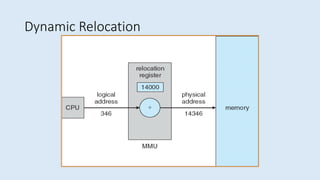
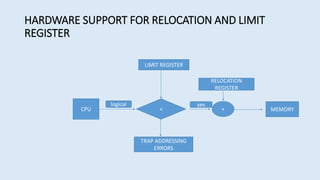
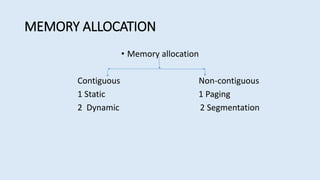
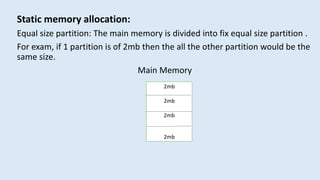
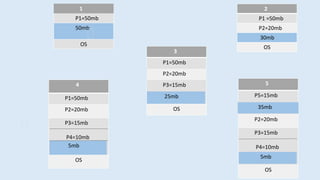
The document discusses memory management in operating systems. It defines logical and physical addresses and how a memory management unit (MMU) maps logical addresses to physical addresses using relocation registers. It describes dynamic relocation and hardware support for relocation and limiting addresses. It also discusses memory allocation techniques like paging, segmentation, and swapping. It concludes that memory management is complex but MMUs efficiently allocate and deallocate memory as needed.