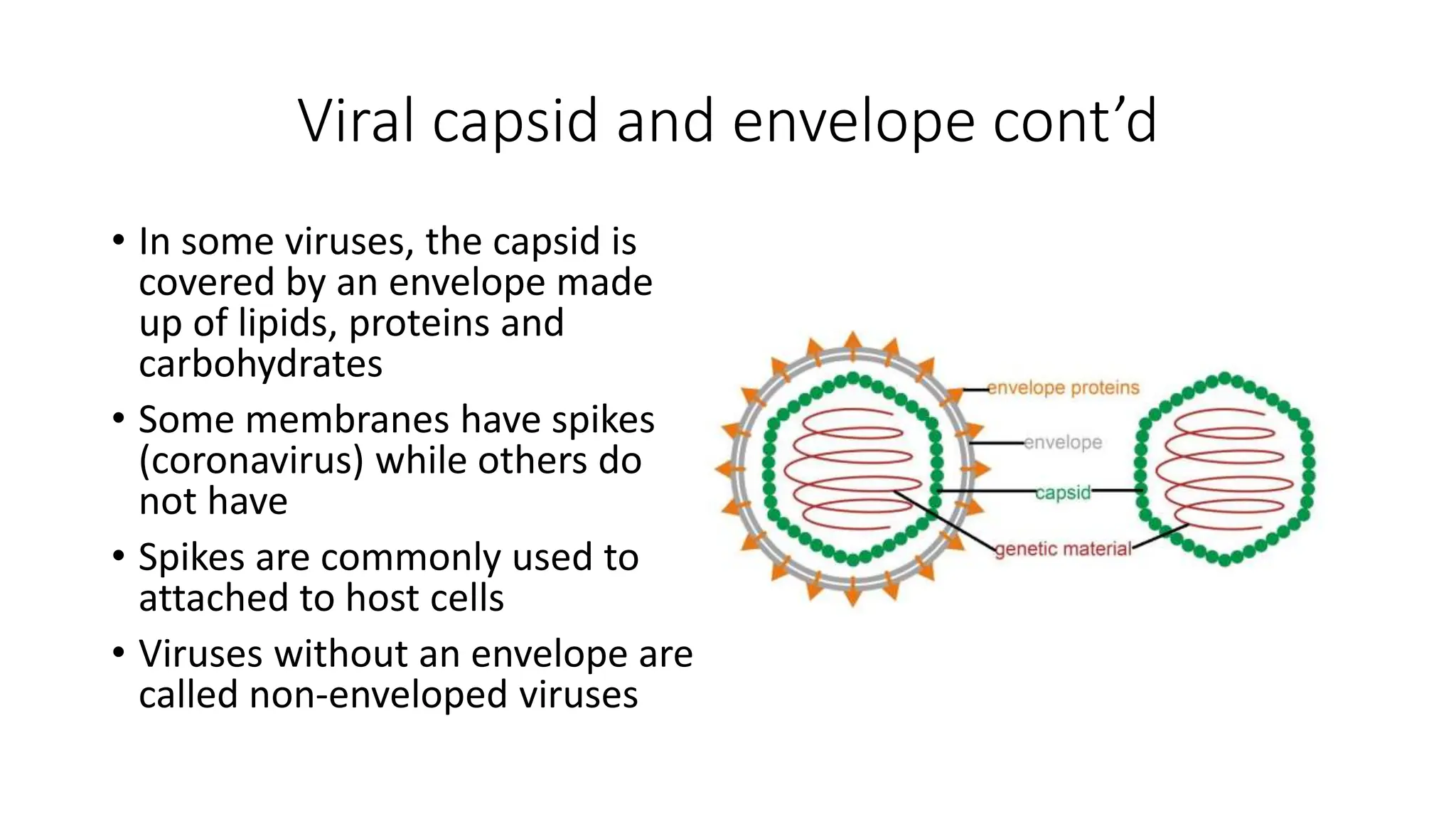
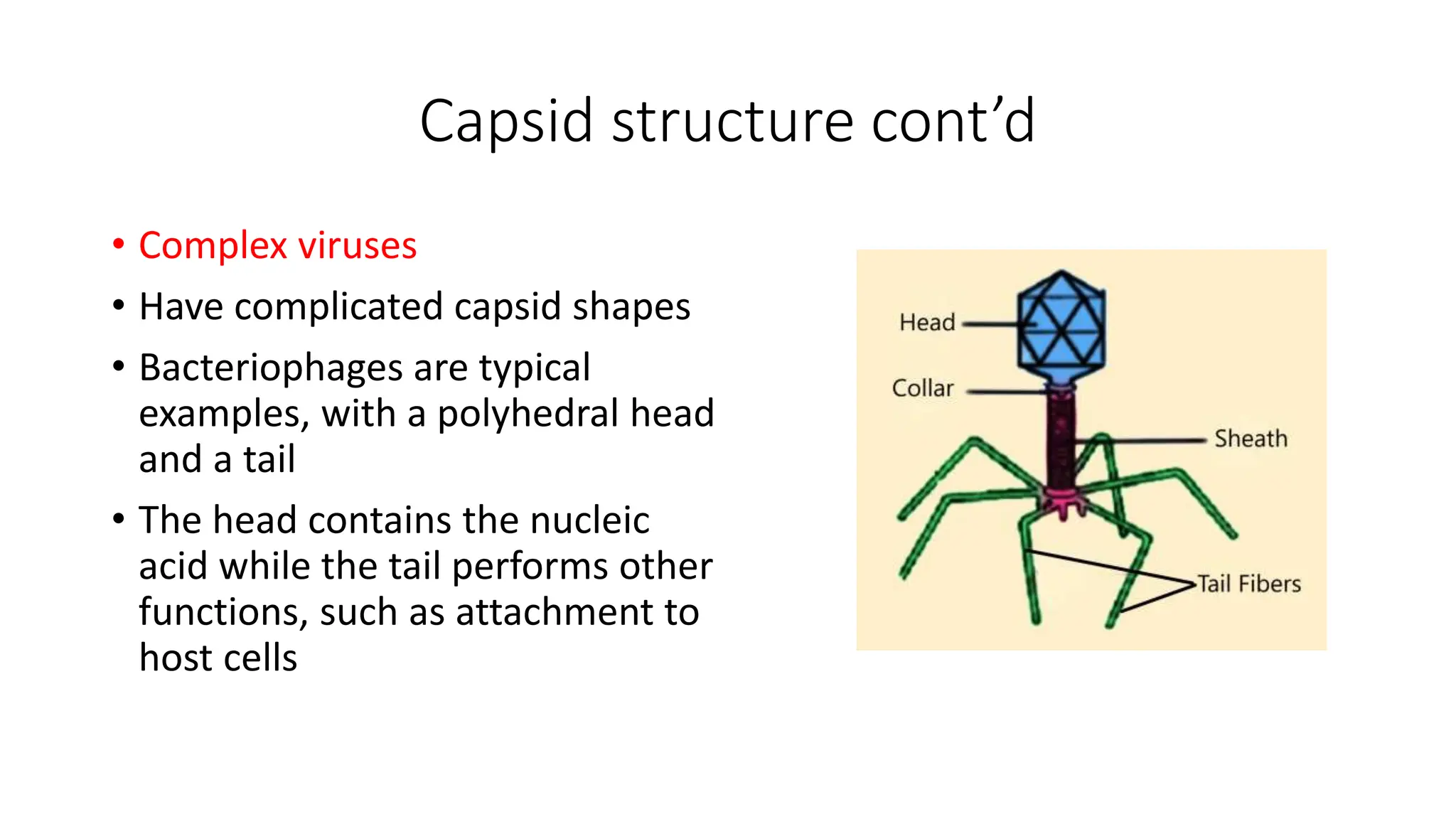
The document discusses virology, which is the study of viruses. Viruses are ubiquitous and can infect all forms of cellular life, causing diseases ranging from mild like the common cold to lethal like AIDS. Virology is important for developing vaccines, drugs, and diagnostic tests. Viruses cause economic losses in agriculture and can be used for applications like phage typing in epidemiology, producing enzymes, and as antibacterial agents or gene vectors for treating diseases and producing proteins. Viruses have a capsid that surrounds their genome and some have an envelope. They are classified based on their structure and nucleic acid.