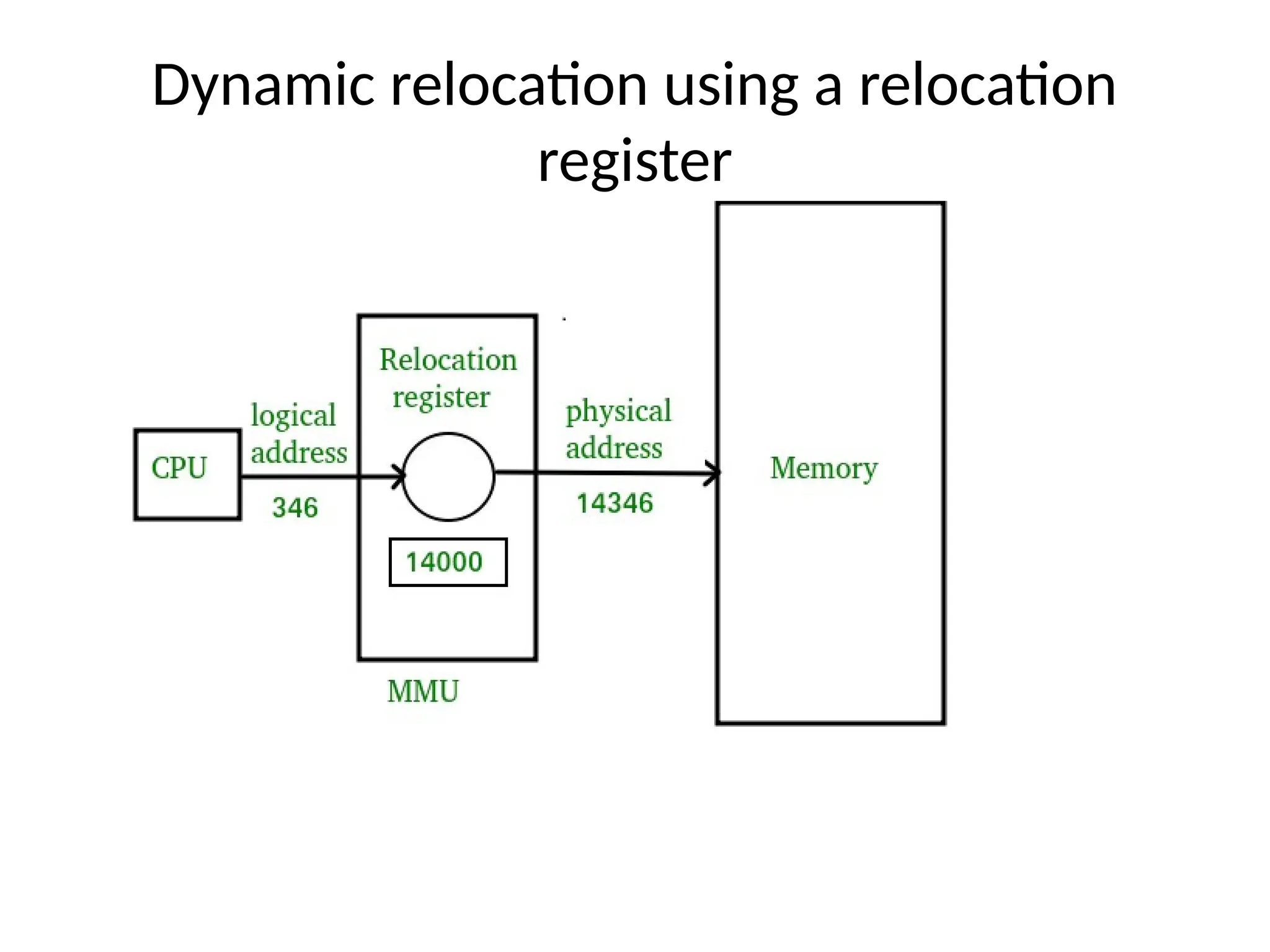
Memory Management in an operating system is the subsystem responsible for controlling and coordinating computer memory, assigning portions to processes when they need it, and freeing it for reuse when they’re done. Its goals are to maximize utilization, provide protection and isolation, and support efficient execution.
---
1. Key Responsibilities
Allocation & Deallocation
Assign memory regions to processes on load or request.
Reclaim memory on process termination or via explicit free calls.
Protection & Isolation
Prevent one process from accessing another’s memory.
Enforce read/write/execute permissions via hardware (MMU).
Sharing & Communication
Map shared libraries or IPC buffers into multiple address spaces.
Support copy‑on‑write to efficiently share pages until modified.
---
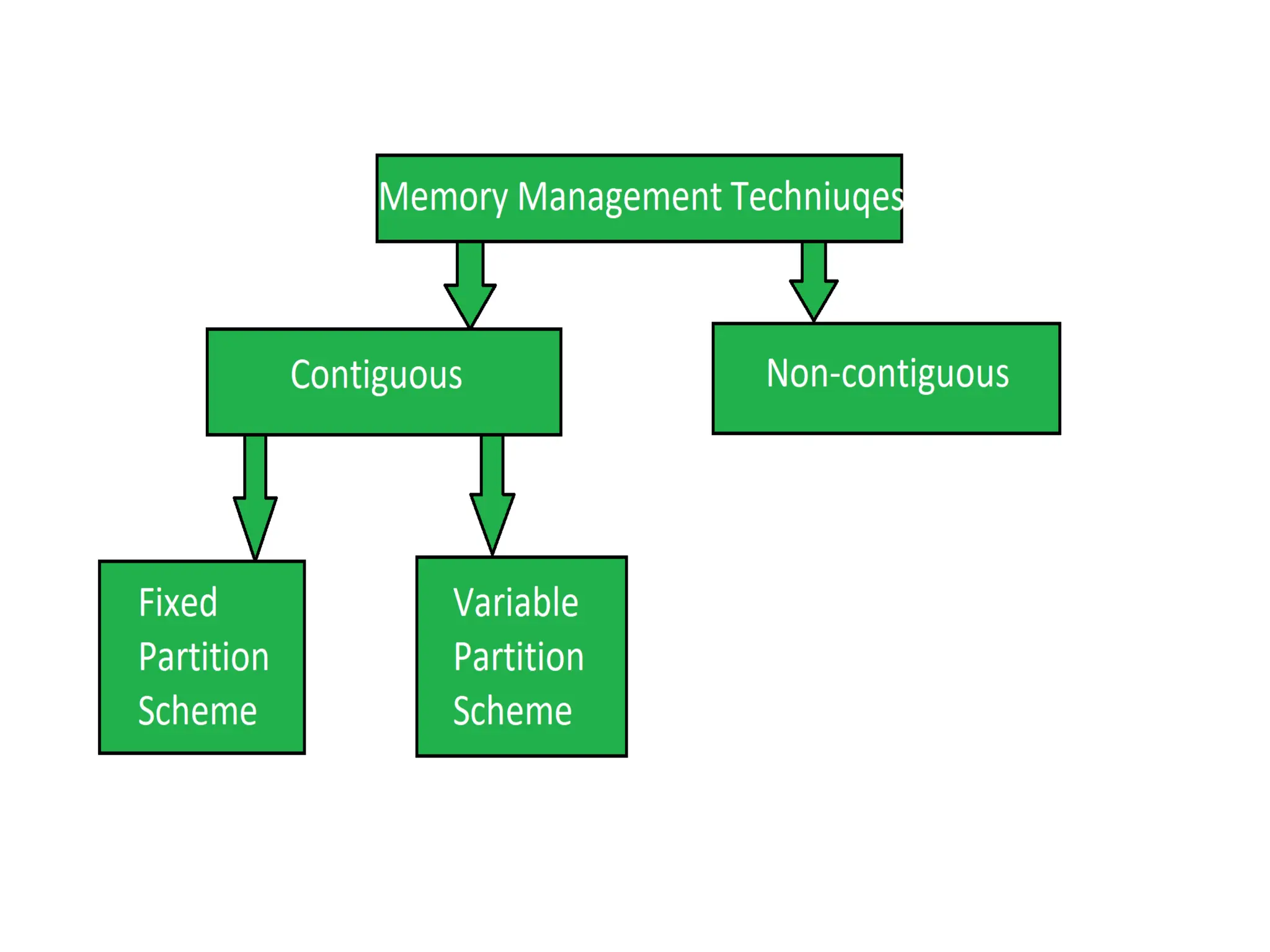
2. Allocation Strategies
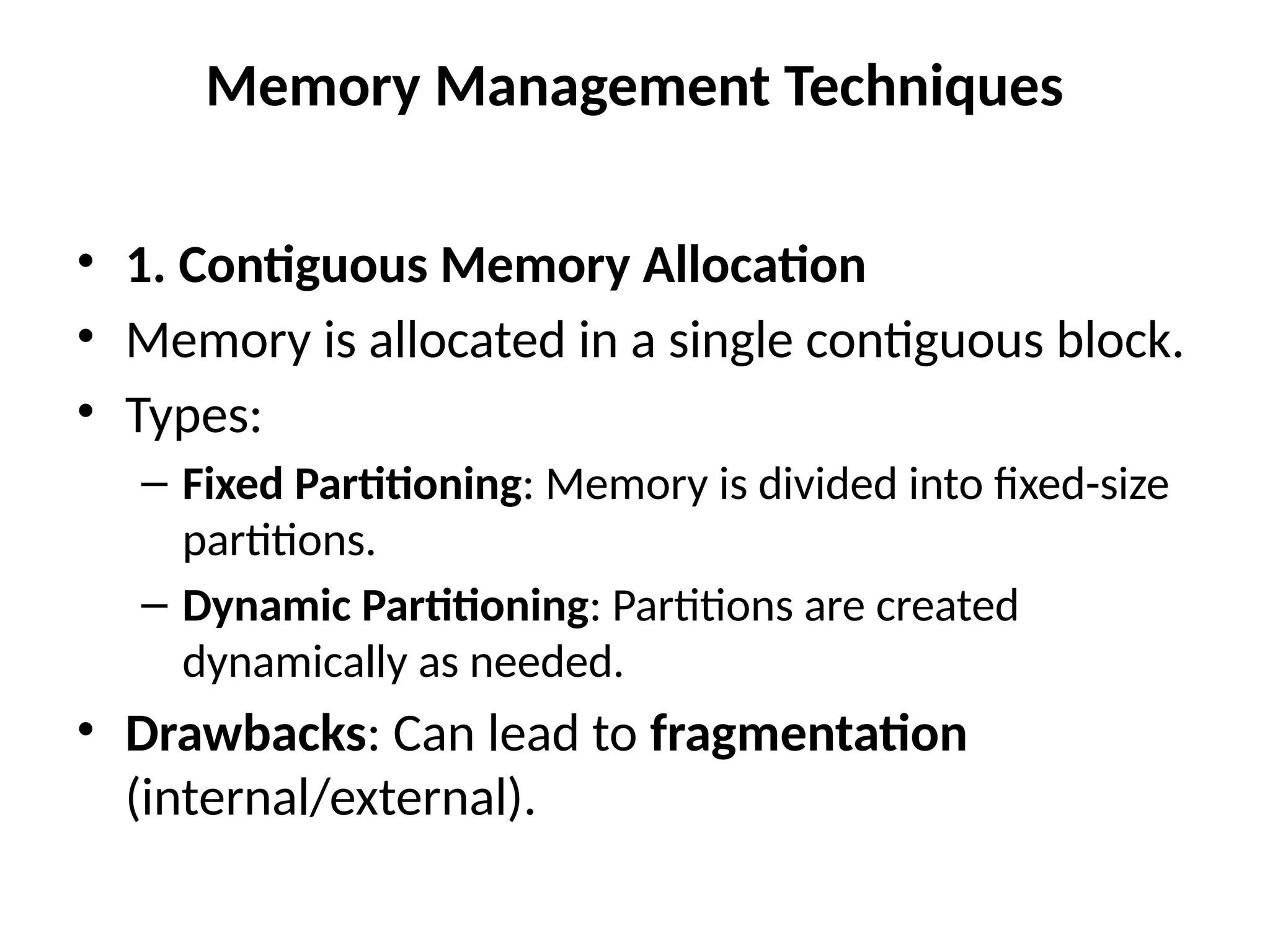
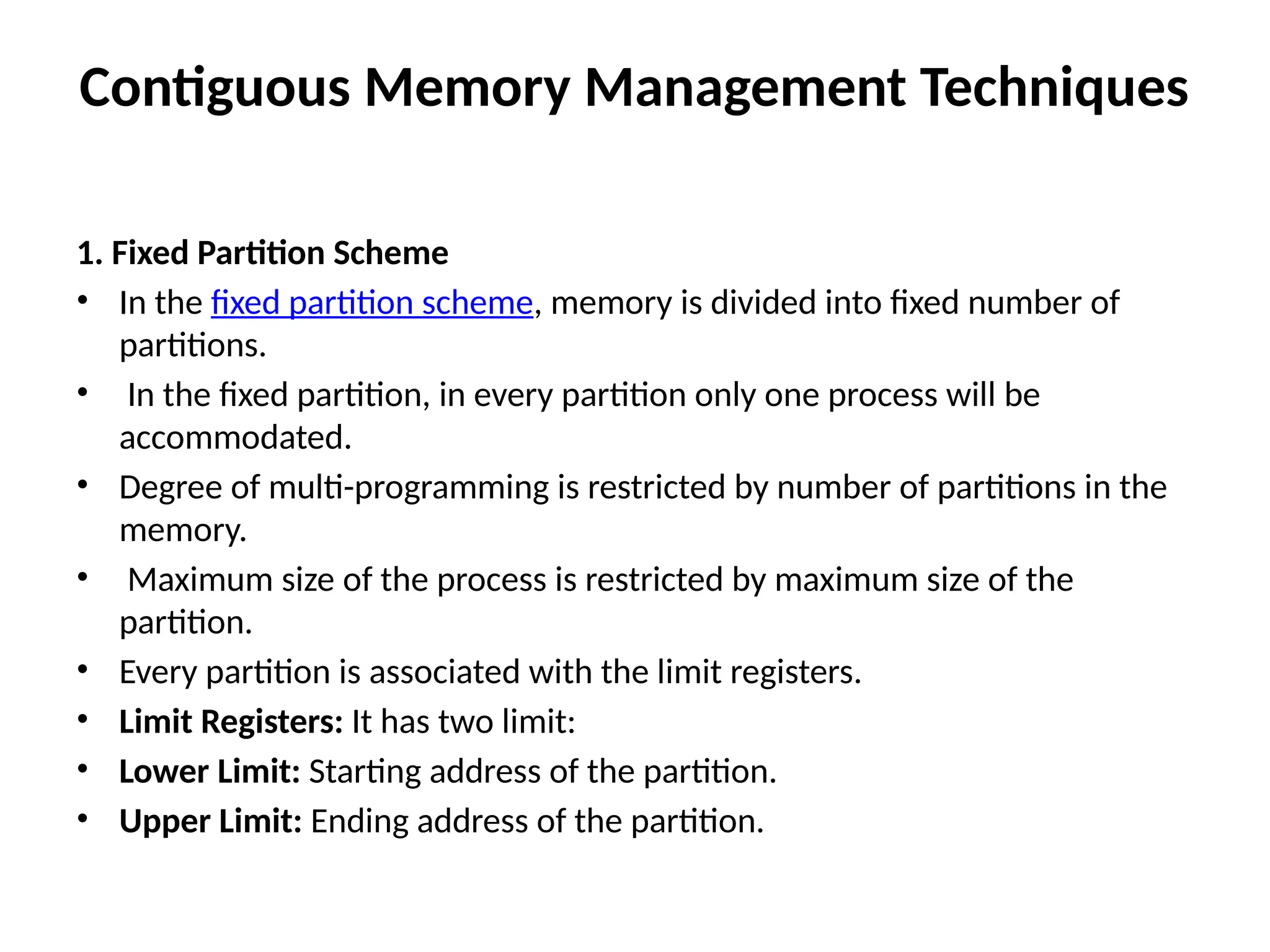
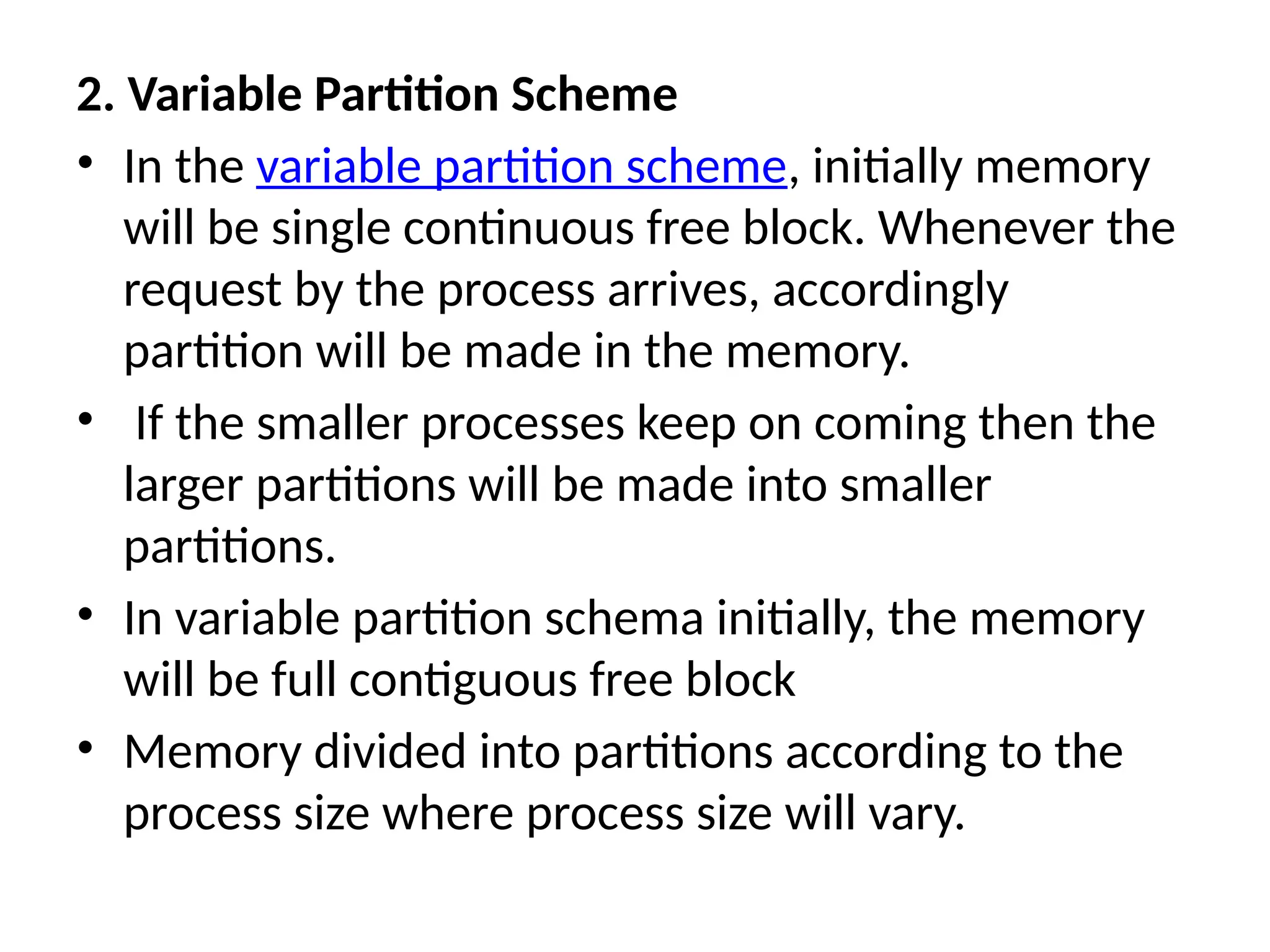
Contiguous Allocation
Fixed partitions: Memory divided into static regions; simple but inflexible.
Dynamic partitions: Fit variable‑sized segments via first‑fit, best‑fit, or worst‑fit; suffers external fragmentation.
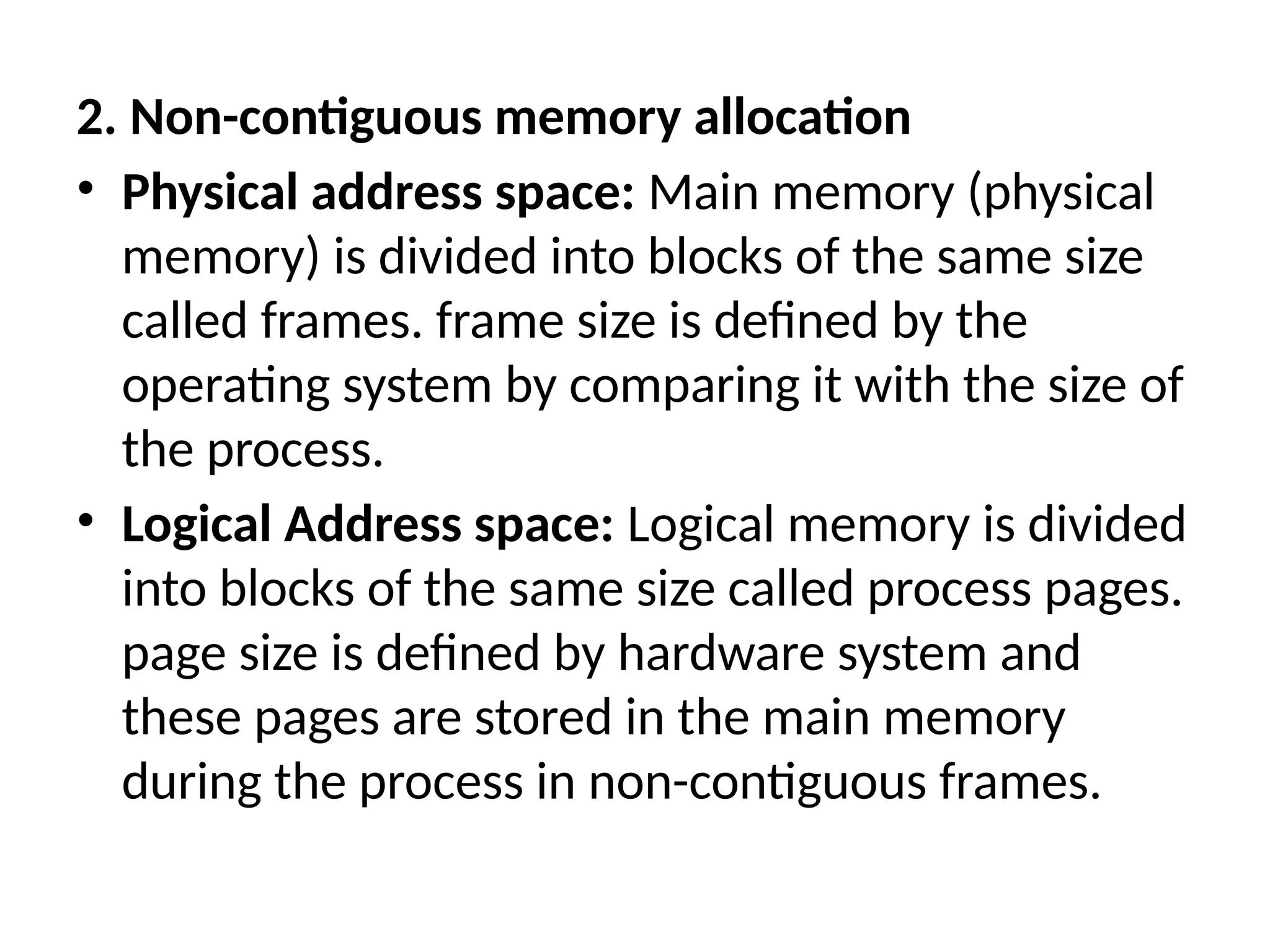
Non‑Contiguous Allocation
Paging: Breaks memory into equal‑sized frames (physical) and pages (logical). Page tables map pages→frames, eliminating external fragmentation.
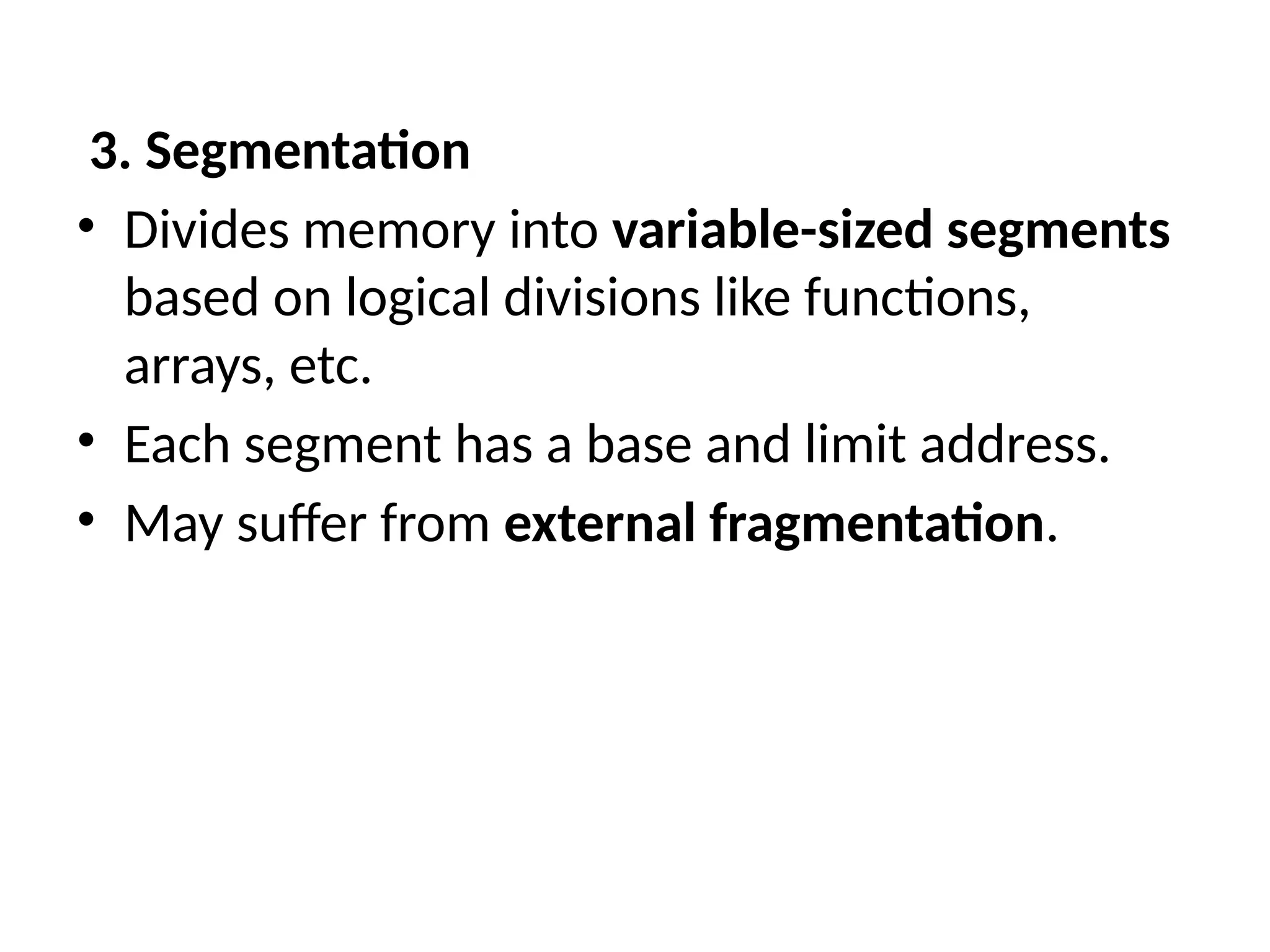
Segmentation: Divides programs into logical segments (code, data, stack) of varying length; supports protection per segment but can fragment.
---
3. Virtual Memory
Concept: Gives each process the illusion of a large, contiguous address space, even if physical RAM is smaller.
Demand Paging: Pages are loaded into RAM only when first accessed (“page fault”).
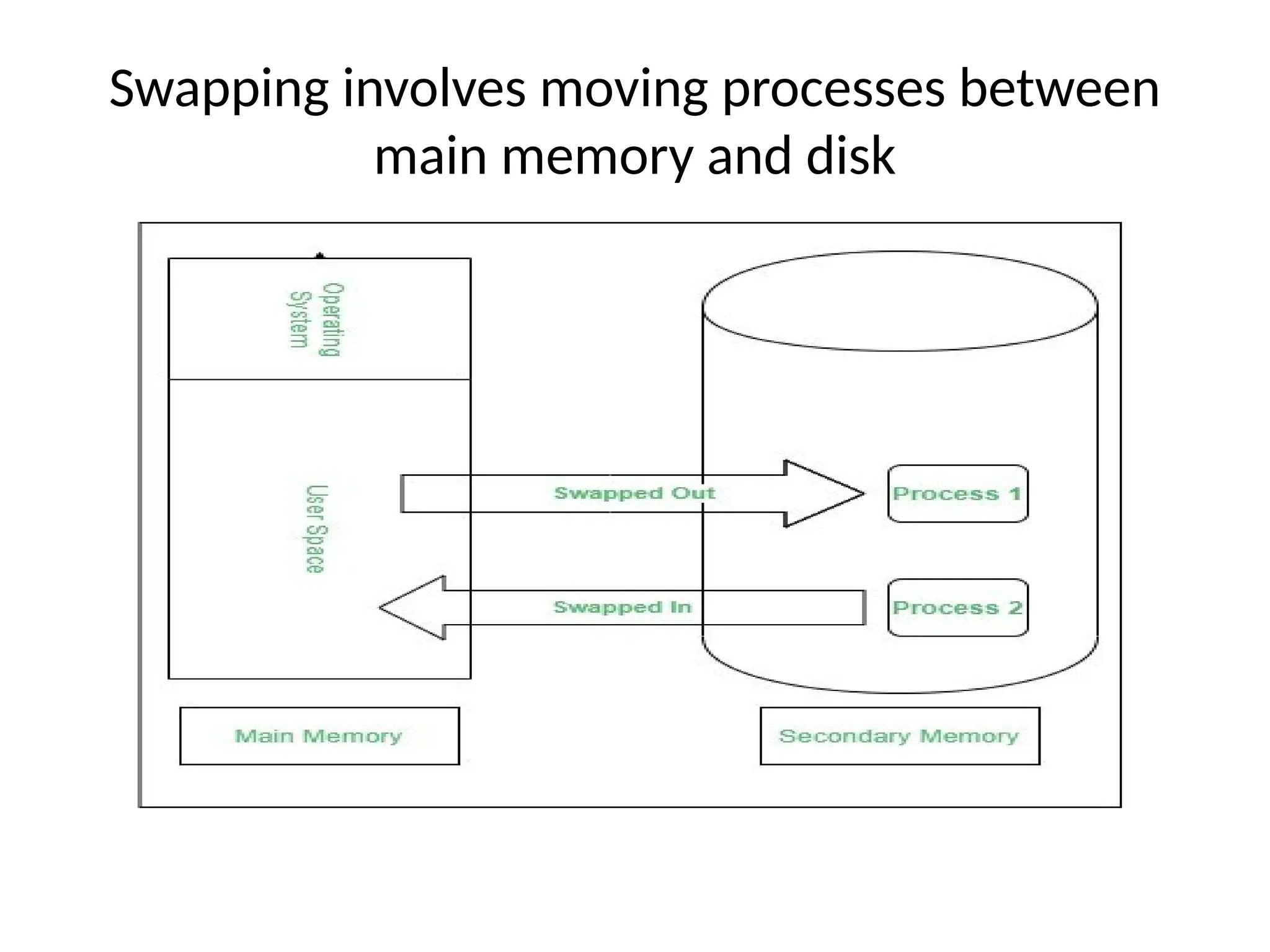
Swapping: Entire processes or individual pages can be moved to disk (swap space) when memory is scarce.
---
4. Page Replacement Algorithms
When RAM is full and a new page is needed, the OS must evict an existing page:
Optimal (Belady’s): Replace the page not needed for the longest future time (theoretical).
Least Recently Used (LRU): Evict the page unused for the longest past time.
First‑In, First‑Out (FIFO): Evict the oldest loaded page.
Clock (Second‑Chance): A circular buffer giving pages a “second chance” before eviction.
---
5. Fragmentation & Compaction
External Fragmentation: Free memory is split into small blocks; can be mitigated by compaction (shifting processes), though costly.
Internal Fragmentation: Occurs when fixed‑size blocks (pages) waste space if a process doesn’t fill the last page completely.
---
6. Hardware Support
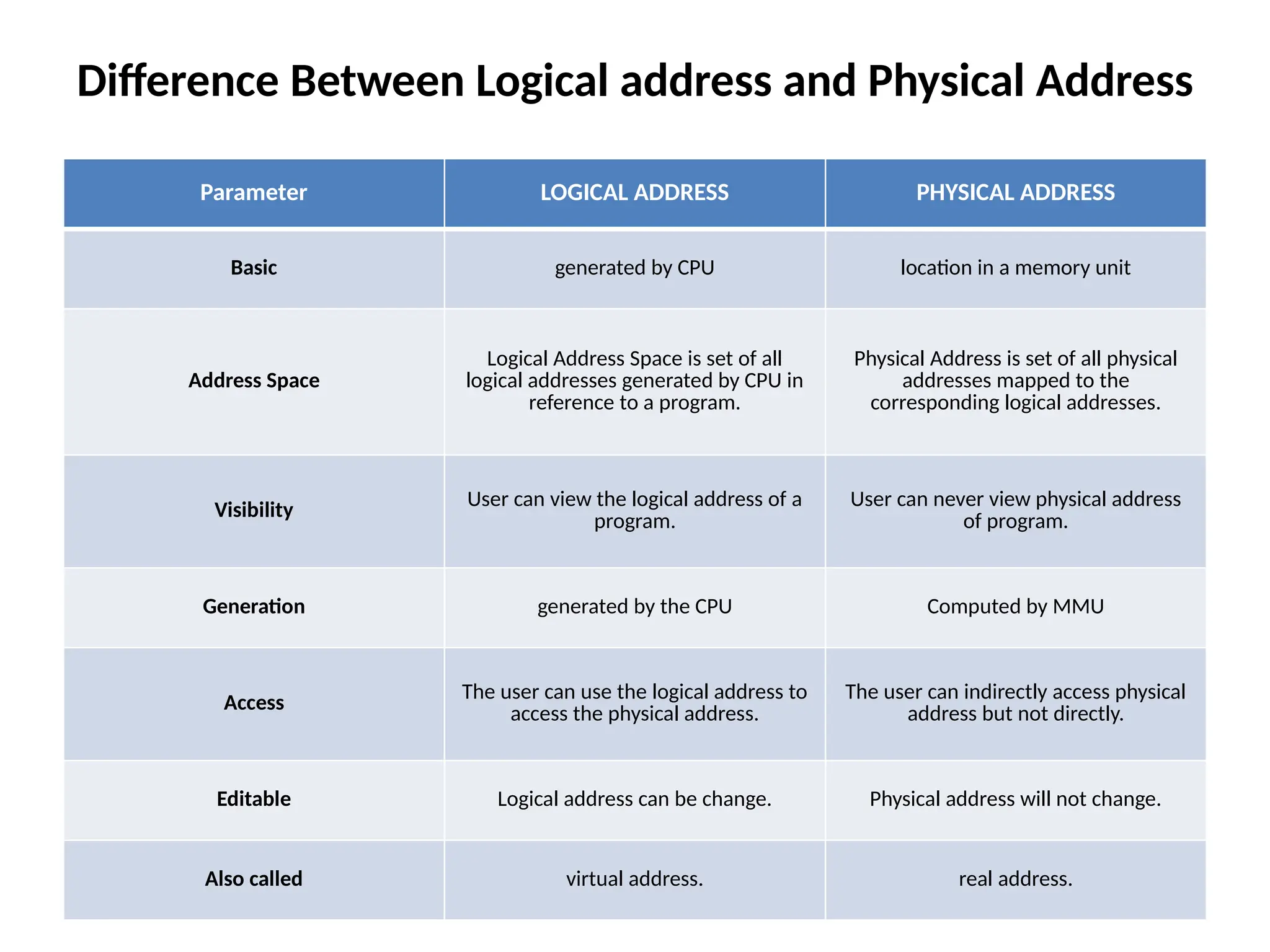
Memory Management Unit (MMU): Translates virtual addresses to physical addresses using page tables.
Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB): A small, fast cache of recent virtual‑to‑physical translations to speed up address translation.
---
7. Advanced Techniques
Hierarchical & Inverted Page Tables: Reduce memory overhead for page tables in large address spaces.
Segmented‑Paging: Combines segmentation’s logical view with paging’s fixed‑size blocks.
Huge Pages: Use larger page sizes (e.g., 2 MiB) to reduce TLB misses for big memo