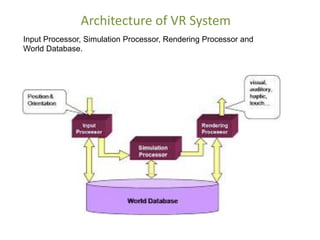
This document presents an overview of virtual reality (VR), including its history, types, technologies, architecture, and applications. VR enables immersive experiences in simulated environments and has potential uses in entertainment, medicine, manufacturing, and education. Current challenges include issues like cybersickness, high costs, and integration difficulties among VR applications.