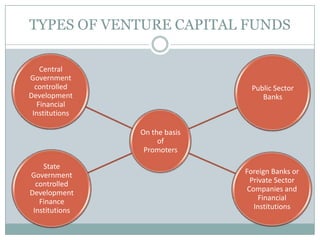
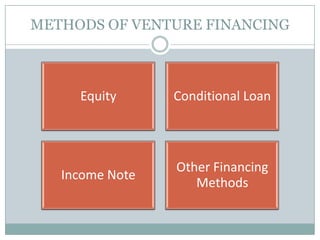
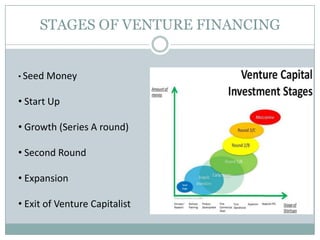
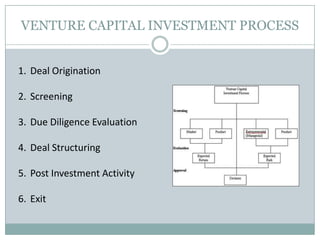
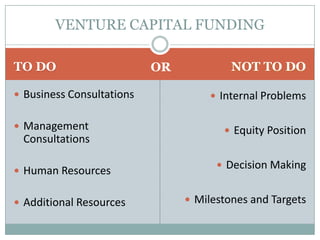
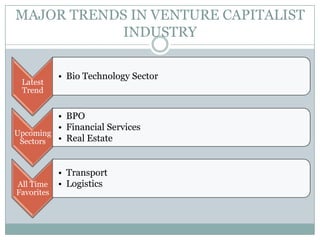
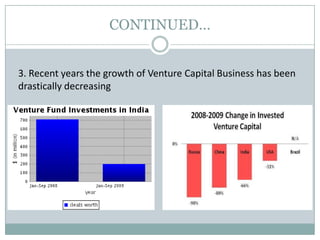
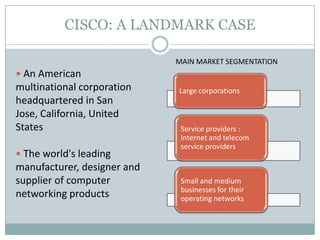
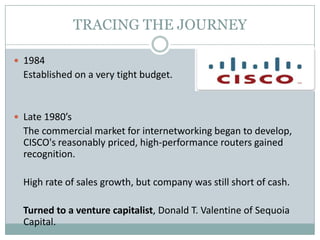
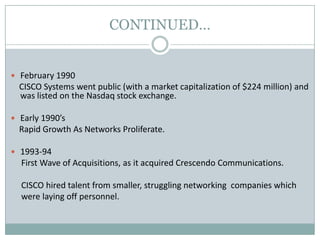
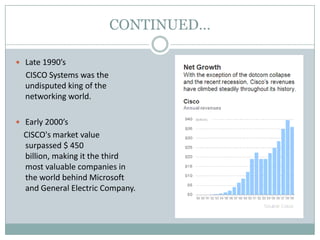
Venture capital is a form of private equity and refers to capital provided to early-stage, emerging firms that have high growth potential. This document discusses venture capital funding and its role in social entrepreneurship. It provides details on the venture capital process, types of funds, and what VCs look for in potential investments. Examples of social ventures like Grameen Bank that received VC funding are discussed, highlighting their success in alleviating poverty and empowering communities. While VC can motivate social initiatives requiring significant capital, the document notes that VCs primarily support experienced entrepreneurs and firms in high-tech sectors.