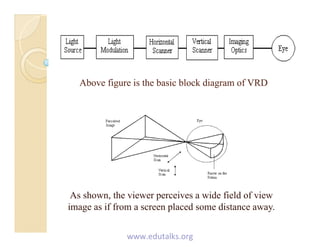
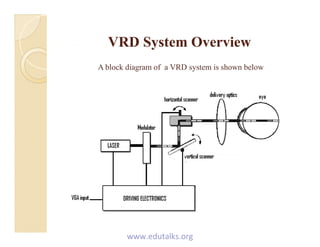
Virtual retinal display (VRD) is a novel display technology that scans light directly onto the retina to create high resolution images without the need for a screen. It works by using light-emitting diodes or lasers to project pixelated images in raster patterns onto the retina. Key advantages of VRDs include their small size, high resolution, wide field of view, and potential applications in areas like medicine, aviation, and augmented reality. Future developments may make VRDs more compact and affordable for widespread use.