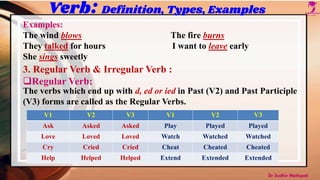
The document defines verbs and their types. It discusses verbs as words that describe actions, states of being, or occurrences. It outlines six main types of verbs: 1) action vs non-action, 2) transitive vs intransitive, 3) regular vs irregular, 4) main vs auxiliary, 5) finite vs non-finite, and 6) linking verbs. Examples are provided to illustrate the differences between each verb type.