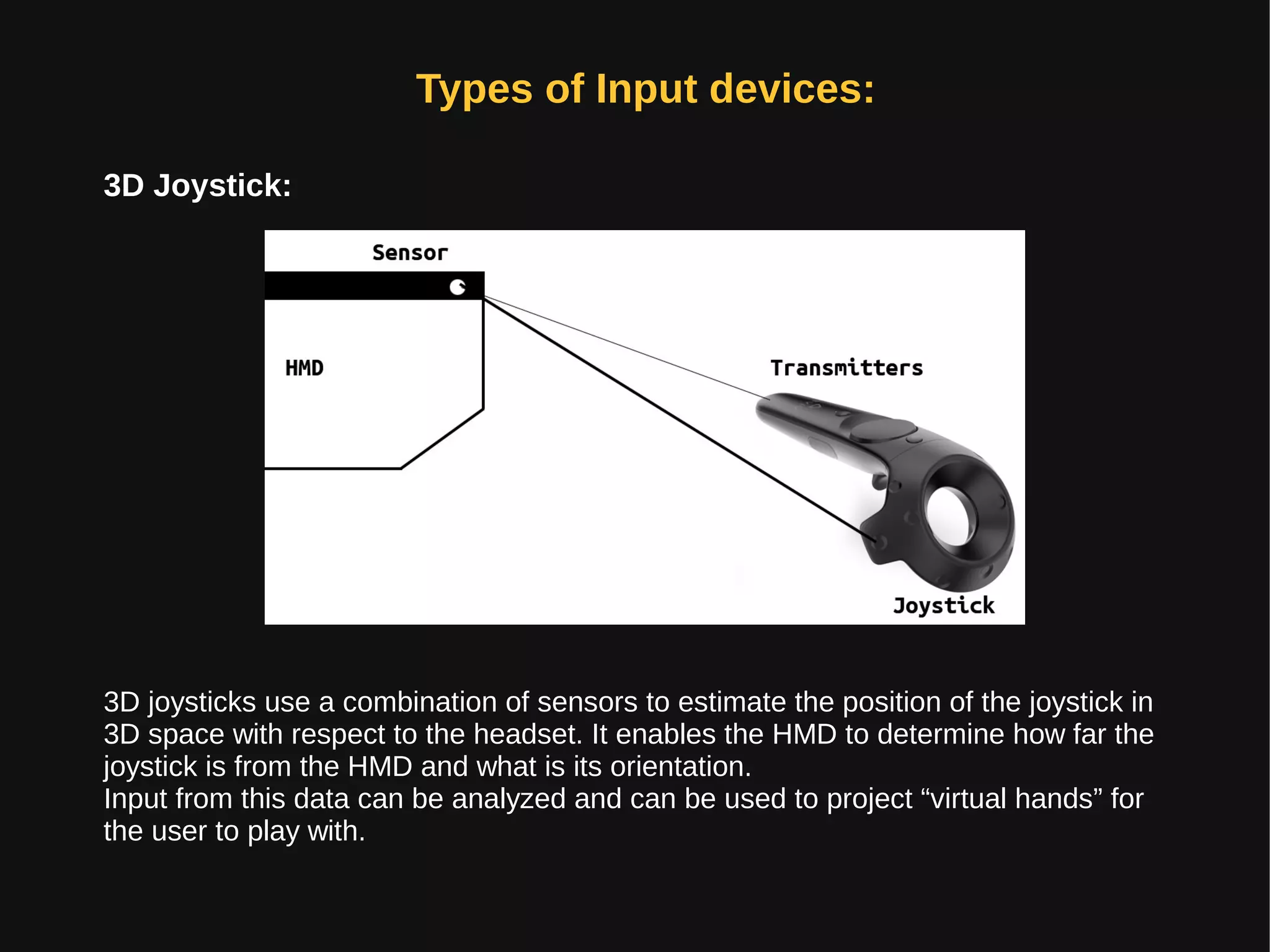
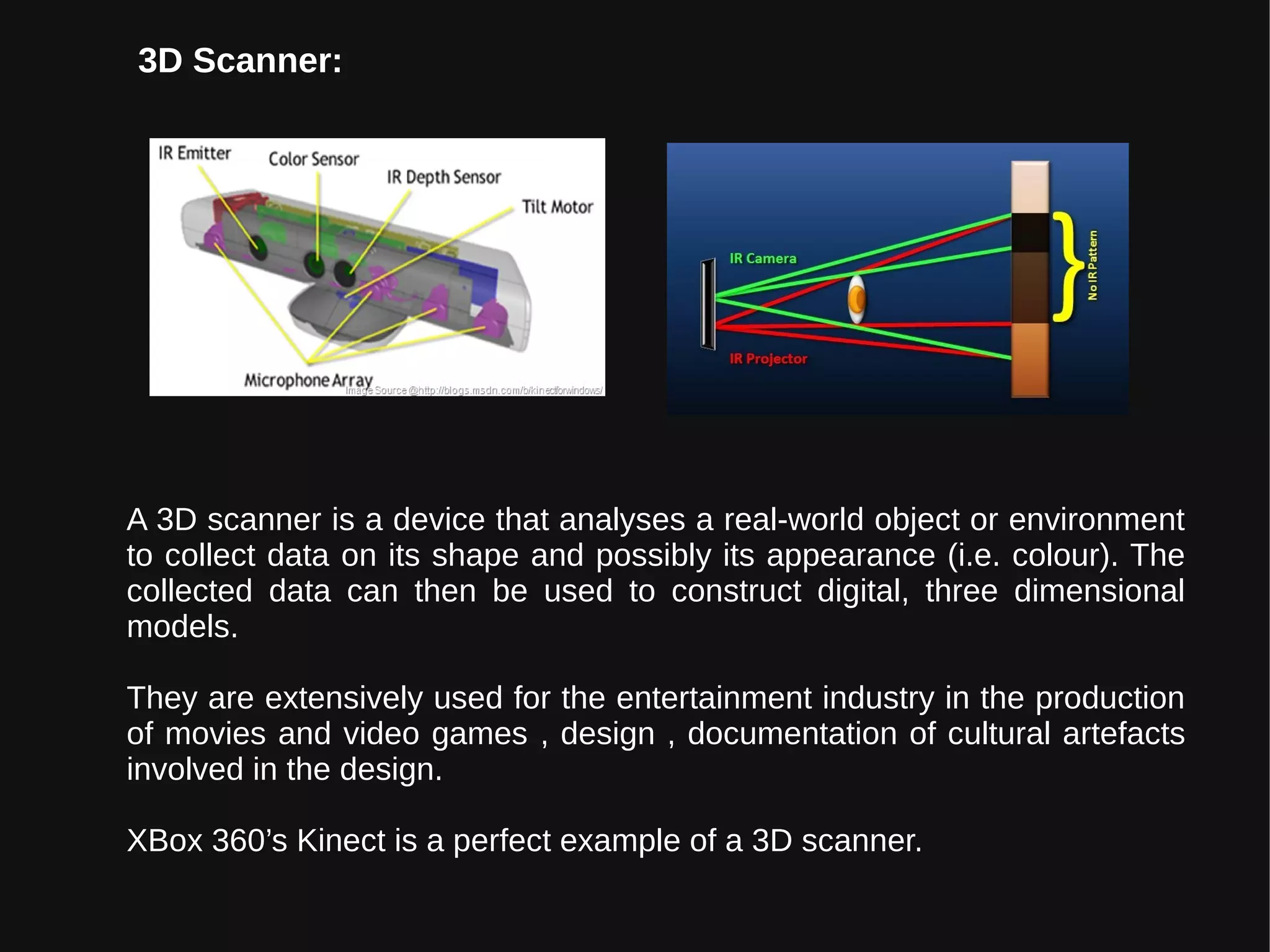
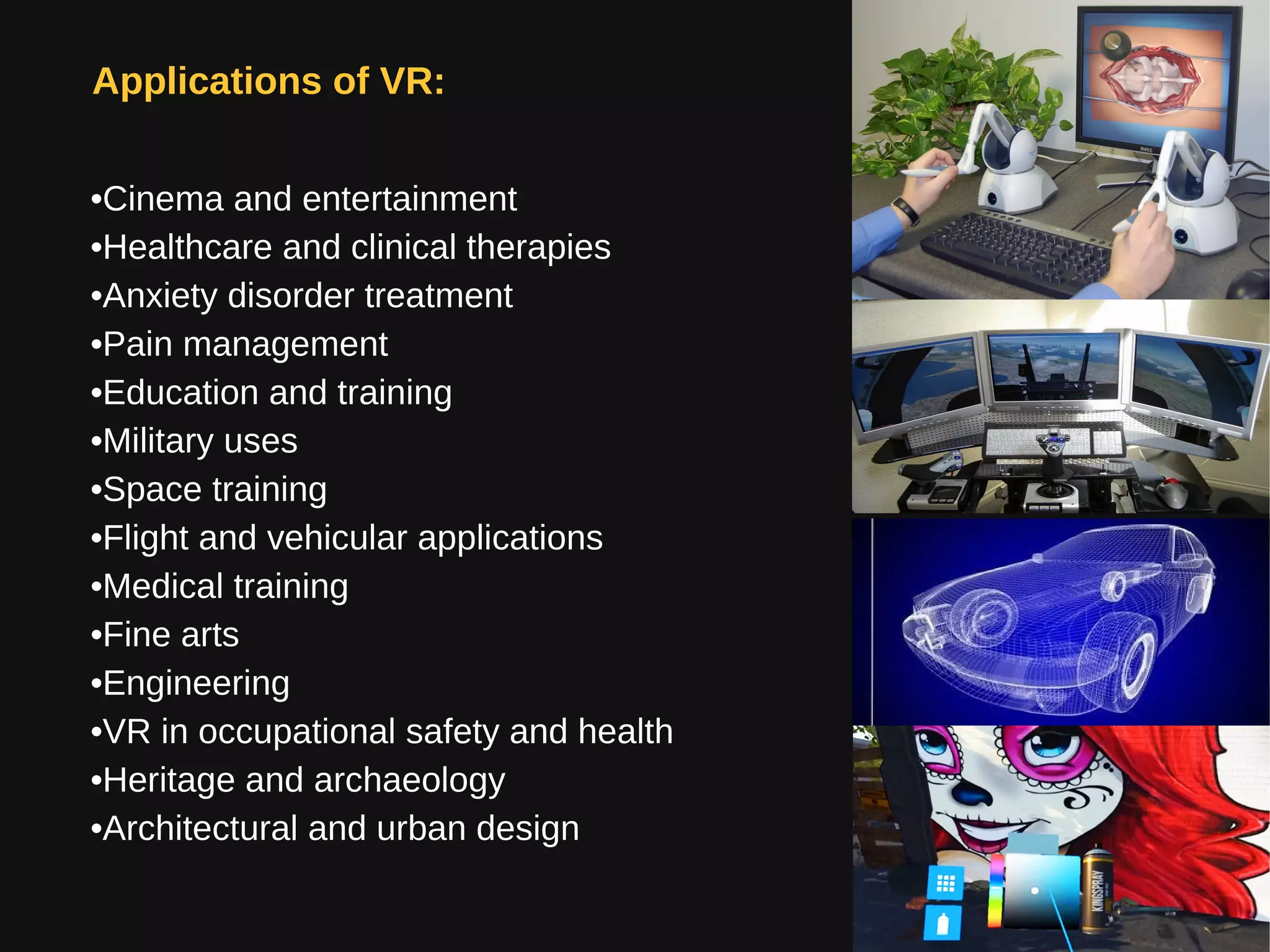
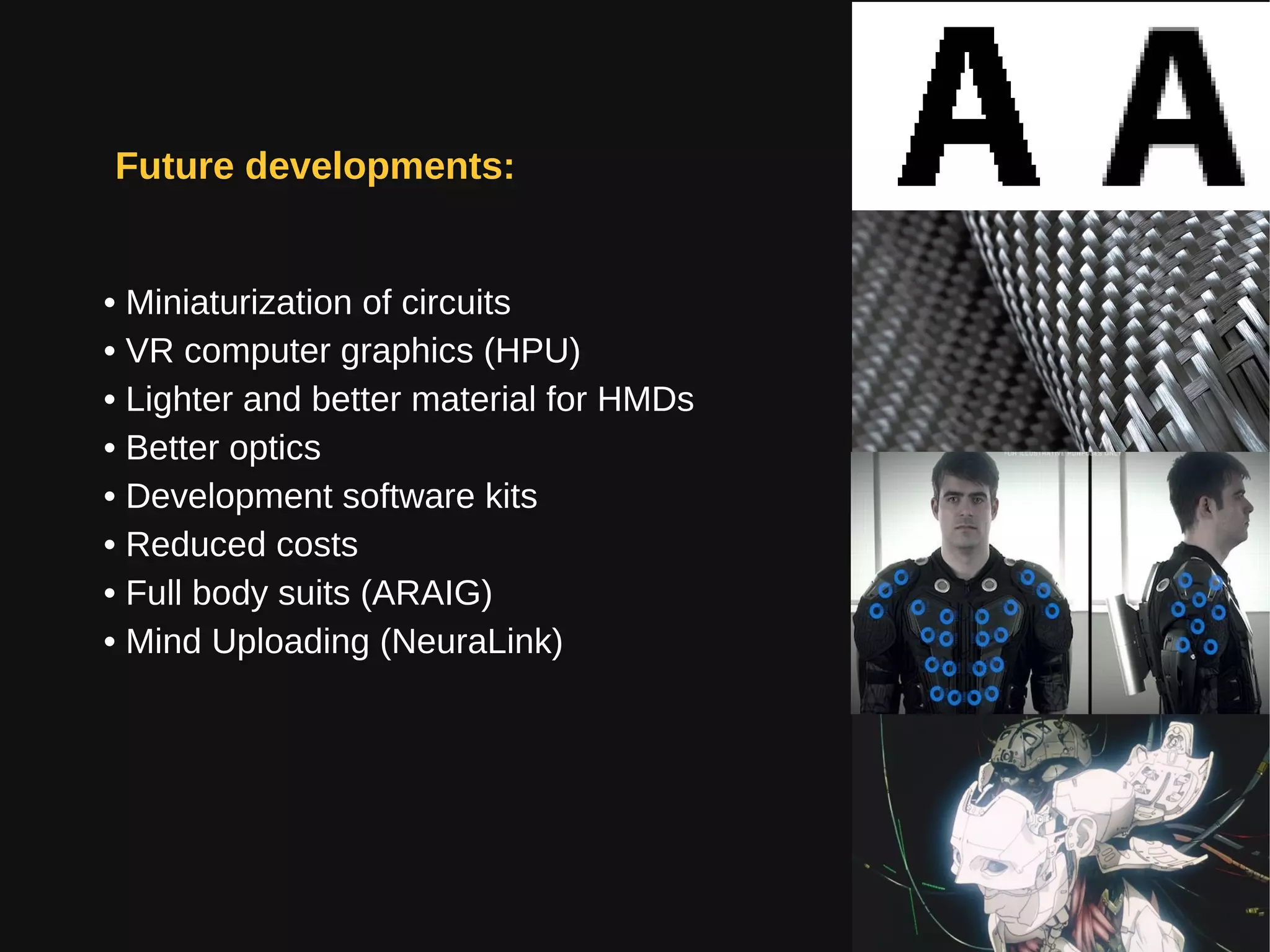
Virtual reality (VR) immerses users in computer-generated environments crafted from human creativity and imagination, made possible by advancements in technology. Key components of VR systems include head-mounted displays (HMDs), input devices like data gloves and joysticks, and a range of applications in various fields such as healthcare, education, and entertainment. With the industry projected to grow significantly, VR poses health hazards that necessitate careful use until further research and advancements in safety are achieved.