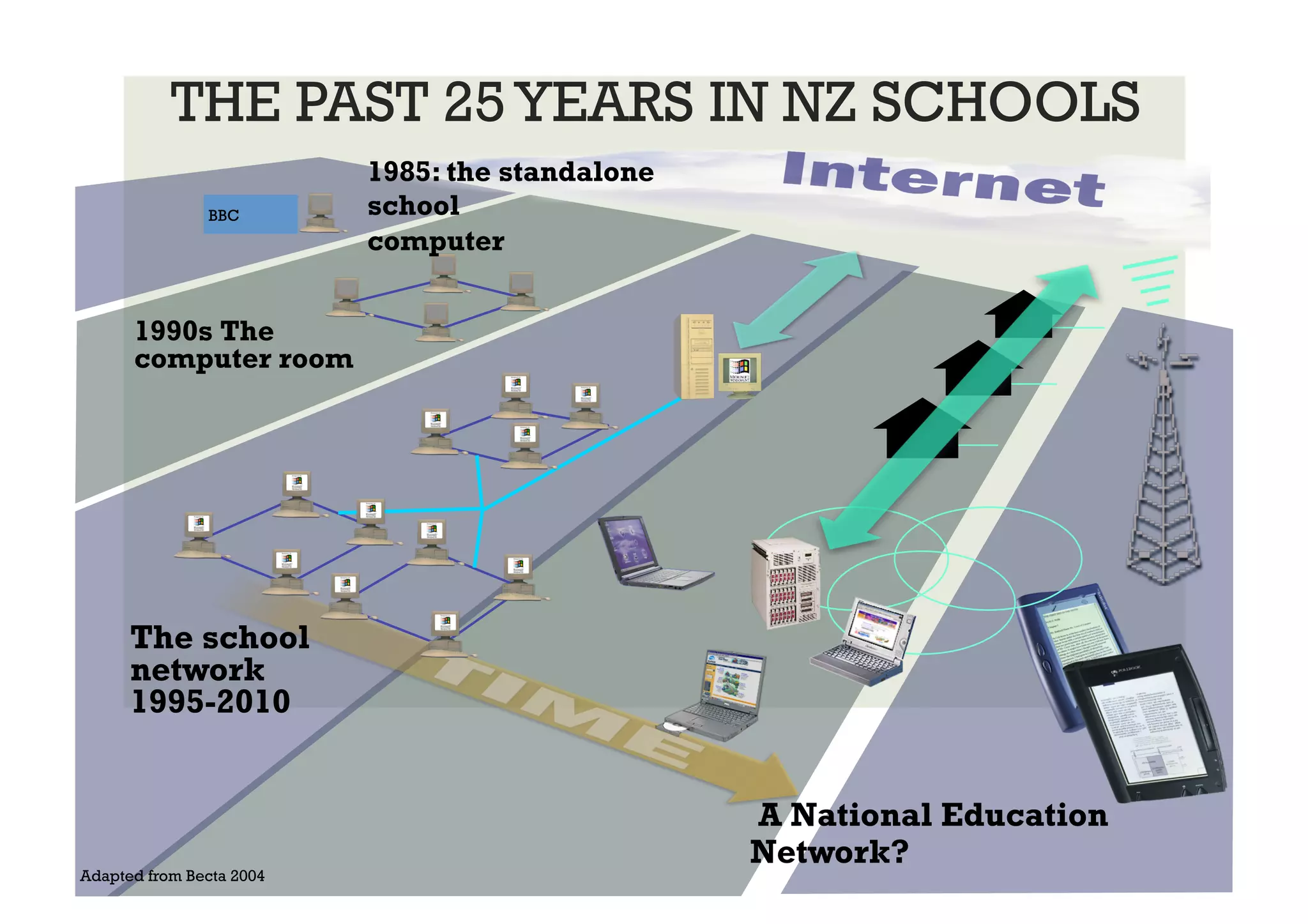
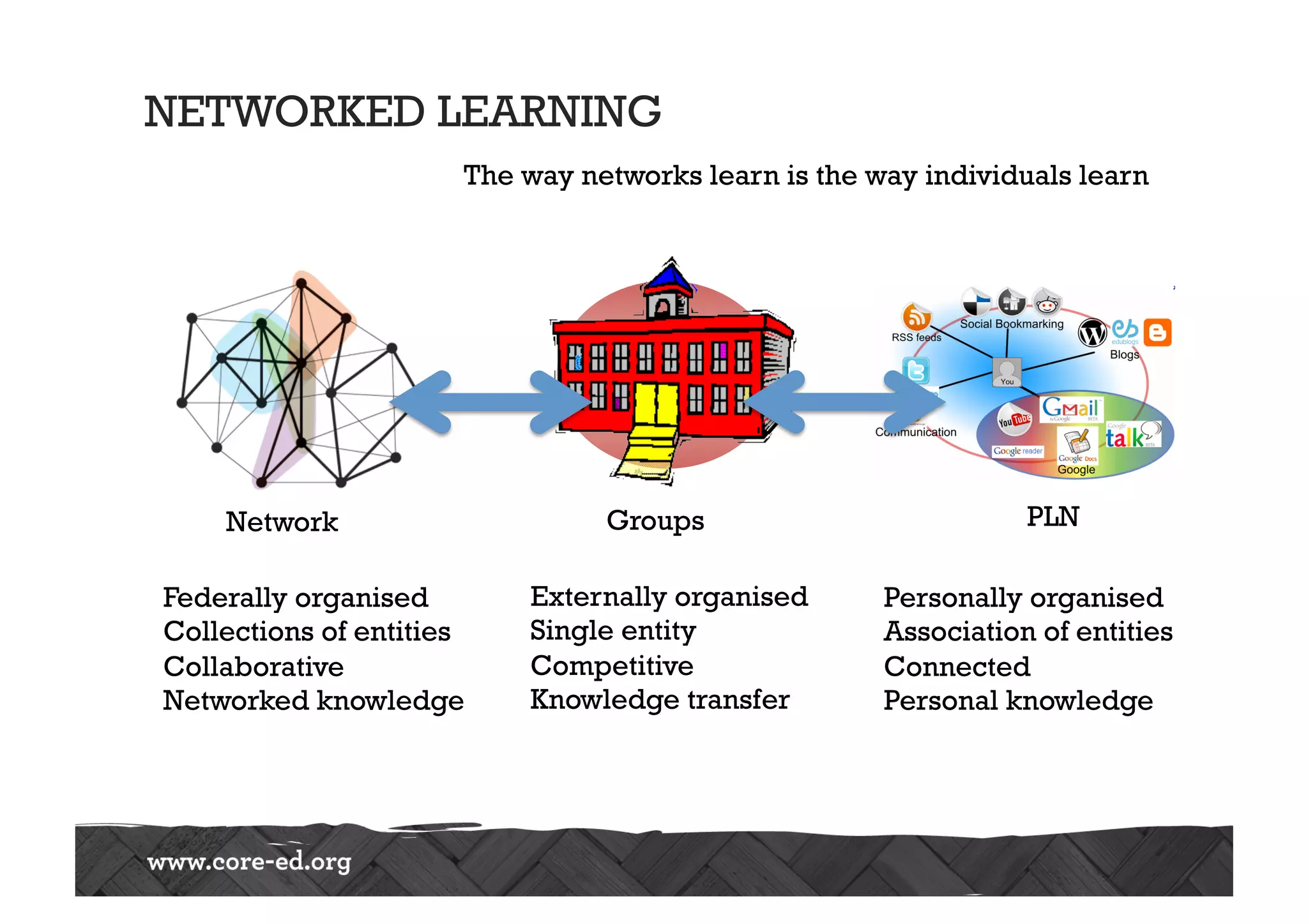
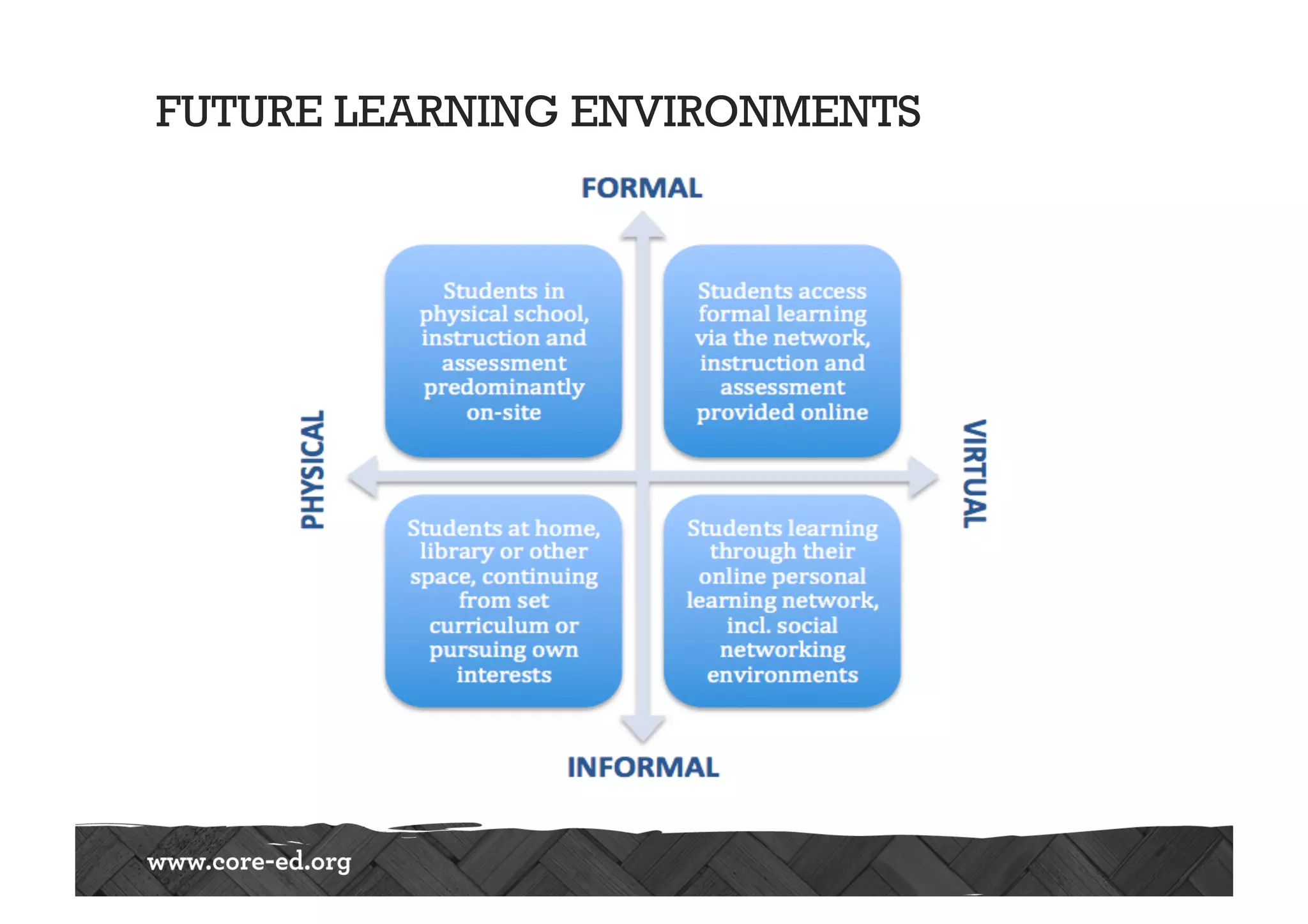
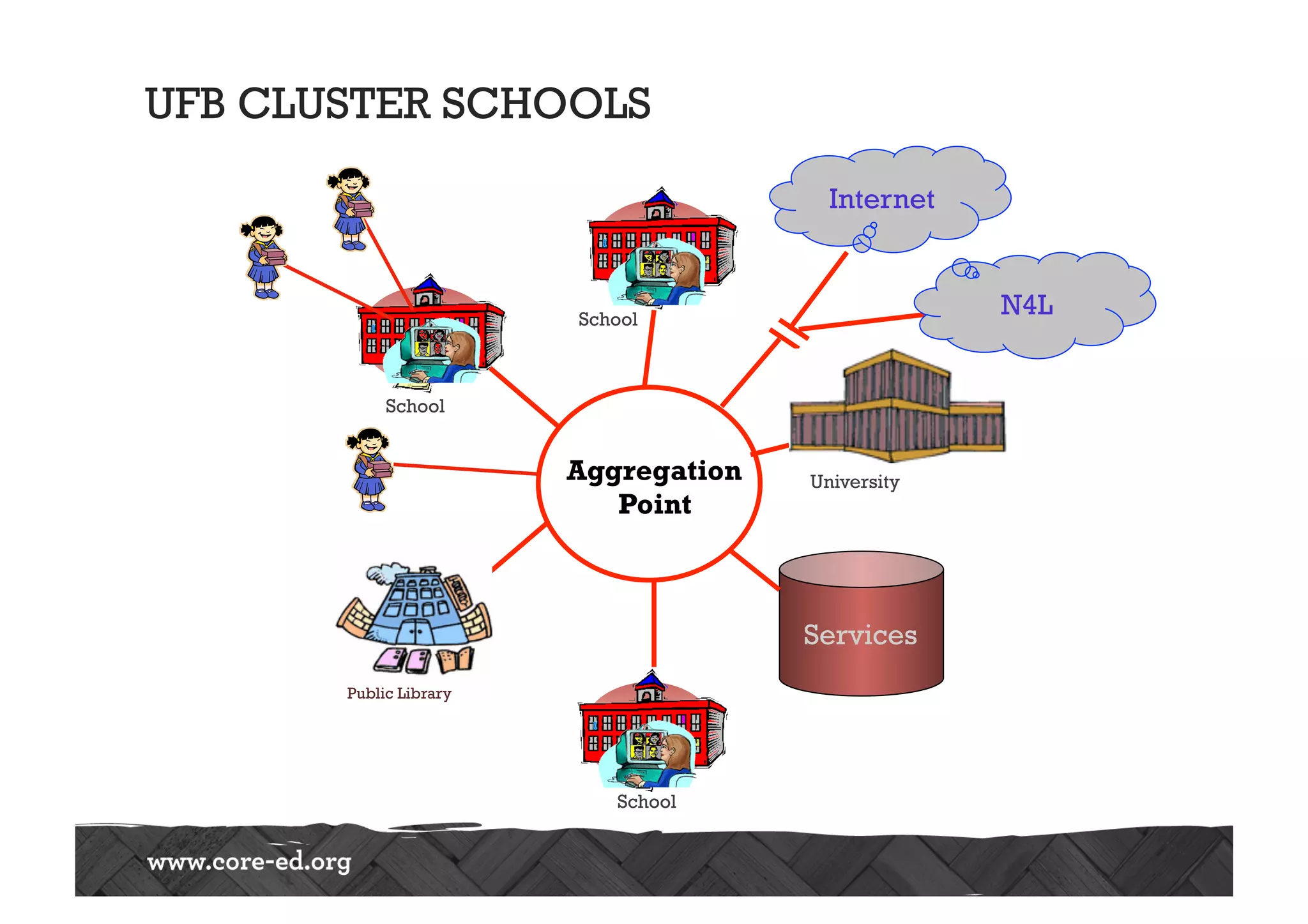
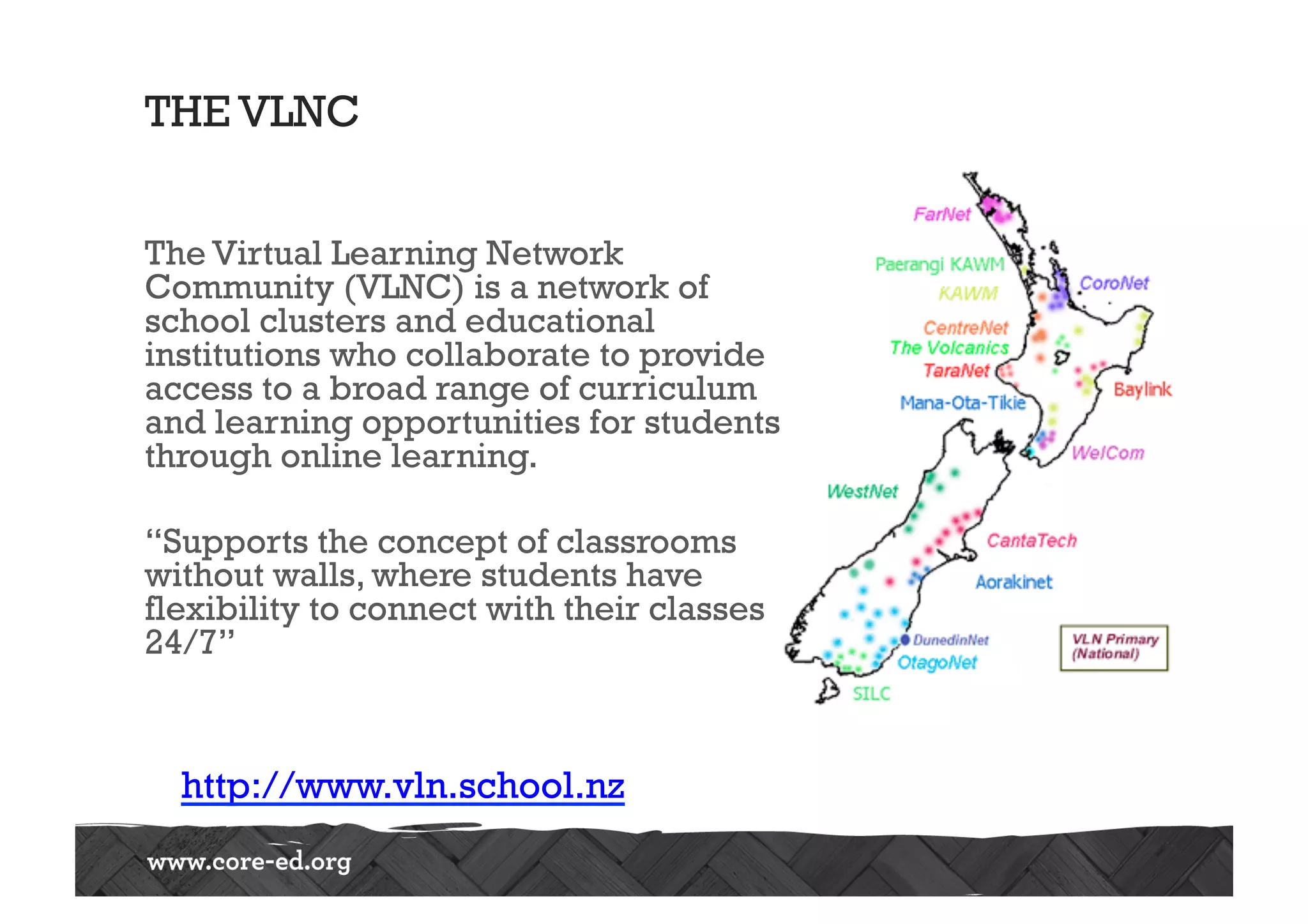
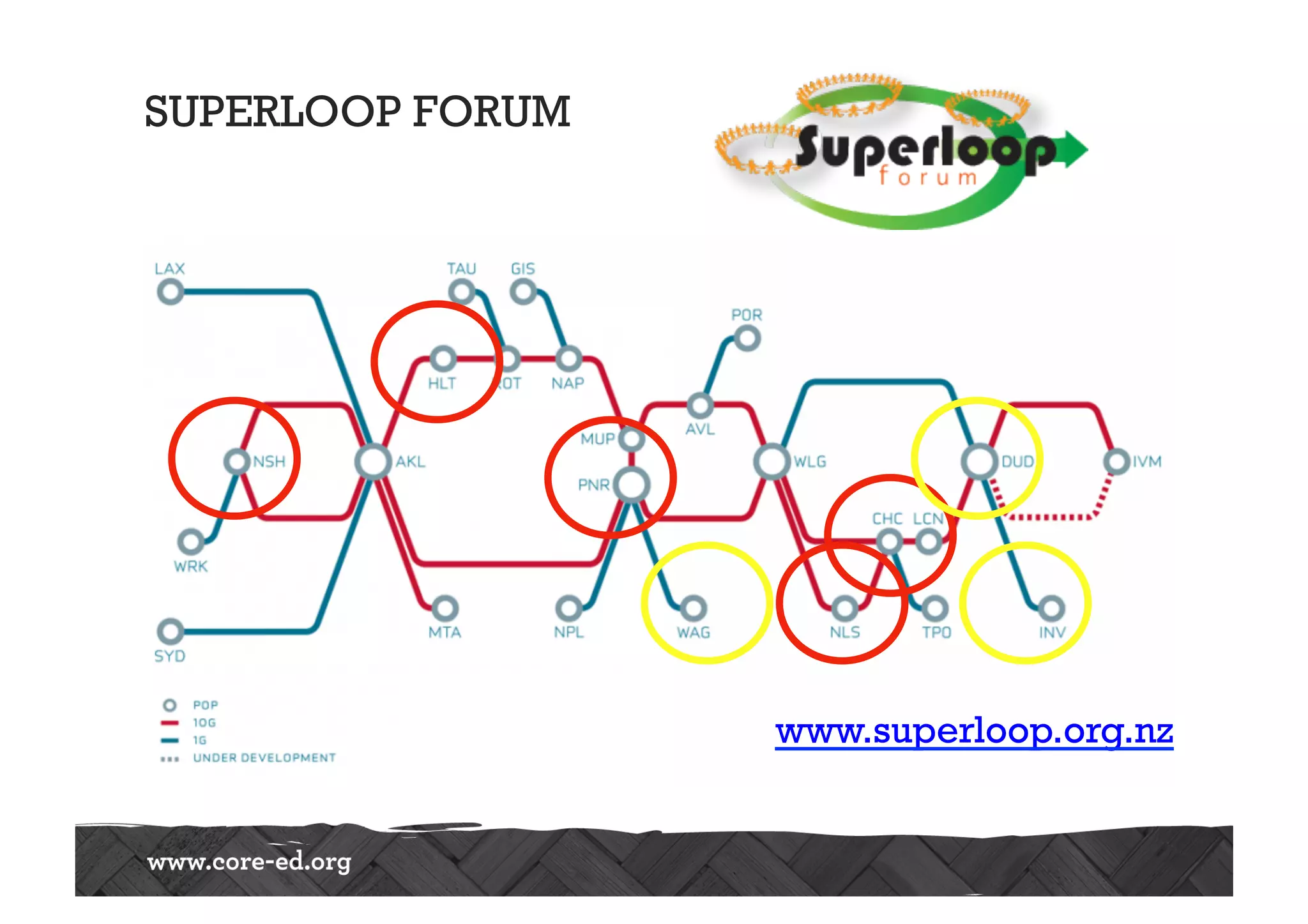
The document discusses predictions for technology, education, and workforce changes by 2033, emphasizing advancements in biotechnology, AI, and an increasingly mobile workforce. It highlights the importance of personalized education, interactive classrooms, and the necessity for teachers to adapt their practices to meet evolving student expectations and technological accessibility. The role of networks in learning and the need for adaptive educational frameworks are also stressed.