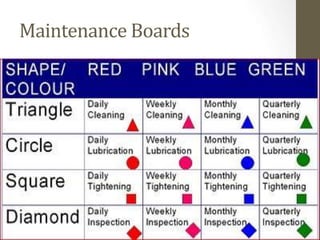
Visual management and control techniques use visual displays and controls to share important information with employees quickly and guide their actions. Examples of visual management include color-coded pipes and wires, shadow boards for tools and parts, indicator lights, and workgroup display boards showing metrics and procedures. The benefits are that visual tools express information in a way that can be understood by all, help keep production running smoothly and safely, and can help prevent mistakes. A key example is an Andon board, which notifies management of quality or process problems using signal lights to show the workstation having an issue.