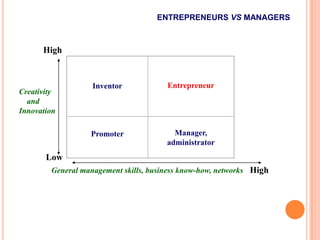
The document discusses key concepts around entrepreneurship including defining entrepreneurs, comparing them to businessmen, and factors that motivate entrepreneurship. It outlines the entrepreneurial process and resources available to entrepreneurs at different stages. The document also explores how entrepreneurship contributes to economic growth and trends in entrepreneurship research in the 21st century. Examples of successful entrepreneurs like Steve Jobs, Baba Ramdev, and Dr. Achuta Samanta are provided.