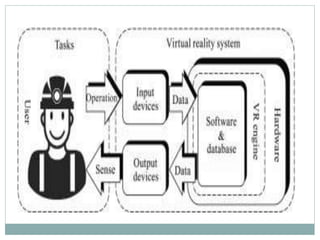
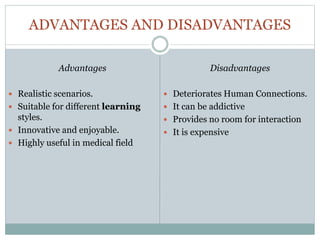
Virtual reality (VR) creates a simulated environment that immerses the user. It works by tracking a user's movements and updating the virtual world accordingly. While early versions date back to the 1950s, commercial VR development began in the 1980s. VR can be non-immersive, augmented, or fully immersive. It has applications in gaming, business, education, engineering, medicine, and entertainment. Potential advantages include realistic training scenarios and innovative learning, while disadvantages include cost and reduced human interaction.