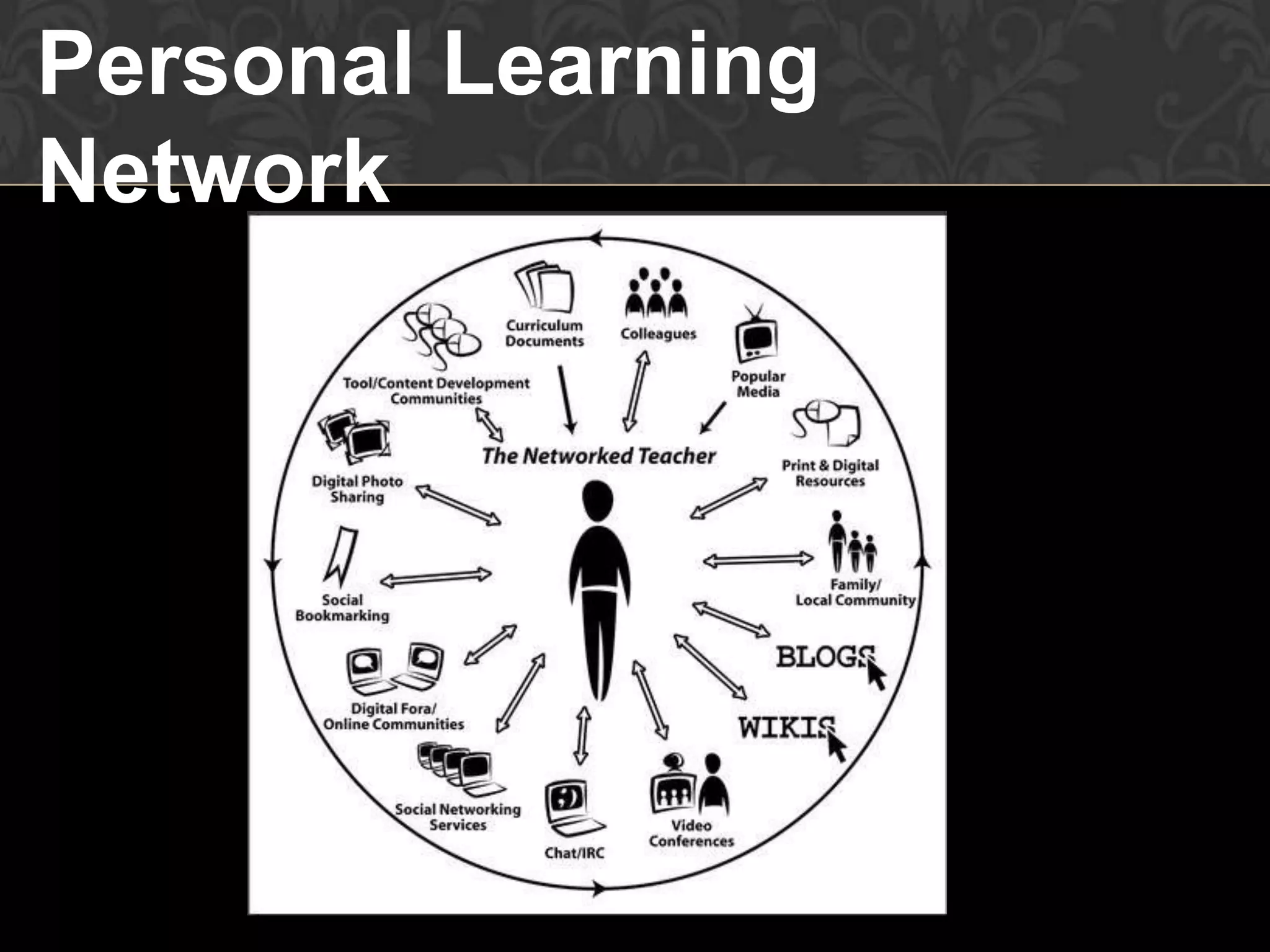
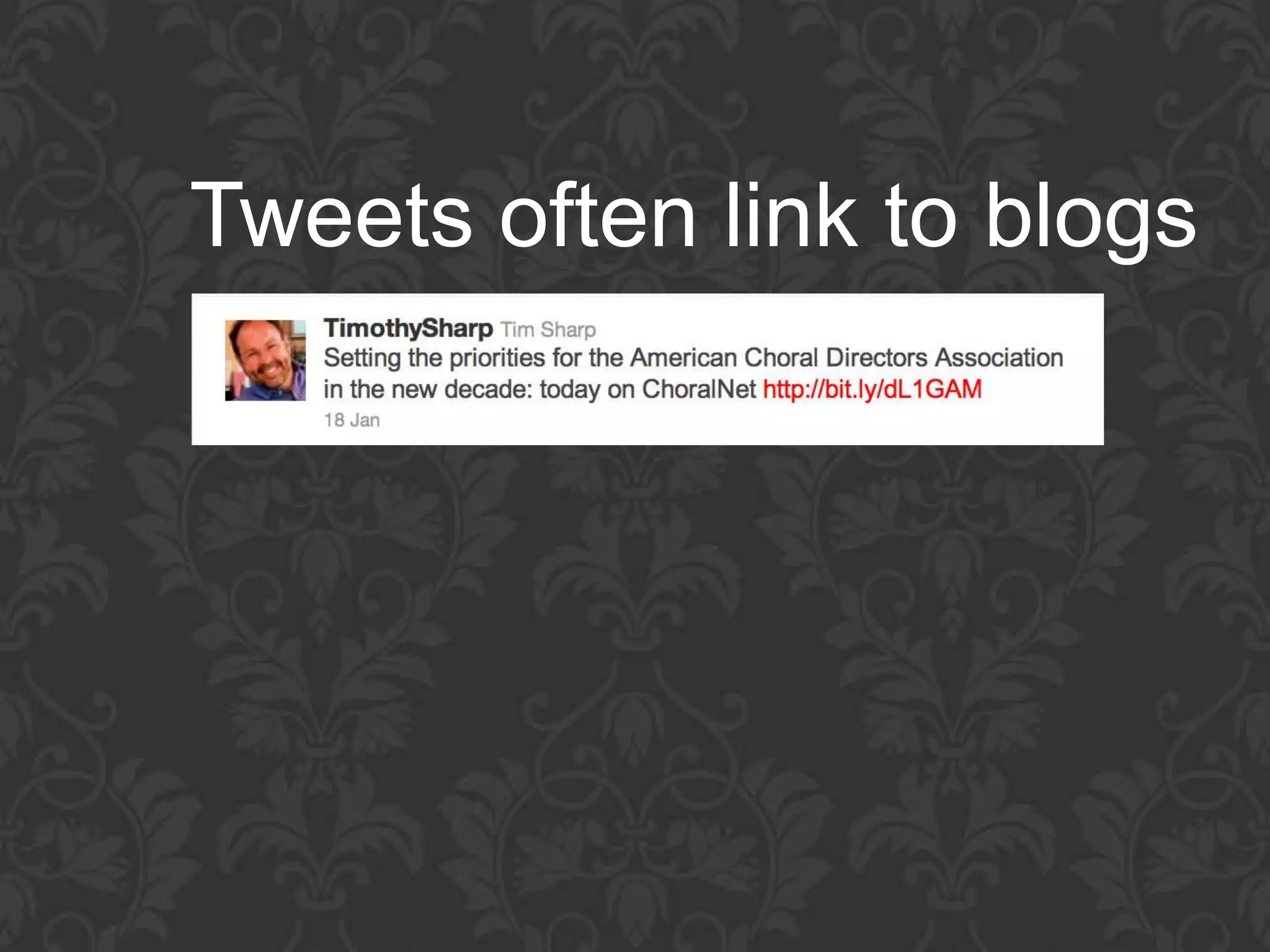
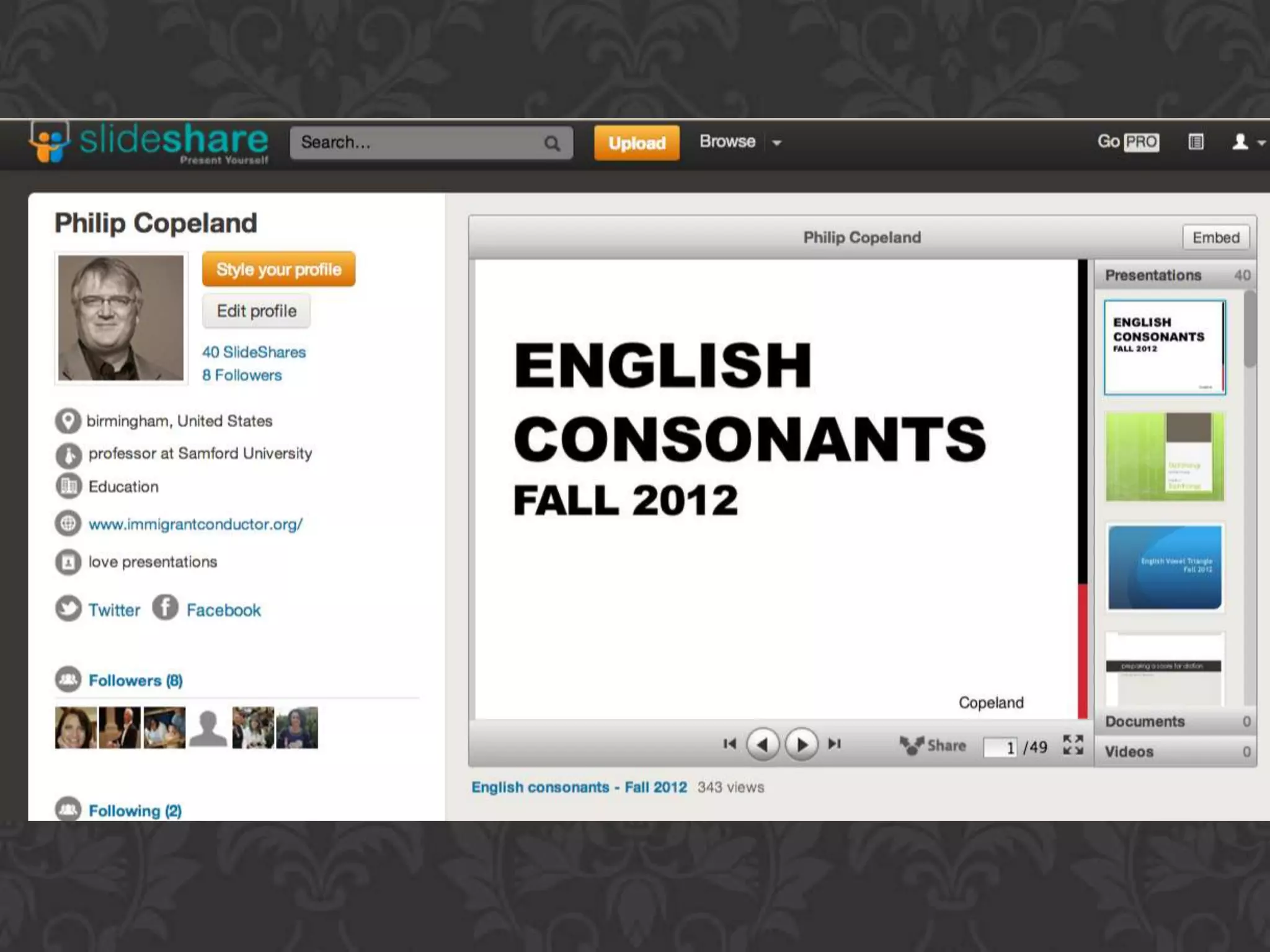
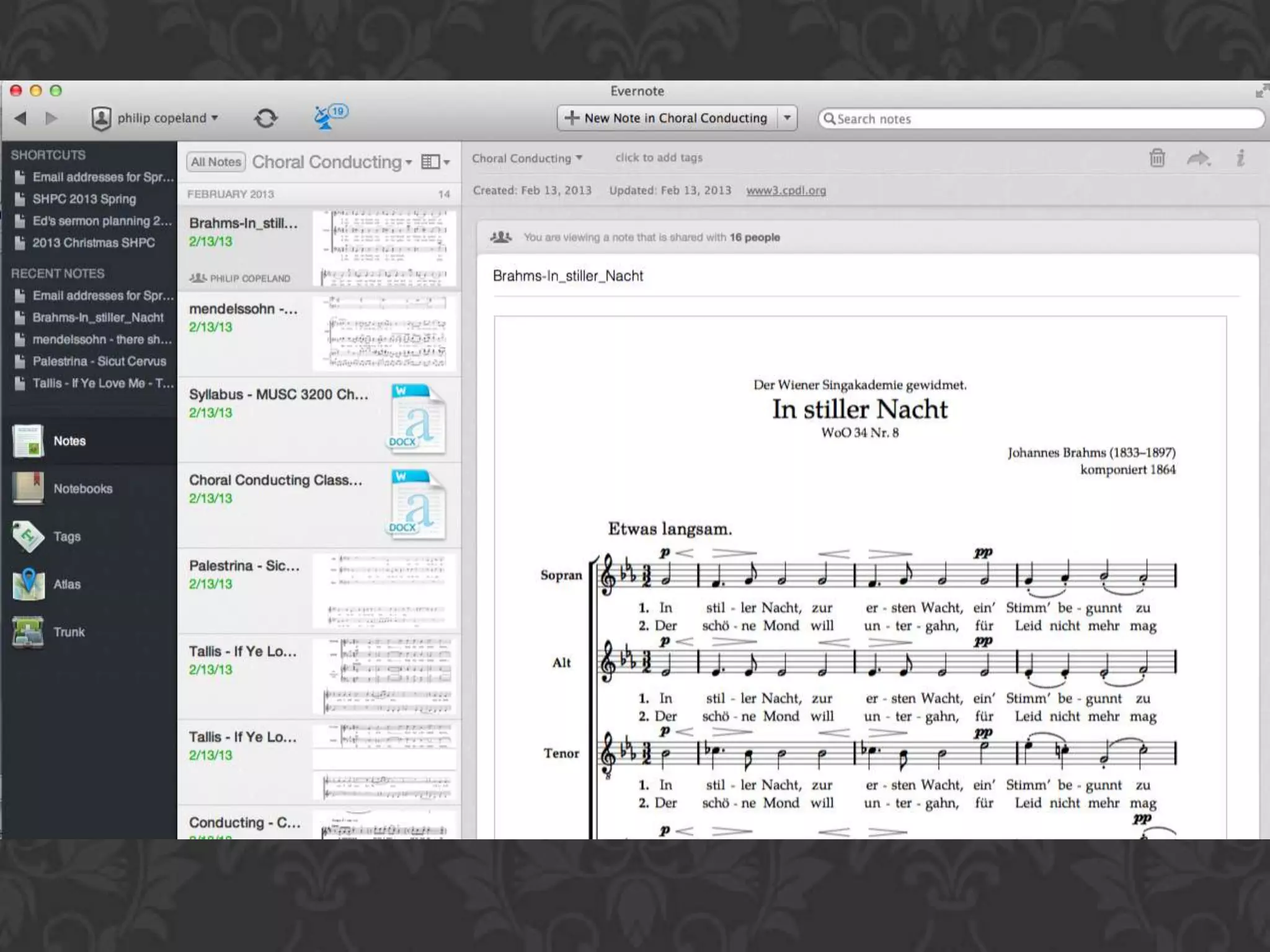
This document discusses how technology is changing education and provides tips for music educators to adapt. It notes that today's students have grown up with technology and are more knowledgeable than the current education system was designed for. It encourages educators to educate themselves on technology to stay relevant. The presentation aims to help educators understand educational technology changes, improve their skills, and work smarter. It promotes creating a personal learning network through blogs, Twitter, YouTube and other tools to collaboratively share ideas. Educators are advised to synchronize their professional development using cloud computing and tools like Dropbox, Evernote, and SlideShare.