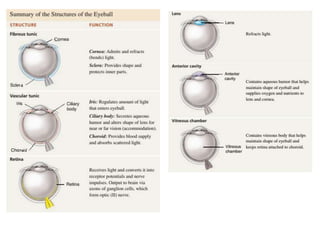
The eye is composed of three layers - the fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, and retina. The fibrous tunic includes the sclera and transparent cornea. The vascular tunic contains the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. The retina lines the inside of the eye and contains light-sensitive rod and cone cells. Light passes through the cornea and lens and strikes the retina, where it is converted to nerve signals sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The iris controls the size of the pupil to regulate light entry. Various structures work together to focus light and maintain the eye's shape and pressure.