Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
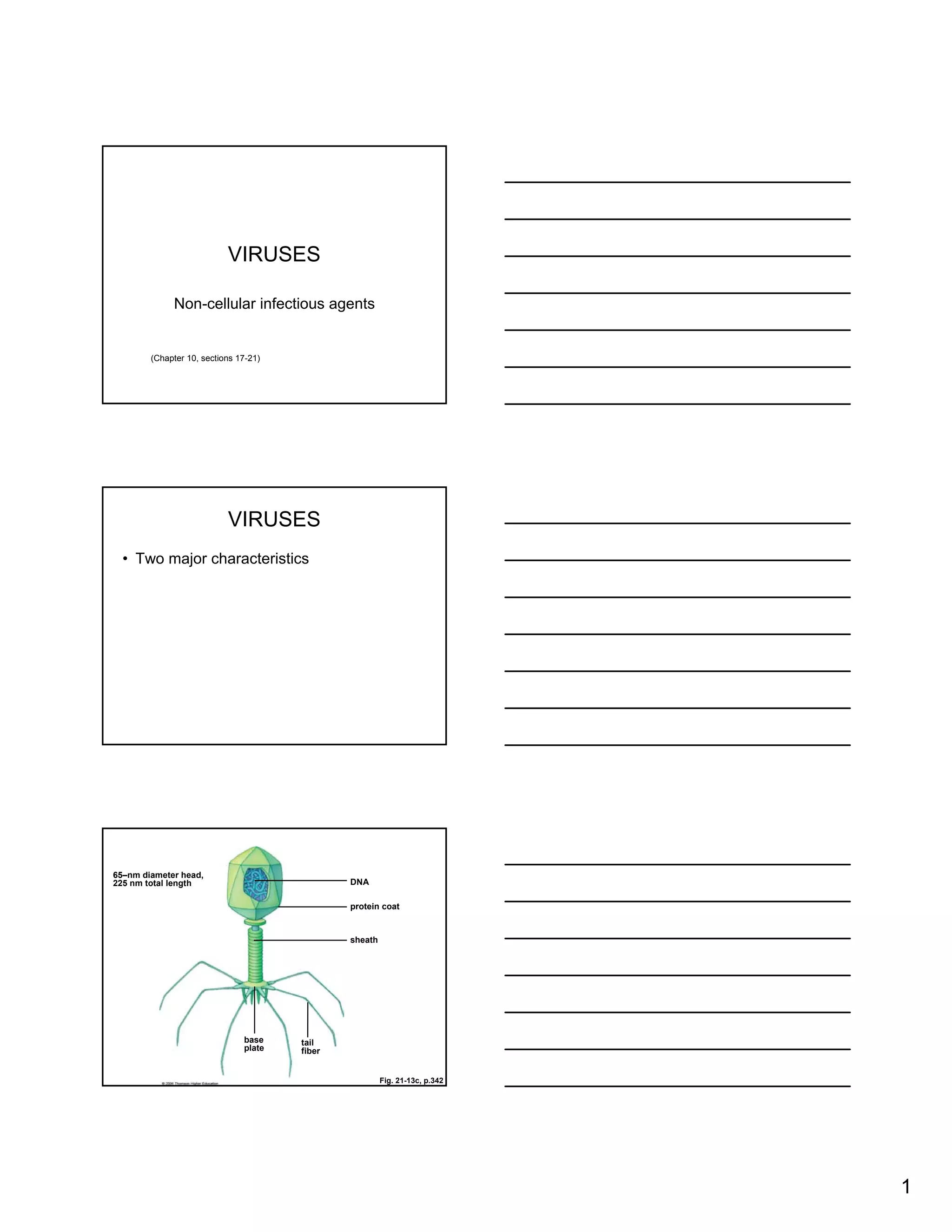
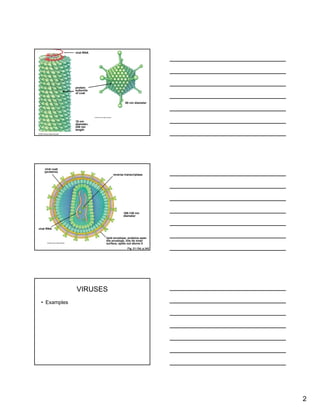

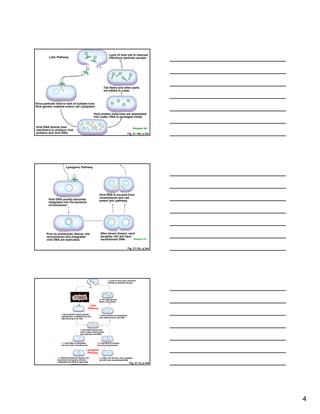




Viruses are non-cellular infectious agents that have two main characteristics: genetic material and a protein coat. Examples include bacteriophages that infect bacteria, as well as viruses like HIV, SARS, and Ebola. Viruses can multiply through either a lytic or lysogenic pathway. They evolve along with their hosts, and new threats can emerge from pathogens like Ebola, drug-resistant strains, and foodborne illnesses such as Salmonella.







