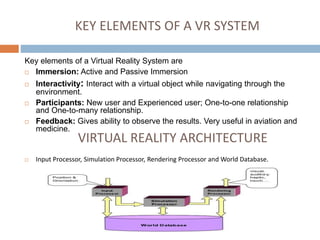
This document provides an overview of virtual reality including its definition, history, taxonomy, hardware, software, applications and future. It defines virtual reality as using computer modeling and simulation to interact with 3D environments. The history section describes early attempts at immersive viewing like Sensorama from the 1960s. It also outlines the key elements of a VR system like immersion, interactivity and feedback. Applications discussed include using VR for training in fields like military, aviation and medicine. The future of VR is presented as advancing towards holograms, augmented reality and more immersive head-mounted displays.


![VITARAMA AND CINERAMA
VITARAMA: 11 Projectors and
dome shaped screen.
CINERMA: Simplified version of
Vitarama. Used as wide-
screen film format in 1939. It used three
projectors onto a deeply
curved screen, subtending 146°
of arc.
SENSORAMA
SENSORAMA: Built in 1962 and was
aimed at 4 senses. [See, Hear, Feel &
Smell] .But the machinery ended up
being too complex.
THE ULTIMATE DISPLAY: For the first
time, Virtual reality was experienced
via a Head-Mounted Display which
was created by Ivan Sutherland in
1965. It was the biggest break
through.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualrealitynew-221123115313-0ce2b38b/85/Virtual_Reality_New-pptx-3-320.jpg)

![TECHNOLOGIES USED [SOFTWARE]
Virtual Reality Modeling Language(VRML):
It is a standard language to represent 3D graphics within the World
Wide Web.
Allows the creator to specify images and the rules for their display.
Aspects of virtual world display, interaction and internetworking
can be specified using VRML without being dependent on special
gear like HMD.
Software packages:
Multiverse – Platform for Massively Multiplayer Online Games.
Virtual Reality Studio – Creates virtual world in Freespace.
Sense8 World Tool Kit (WTK)
Autodesk Cyberspace Development kit – Runs VR programming
from keystroke commands to glove-helmet interaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualrealitynew-221123115313-0ce2b38b/85/Virtual_Reality_New-pptx-5-320.jpg)