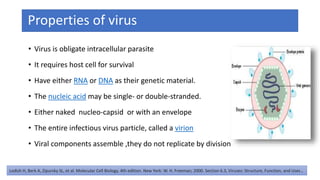
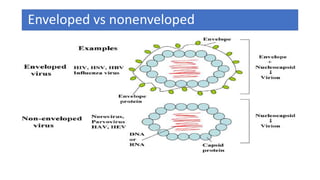
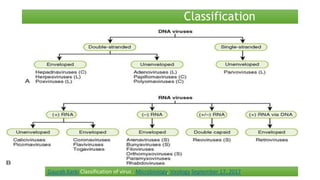
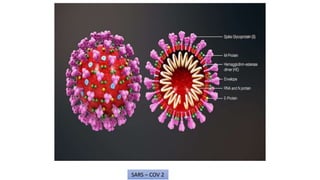
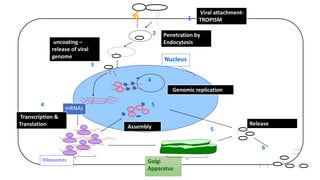
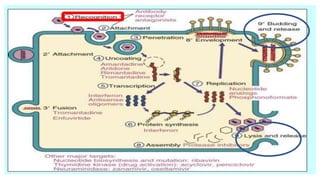
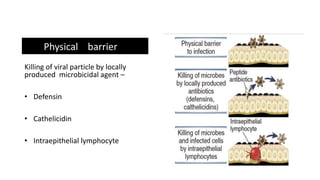
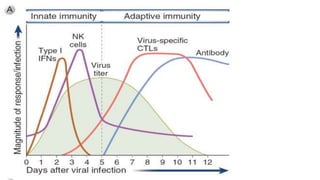
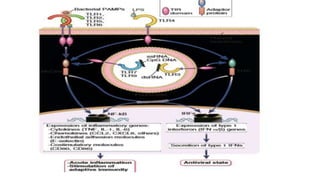
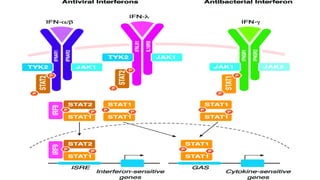
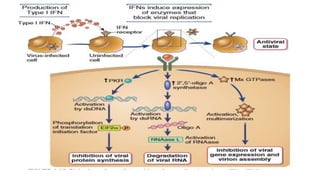
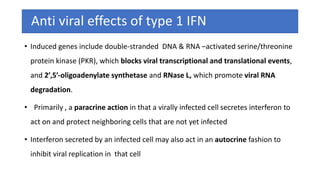
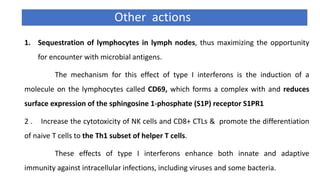
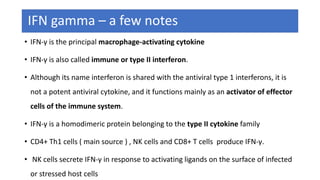
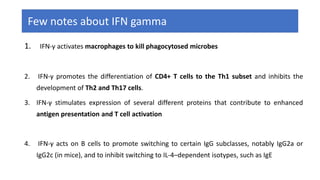
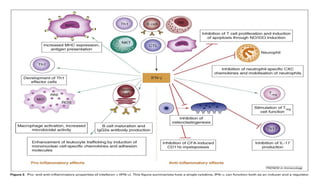
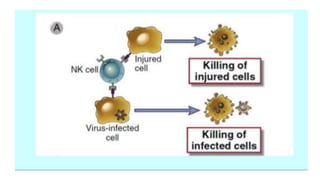
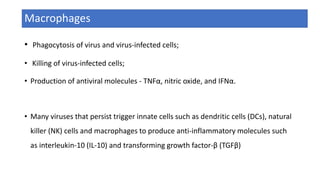
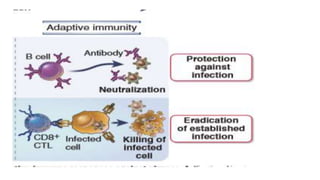
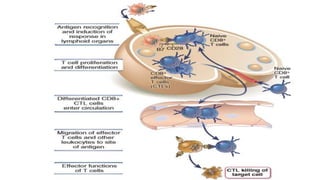
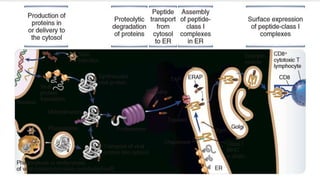
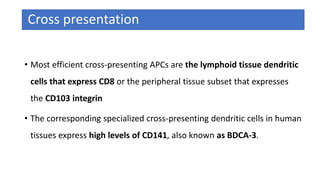
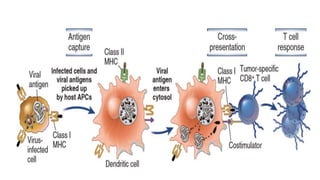
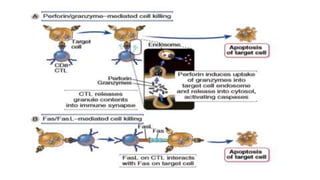
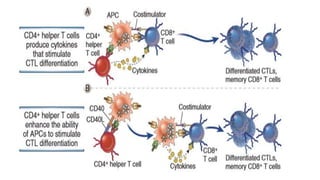
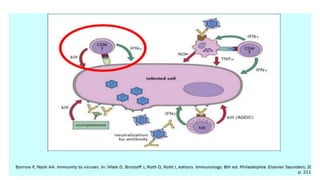
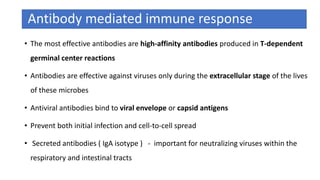
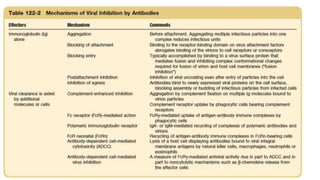
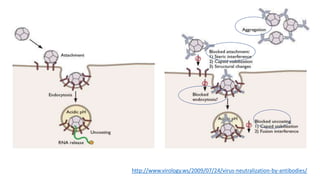
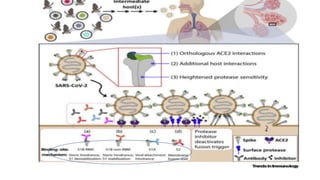
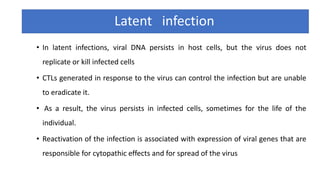
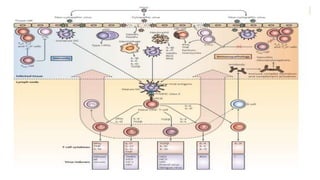
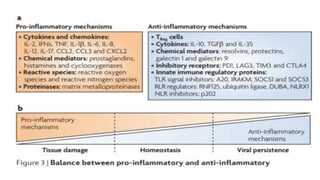
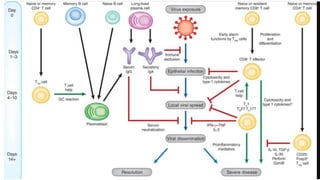
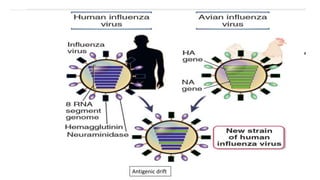
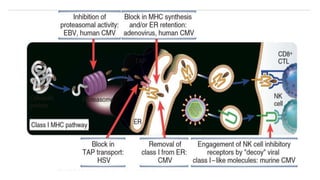
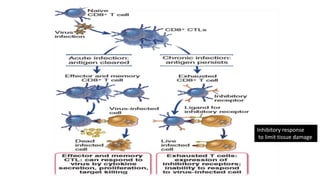
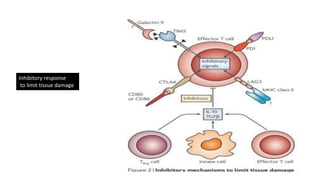
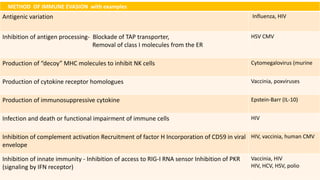
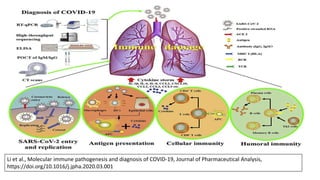
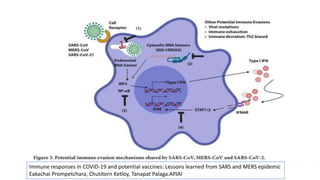
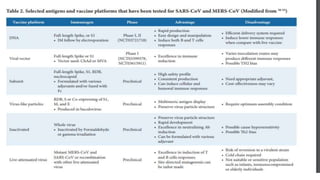
The document discusses the immune response to viruses. It begins by describing viral properties and replication cycles. The innate immune response includes epithelial barriers, interferons, natural killer cells, and macrophages. Adaptive immunity involves antigen presentation, CD4+ T cell help, CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity, and antibody production. Viruses employ various evasion strategies like antigenic variation. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis is still under research but involves interfering with interferon induction and signaling pathways. The take-home message is that immune responses aim to control viral replication through innate effectors and generate adaptive memory, while viruses evolve ways to evade these defenses.