This document discusses static import and access control in Java. It explains that static import allows importing static members without specifying the class name. This improves readability. Access specifiers like private, default, protected, and public define the scope and visibility of class members. Private members can only be accessed within the class, while public members can be accessed anywhere. The document provides examples to illustrate static import and how access specifiers work.



![Static Import
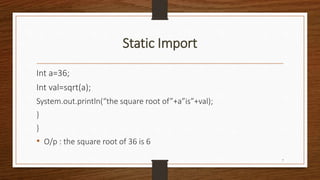
For Example:
class A
{
Public static void main(String a[])
{
Int a=36;
Int val=Math.sqrt(a);
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaala1-170828133023/85/Static-Import-and-access-modifiers-4-320.jpg)
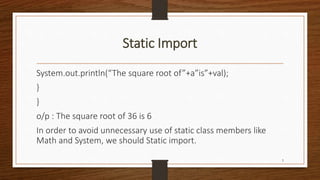
![Static Import
Import static java.lang.System.out;
Import static java.lang.Math.sqrt;
class A
{
Public static void main(String a[])
{
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaala1-170828133023/85/Static-Import-and-access-modifiers-6-320.jpg)



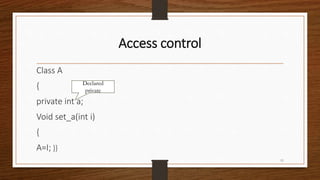

![Access control
C=a*b;
System.out.println(“mul is”+c);}}
class xyz
{
Public static void main(String a[])
{
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaala1-170828133023/85/Static-Import-and-access-modifiers-13-320.jpg)


