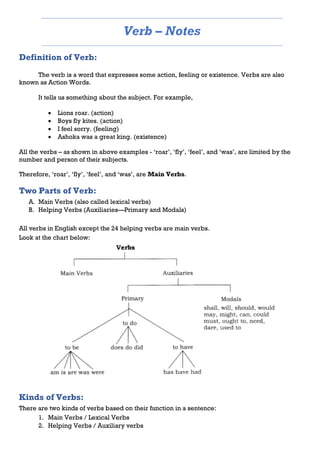
The document defines verbs as words that express action, feeling, or existence, and categorizes them into main (lexical) and helping (auxiliary) verbs. It further classifies main verbs into finite and non-finite, and transitive and intransitive types, explaining their functions in sentences. Additionally, it discusses the forms of verbs through conjugation and distinguishes between complete and incomplete predication.