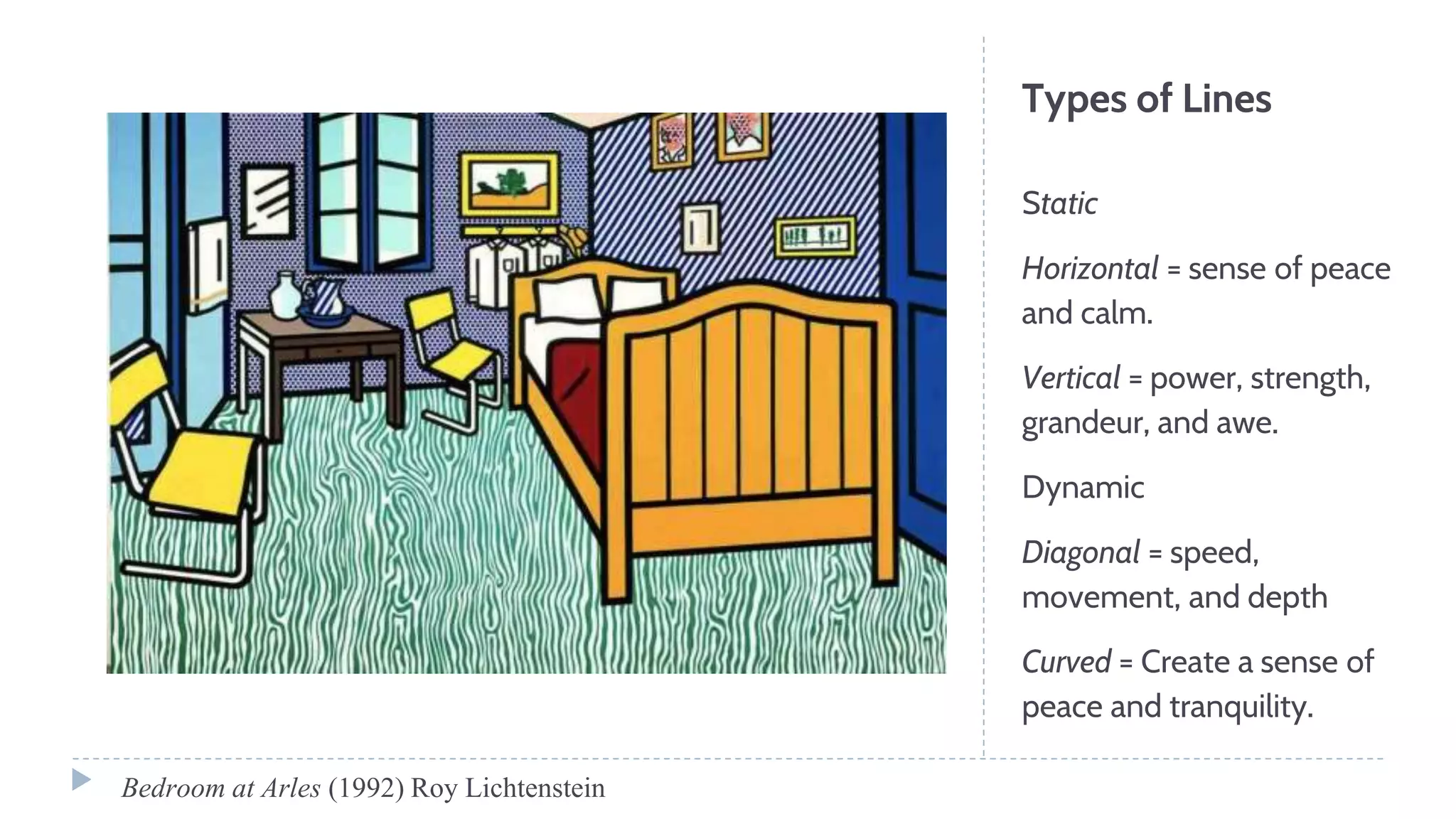
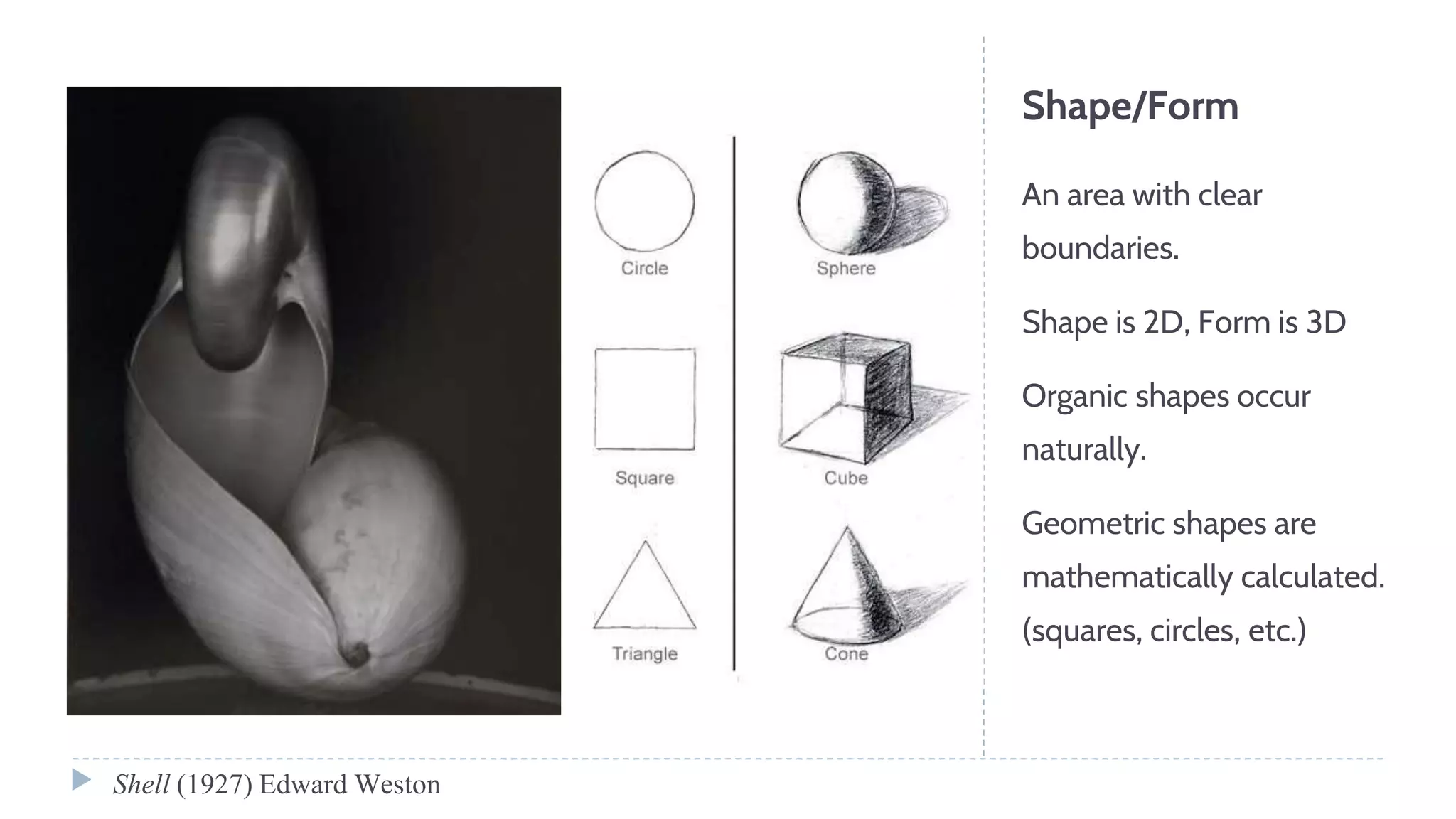
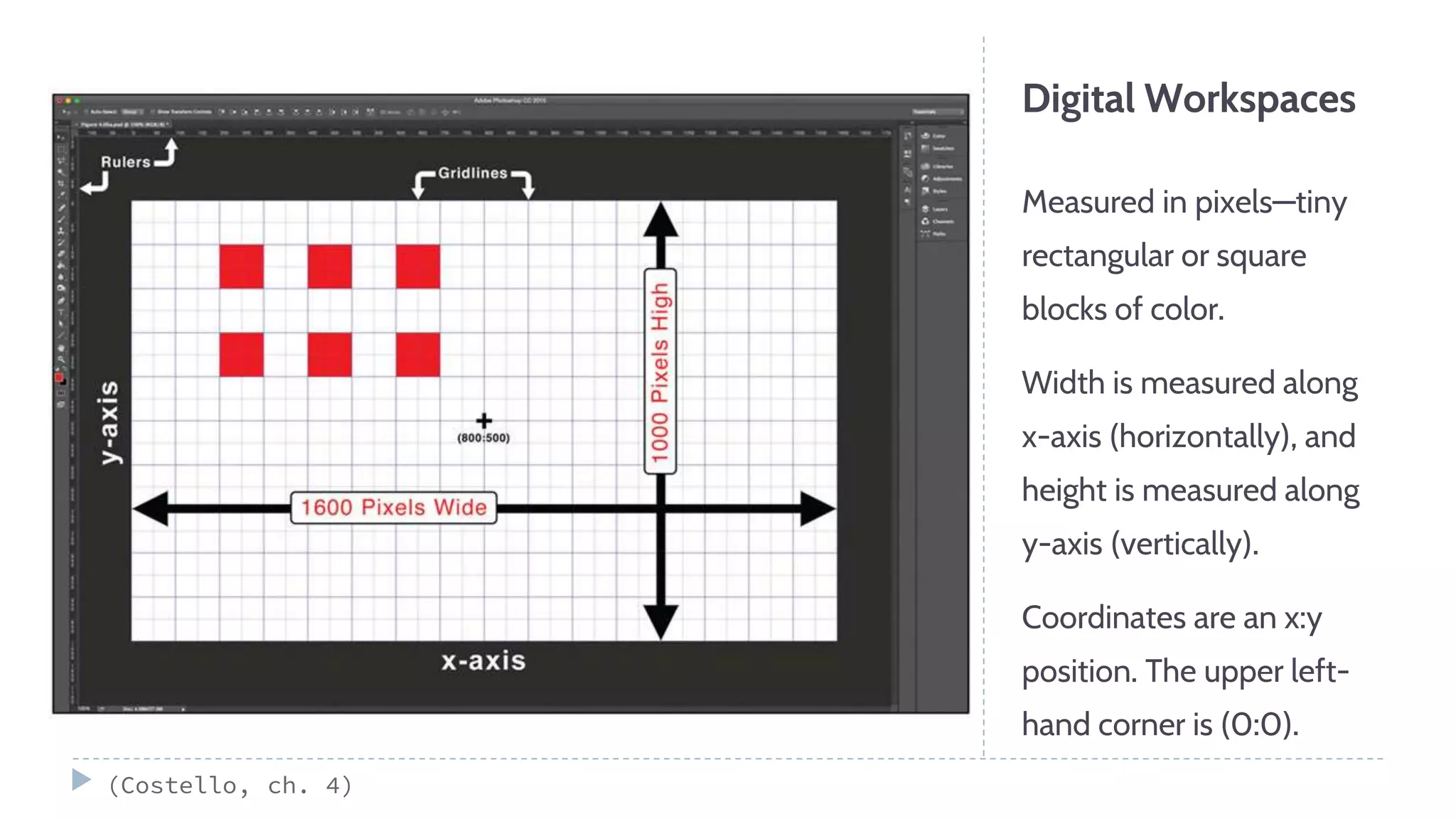
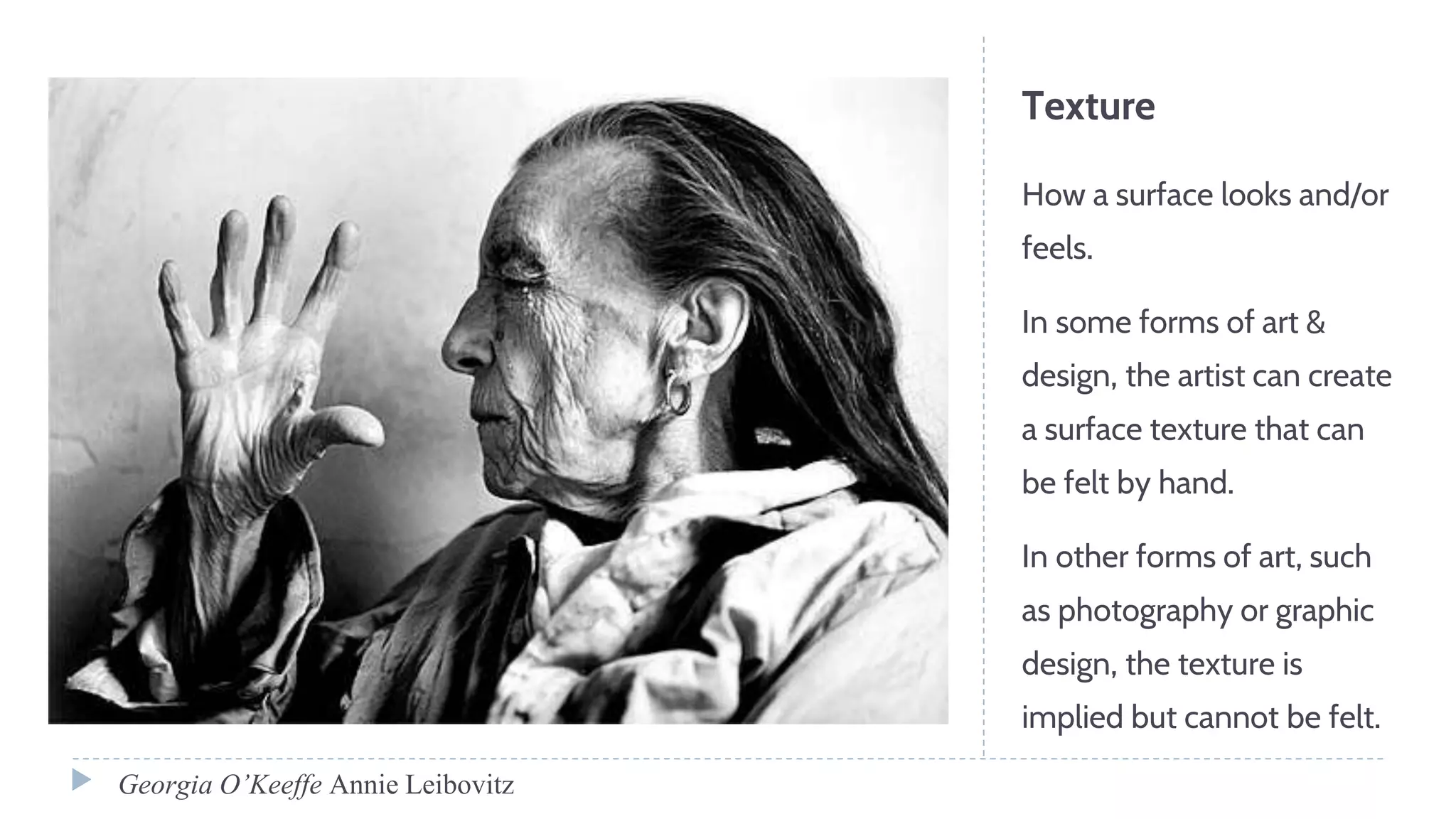
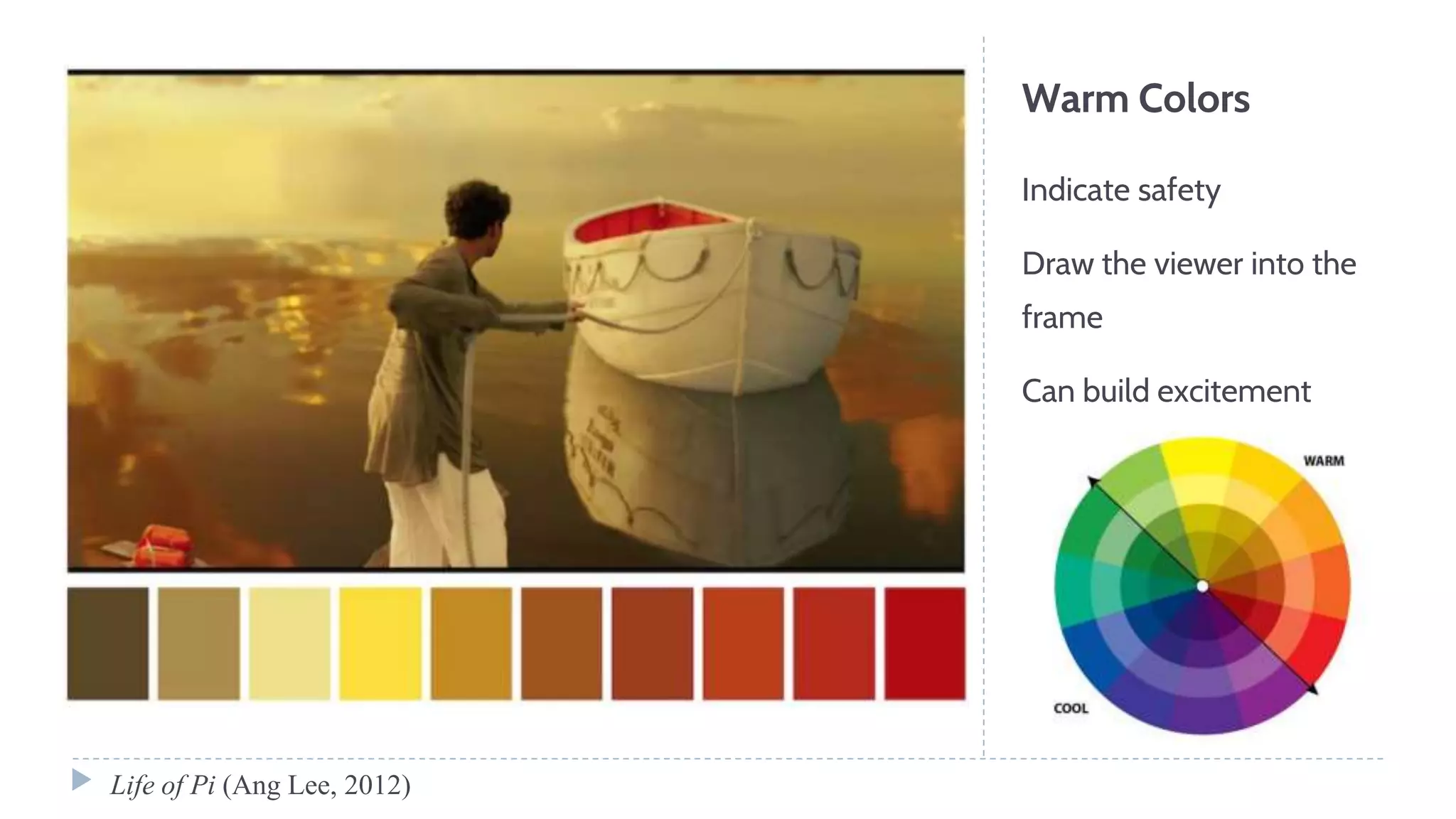
The document discusses various visual elements of design including line, shape, space, texture, value, and color. It defines different types of lines such as static, dynamic, and leading lines. It explains the differences between shapes and forms, as well as positive and negative space. The document also covers texture, value, color theory including complementary, analogous, warm, and cool colors.